Abstract
A comprehensive understanding of the relationships between greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions and industrial structure and economic growth holds great significance for China to realize the development of a green economy. This paper calculates GHG emissions based on China’s energy consumption, divides the industrial structure in detail, and uses the extended Stochastic Impacts by Regression on Population, Affluence, and Technology model that is realized by PLS method and Tapio decoupling model to study the relationship of GHG emissions to industrial structure and economic growth. The results show that (1) China’s total GHG emissions showed a year-on-year growth trend from 2000 to 2017. For CO2, CH4, and N2O, only N2O emission showed a significant downward trend, while CO2 and CH4 emissions showed a slow growth trend. (2) The proportions of added value of industry and construction are positively correlated with GHG emissions, while those of farming, forestry, animal husbandry, and fishery; wholesale and retail trade; transport; and accommodation and catering are negatively correlated with GHG emissions. (3) China’s GHG emissions and overall economic growth are in a decoupling state, but in the energy field, N2O emission reduction control has the best effect. Additionally, the overall economic growth of China’s industrial sector and GHG emissions have experienced the process of decoupling-link-negative decoupling-link-decoupling.

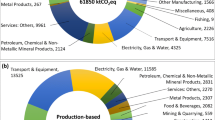
Graphical abstract








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ang BW (2004) Decomposition analysis for policy making in energy: which is the preferred method? Energy Policy 32(9):1131–1139. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0301-4215(03)00076-4
Ang BW, Huang H, Mu AR (2009) Properties and linkages of some index decomposition analysis methods. Energy Policy 37(11):4624–4632. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2009.06.017
Chang N (2015) Changing industrial structure to reduce carbon dioxide emissions: a Chinese application. J Clean Prod 103:40–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2014.03.003
Che LL, Han X, Zhao LS, Wu CY (2015) Coal use efficiency evaluation and decoupling analysis between coal use efficiency and economic growth in China. China Popul Resour Environ 25(3):104–110. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1002-2104.2015.03.014
Chen Q, Su LY, Ru XJ (2010) Carbon emission and GDP: causality relationship in 6 developed countries. Ecol Econ 4:52–55
Chen CC, Liu CL, Wang H, Guan J, Chen L (2014) Examining the impact factors of energy consumption related carbon footprints using the STIRPAT model and PLS model in Beijing. China Environ Sci 34(6):1622–1632. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2014.06.035
Dietz T, Rosa EA (1994) Rethinking the environmental impacts of population, affluence and technology. Hum Ecol Rev 1(2):277–300 https://www.jstor.org/stable/24706840
Dinda SA (2005) Theoretical basis for the environmental Kuznets curve. Ecol Econ 53(3):403–413. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolecon.2004.10.007
Dong J, He J, Li XT, Mou XD, Dong Z (2020) The effect of industrial structure change on carbon dioxide emissions: a cross-country panel analysis. J Syst Sci Inform 8(1):1–16. https://doi.org/10.21078/JSSI-2020-001-16
Gao F, Sun CQ, Qu JS (2001) New understanding of global climate change research—summary of the first working group report of the IPCC third climate assessment report. Adv Earth Science 16(3):442–445. https://doi.org/10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.2001.03.022
Goldewijk KK, Ramankutty N (2004) Land cover change over the last three centuries due to human activities: the availability of new global data sets. GeoJournal 61:335–344. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10708-004-5050-z
Grossman GM, Krueger AB (1991) Environmental impacts of a North American free trade agreement. NBER Working Paper 3914:1–57. https://doi.org/10.3386/w3914
Guo SD, Qian YB, Zhao Y (2018) Analysis of agricultural carbon emission efficiency and convergence in western China--based on SBM-undesirable model. Rural Econ 11:80–87
He YG, Yu JH (2018). Study on China’s carbon emission and industrial structure optimization based on STIRPAT model. Environ Eng 36(07):179-183+189. https://doi.org/10.13205/j.hjgc.201807035
Hojjati B, Wade SH (2012) US household energy consumption and intensity trends: a decomposition approach. Energy Policy 48:304–314. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2012.05.024
IPCC, 2013: Climate change 2013: the physical science basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change [Stocker, T.F., D. Qin, G.-K. Plattner, M. Tignor, S.K. Allen, J. Boschung, A. Nauels, Y. Xia, V. Bex and P.M. Midgley (eds.)]. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom and New York, NY, USA, 1535 pp. https://www.ipcc.ch/report/ar5/wg1/
Jiang P, Xu Q, Yang ZS (2019) Elementary course of national economic accounting. China Statistics Press, Beijing
Li GZ, Li ZZ, Zhou M (2011) Empirical analysis on relationship between carbon emissions and agricultural economic growth. Agr Econ Manag 4:32–39
Li HM, Wu T, Zhao XF, Wang X, Qi Y (2014) Regional disparities and carbon “outsourcing”: the political economy of China’s energy policy. Energy 66:950–958. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2014.01.013
Liu Z, Geng Y, Lindner S, Guan DB (2012) Uncovering China’s greenhouse gas emission from regional and sectoral perspectives. Energy 45(1):1059–1068. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2012.06.007
Liu JL, Xiahou QR, Wang K, Zhou J, Kong Y (2019). Study on mid- and long-term low carbon development pathway of China’s industry sector. China Soft Sci (11):31-41+54
Long RY, Li JQ, Chen H, Zhang LL, Li QW (2018) Embodied carbon dioxide flow in international trade: a comparative analysis based on China and Japan. J Environ Manag 209:371–381. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2017.12.067
Ma DL, Wu WL, Dong ZM (2017) Industrial carbon emission performance and its influencing factors in China: based on an empirical study of spatial panel data model. China Econo Stud 01:121–135. https://doi.org/10.19365/j.issn1000-4181.2017.01.11
Ma XJ, Chen RM, Dong BY, Niu XQ (2019) Factor decomposition and decoupling effect of China’s industrial carbon emissions. China Environ Sci 39(08):3549–3557. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2019.08.050
Mamun A, Sohag K, Mia AH, Uddin GS, Ozturk I (2014) Regional differences in the dynamic linkage between CO2 emissions, sectoral output and economic growth. Renew Sust Energ Rev 38:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2014.05.091
Mulder P, De-Groot HLF, Pfeiffer B (2014) Dynamics and determinants of energy intensity in the service sector: a cross-country analysis, 1980–2005. Ecol Econ 100:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolecon.2014.01.016
National Statistical Bulletin of 2019. National Bureau of Statistics, 2020-2-28
Nie HG, Kemp R (2014) Index decomposition analysis of residential energy consumption in China: 2002-2010. Appl Energy 121:10–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2014.01.070
Nie HG, Kemp R, Xu JH, Vasseur V, Fan Y (2018) Drivers of urban and rural residential energy consumption in China from the perspectives of climate and economic effects. J Clean Prod 172(pt.3):2954–2963. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.11.117
Nordhaus WD (1977) Economic growth and climate: the carbon dioxide problem. Am Econ Rev 67(1):341–346 https://www.jstor.org/stable/1815926
Qu FT, Lu N, Feng SY (2011) Effects of land use change on carbon emissions. China Popul Resour Environ 21(10):76–83 1002-2104 (2011) 10-0076-08
Rhee HC, Chung HS (2006) Change in CO2 emission and its transmissions between Korea and Japan using international input-output analysis. Ecol Econ 58(4):788–800. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolecon.2005.09.005
Robaina-Alves M, Moutinho V (2014) Decomposition of energy-related GHG emissions in agriculture over 1995-2008 for European countries. Appl Energy 114:949–957. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2013.06.059
Roberts JT, Grimes PE (1997) Carbon intensity and economic development 1962-91: a brief exploration of the environmental Kuznets Curve. World Dev 25(2):191–198. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0305-750X(96)00104-0
Saboori B, Sulaiman J, Mohd S (2012) Economic growth and CO2 emissions in Malaysia: a cointegration analysis of the Environmental Kuznets Curve. Energy Policy 51:184–191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2012.08.065
Tian X, Chang M, Shi F, Tanikawa H (2014) How does industrial structure change impact carbon dioxide emissions? A comparative analysis focusing on nine provincial regions in China. Environ Sci Pol 37:243–254. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envsci.2013.10.001
Uddin MGS, Bidisha SH, Ozturk I (2016) Carbon emissions, energy consumption, and economic growth relationship in Sri Lanka. Energy Sources Part B 11(3):282–287. https://doi.org/10.1080/15567249.2012.694577
Verbeke T, Clercq MD (2006) The income-environment relationship: evidence from a binary response model. Ecol Econ 59(4):419–428. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolecon.2005.11.011
Wang Y, He X (2019) Spatial economic dependency in the Environmental Kuznets Curve of carbon dioxide: the case of China. J Clean Prod 218:498–510. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.01.318
Wang SJ, Huang YY (2019) Spatial spillover effect and driving forces of carbon emission intensity at city level in China. Acta Geogr Sinica 74(06):1131–1148. https://doi.org/10.11821/dlxb201906005
Wang ZX, Ye DJ (2017) Forecasting Chinese carbon emissions from fossil energy consumption using non-linear grey multivariable models. J Clean Prod 142(PT.2):600–612. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.08.067
Wang K, Shao HQ, Zhou TT, Deng CX (2018) EKC framework analysis of the effects of tourism development on regional carbon emissions: based on China’s 1995-2015 panel data. Geogr Res 37(04):742–750. https://doi.org/10.11821/dlyj201804008
Wang FT, Fang K, Yu C (2019) Decoupling between industrial energy-related carbon emissions and economic growth and its driving factors in Beijing, Tianjin and Hebei urban agglomeration-empirical study based on Tapio decoupling and LMDI model. J Ind Technol Econ 38(08):32–40. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1004-910X.2019.08.004
Wu F, Fan LW, Zhou P, Zhou DQ (2012) Industrial energy efficiency with CO2 emissions in China: a nonparametric analysis. Energy Policy 49:164–172. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2012.05.035
Xu JH, Fleiter T, Fan Y, Eichhammer W (2014) CO2 emissions reduction potential in China’s cement industry compared to IEA’s Cement Technology Roadmap up to 2050. Appl Energy 130:592–602. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2014.03.004
Yu Y D, Chen DJ , Zhu B, Hu SY (2013) Eco-efficiency trends in China, 1978-2010: Decoupling environmental pressure from economic growth. Ecol Indic 24:177–184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2012.06.007
Yu SW, Zhang JJ, Zheng SH, Sun H (2015) Provincial carbon intensity abatement potential estimation in China: a PSO–GA-optimized multi-factor environmental learning curve method. Energy Policy 77:46–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2014.11.035
Yuan Y, Xi QM, Sun TS, Li GP (2016) The impact of the industrial structure on regional carbon emission: empirical evidence across countries. Geogr Res 35(01):82–94
Zhang YG (2010) Economic development pattern change impact on China’s carbon intensity. Econ Res J 45(04):120–133
Zhang FM, Wang YX (2016) Study on world carbon emission prediction model based on system clustering and BP neural network. Math Pract Th 1:77–84
Zhang B, Chen GQ, Chen B (2012) National strategies for addressing climate change via methane emissions. China Popul Resour Environ 22(07):8–14. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1002-2104.2012.07.002
Zhou J, Wang YX, Liu XR, Shi XC, Cai CM (2019) Study on spatial-temporal difference and carbon compensation of provincial carbon emissions in China based on land use change. Sci Geogr Sin 39(12):1955–1961. https://doi.org/10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2019.12.014
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Nicholas Apergis
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Z., Ma, X., Lian, X. et al. Research on the relationship between China’s greenhouse gas emissions and industrial structure and economic growth from the perspective of energy consumption. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27, 41839–41855 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-10091-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-10091-w