Abstract
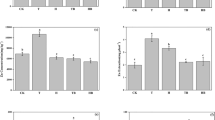
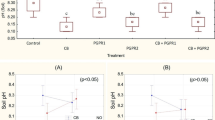
Microbe-assisted phytoremediation provides an eco-friendly and cost-effective approach to reclaim Cd- and Pb-contaminated soils. In this work, incubation and pot experiments were established to investigate the effect of Streptomyces pactum (Act12) combined with compost on soil physicochemical properties, enzymatic activities, and thereby acted on phytoextraction of Cd and Pb by using potherb mustard (Brassica juncea Coss.). The addition of Act12 and compost increased EC (7.2%), available phosphorus (P) (14.9%), available potassium (K) (17.0 folds), DOC (37.7%), OM (2.8 folds), urease (49.8%), dehydrogenase (2.2 folds), and alkaline phosphatase (23.0 folds) of soil, while reduced pH (7.7%) compared with control. Significant decrease of available Cd and Pb uptake was observed after adding compost and Act12 by 29.1% and 32.2%. Presence of compost and Act12 enhanced the biomass by 3.98 folds and 1.83 folds in shoots and roots of plant. Results showed the assimilation of Cd and Pb in shoots was increased by 103.8% and 48.7% due to the increased of biomass. Meanwhile, the rhizosphere effect of soil microorganisms increased the uptake of Cd (60.4%) and Pb (19.2%) in roots. These findings suggested that Act12 joined with compost-strengthened potherb mustard phytoremediation of Cd- and Pb-polluted soils, which may provide new insights into the clean-up of mining-contaminated soils in field practice.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abujabhah IS, Bound SA, Doyle R, Bowman JP (2016) Effects of biochar and compost amendments on soil physico-chemical properties and the total community within a temperate agricultural soil. Appl Soil Ecol 98:243–253
Ali H, Khan E, Sajad MA (2013) Phytoremediation of heavy metals-concepts and applications. Chemosphere 91:869–881
Ali A, Guo D, Mahar A, Wang P, Ma F, Shen F, Li RH, Zhang ZQ (2017a) Phytoextraction of toxic trace elements by Sorghum bicolor inoculated with Streptomyces pactum (Act12) in contaminated soils. Ecotox Environ Safe 139:202–209
Ali A, Guo D, Mahar A, Wang Z, Muhammad D, Li RH, Wang P, Shen F, Xue Q, Zhang ZQ (2017b) Role of Streptomyces pactum in phytoremediation of trace elements by Brassica juncea in mine polluted soils. Ecotox Environ Safe 144:387–395
Ansari MI, Malik A (2007) Biosorption of nickel and cadmium by metal resistant bacterial isolates from agricultural soil irrigated with industrial wastewater. Bioresour Technol 98:3149–3153
ASTM D2974 (1916) Standard Test Methods for Moisture, Ash, and Organic Matter of Peat and Organic Soils. The American Society of Testing and Materials, Race Street, Philadelphia, p PA19103
Babu AG, Reddy MS (2011) Dual inoculation of arbuscular mycorrhizal and phosphate solubilizing fungi contributes in sustainable maintenance of plant health in fly ash ponds. Water Air Soil Pollut 219:3–10
Bolan NS, Adriano DC, Kunhikrishnan A, James T, McDowell R, Senesi N (2011) Dissolved organic matter: biogeochemistry, dynamics, and environmental significance in soils. Adv Agron 110:1–75
Bowles TM, Acosta-Martinez V, Calderon F, Jackson LE (2014) Soil enzyme activities, microbial communities, and carbon and nitrogen availability in organic agroecosystems across an intensively-managed agricultural landscape. Soil Biol Biochem 68:252–262
Burges A, Epelde L, Benito G, Artetxe U, Becerril JM, Garbisu C (2016) Enhancement of ecosystem services during endophyte-assisted aided phytostabilization of metal contaminated mine soil. Sci Total Environ 562:480–492
Bustamante MA, Said-Pullicino D, Agullo E, Andreu J, Paredes C, Moral R (2011) Application of winery and distillery waste composts to a Jumilla (SE Spain) vineyard: effects on the characteristics of a calcareous sandy-loam soil. Agric Ecosyst Environ 140:80–87
Cao SM, Wang WK, Wang F, Zhang J, Wang ZF, Yang SK, Xue QH (2016) Drought-tolerant Streptomyces pactum Act12 assist phytoremediation of cadmium-contaminated soil by Amaranthus hypochondriacus: great potential application in arid/semi-arid areas. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:14898–14907
Caporale AG, Pigna M, Sommella A, Dynes JJ, Cozzolino V, Violante A (2013) Influence of compost on the mobility of arsenic in soil and its uptake by bean plants (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) irrigated with arsenite-contaminated water. J Environ Manag 128:837–843
Cheng FM, Zhao NC, Xu HM, Li Y, Zhang WF, Zhu ZW, Chen MX (2006) Cadmium and lead contamination in japonica rice grains and its variation among the different locations in southeast China. Sci Total Environ 359:156–166
Cordero I, Snell H, Bardgett RD (2019) High throughput method for measuring urease activity in soil. Soil Biol Biochem 134:72–77
De Corato U, Patruno L, Avella N, Lacolla G, Cucci G (2019) Composts from green sources show an increased suppressiveness to soilborne plant pathogenic fungi: relationships between physicochemical properties, disease suppression, and the microbiome. Crop Prot 124: 104870.
Duan CM, Xue QH, Zhao J, Hu SB, Chen Q, Wang LN, Shen GH, Xue L (2010) Effects of antimicrobial actinomyces on growth and PPO activity in cucumber. Acta Agric Bori–Occid Sin 19:48–54
Feng XB, Dai QQ, Qiu GL, Li GH, He L, Wang DY (2006) Gold mining related mercury contamination in Tongguan, Shaanxi Province, PR China. Appl Geochem 21:1955–1968
Frouz J (2018) Effects of soil macro- and mesofauna on litter decomposition and soil organic matter stabilization. Geoderma 332:161–172
Gopalakrishnan S, Srinivas V, Vidya MS, Rathore A (2013) Plant growth-promoting activities of Streptomyces spp. in sorghum and rice. Springerplus 2:574
Guala SD, Vega FA, Covelo EF (2010) The dynamics of heavy metals in plant–soil interactions. Ecol Model 221:1148–1152
Guarino C, Sciarrillo R (2017) Effectiveness of in situ application of an integrated phytoremediation system (IPS) by adding a selected blend of rhizosphere microbes to heavily multi-contaminated soils. Ecol Eng 99:70–82
Gul S, Whalen JK, Thomas BW, Sachdeva V, Deng HY (2015) Physico-chemical properties and microbial responses in biochar-amended soils: mechanisms and future directions. Agric Ecosyst Environ 206:46–59
Guo D, Ali A, Ren CY, Du J, Li RH, Lahori AH, Xiao R, Zhang ZY, Zhang ZQ (2019) EDTA and organic acids assisted phytoextraction of Cd and Zn from a smelter contaminated soil by potherb mustard (Brassica juncea, Coss) and evaluation of its bioindicators. Ecotox Environ Safe 167:396–403
Houben D, Evrard L, Sonnet P (2013) Mobility, bioavailability and pH-dependent leaching of cadmium, zinc and lead in a contaminated soil amended with biochar. Chemosphere 92:1450–1457
Hu XF, Jiang Y, Shu Y, Hu X, Liu LM, Luo F (2014) Effects of mining wastewater discharges on heavy metal pollution and soil enzyme activity of the paddy fields. J Geochem Explor 147:139–150
Husson O (2013) Redox potential (Eh) and pH as drivers of soil/plant/microorganism systems: a transdisciplinary overview pointing to integrative opportunities for agronomy. Plant Soil 362:389–417
Jadia CD, Fulekar MH (2008) Phytoremediation: the application of vermicompost to remove zinc, cadmium, copper, nickel and Lead by sunflower plant. Environ Eng Manag J 7:547–558
Kaur G, Reddy MS (2014) Role of phosphate-solubilizing bacteria in improving the soil fertility and crop productivity in organic farming. Arch Agron Soil Sci 60:549–564
Lammirato C, Miltner A, Kaestner M (2011) Effects of wood char and activated carbon on the hydrolysis of cellobiose by beta-glucosidase from Aspergillus niger. Soil Biol Biochem 43:1936–1942
Li RH, Wang JJ, Zhang ZQ, Shen F, Zhang GJ, Qin R, Li XL, Xiao R (2012) Nutrient transformations during composting of pig manure with bentonite. Bioresour Technol 121:362–368
Li JJ, Zhou XM, Yan JX, Li HJ, He JZ (2015) Effects of regenerating vegetation on soil enzyme activity and microbial structure in reclaimed soils on a surface coal mine site. Appl Soil Ecol 87:56–62
Li RH, Deng HX, Zhang XF, Wang JJ, Awasthi MK, Wang Q, Xiao R, Zhou B, du J, Zhang Z (2019) High-efficiency removal of Pb (II) and humate by a CeO2–MoS2 hybrid magnetic biochar. Bioresour Technol 273:335–340
Liu LJ, Sun CL, He XL, Liu XX, Wu H, Liu M, Tang CX, Zhang YS (2016) The secondary compost products enhances soil suppressive capacity against bacterial wilt of tomato caused by Ralstonia solanacearum. Eur J Soil Biol 75:70–78
Ma Y, Rajkumar M, Luo YM, Freitas H (2011) Inoculation of endophytic bacteria on host and non-host plants-effects on plant growth and Ni uptake. J Hazard Mater 195:230–237
Ma SC, Zhang HB, Ma ST, Wang R, Wang GX, Shao Y, Li CX (2015) Effects of mine wastewater irrigation on activities of soil enzymes and physiological properties, heavy metal uptake and grain yield in winter wheat. Ecotox Environ Safe 113:483–490
Mahar A, Wang P, Ali A, Guo ZY, Awasthi MK, Lahori AH, Wang Q, Shen F, Li RH, Zhang ZQ (2016) Impact of CaO, fly ash, sulfur and Na2S on the (im)mobilization and phytoavailability of Cd, Cu and Pb in contaminated soil. Ecotox Environ Safe 134:116–123
Melo EEC, Costa ETS, Guilherme LRG, Faquin V, Nascimento CWA (2009) Accumulation of arsenic and nutrients by castor bean plants grown on an As-enriched nutrient solution. J Hazard Mater 168:479–483
Mench M, Lepp N, Bert V, Schwitzguebel JP, Gawronski SW, Schroder P, Vangronsveld J (2010) Successes and limitations of phytotechnologies at field scale: outcomes, assessment and outlook from COST Action 859. J Soils Sediments 10:1039–1070
Page AL, Miller RH, Keeney Dennis R (1982) Methods of soil analysis. Catena 15:99–100
Rao MA, Scelza R, Acevedo F, Diez MC, Gianfreda L (2014) Enzymes as useful tools for environmental purposes. Chemosphere 107:145–162
Schutze E, Weist A, Klose M, Wach T, Schumann M, Nietzsche S, Merten D, Baumert J, Majzlan J, Kothe E (2013) Taking nature into lab: biomineralization by heavy metal-resistant streptomycetes in soil. Biogeosciences 10:3605–3614
Sharma P, Kumar A, Bhardwaj R (2016) Plant steroidal hormone epibrassinolide regulate - heavy metal stress tolerance in Oryza sativa L. by modulating antioxidant defense expression. Environ Exp Bot 122:1–9
Smith SR (2009) A critical review of the bioavailability and impacts of heavy metals in municipal solid waste composts compared to sewage sludge. Environ Int 35:142–156
Tan XP, Wang ZQ, Lu GN, He WX, Wei GH, Huang F, Xu XL, Shen WJ (2017) Kinetics of soil dehydrogenase in response to exogenous cd toxicity. J Hazard Mater 329:299–309
Tian HX, Kong L, Megharaj M, He WX (2017) Contribution of attendant anions on cadmium toxicity to soil enzymes. Chemosphere 187:19–26
Wang JL, Li T, Liu GY, Smith JM, Zhao ZW (2016) Unraveling the role of dark septate endophyte (DSE) colonizing maize (Zea mays) under cadmium stress: physiological, cytological and genic aspects. Sci Rep 6:22028
Xian Y, Wang ME, Chen WP (2015) Quantitative assessment on soil enzyme activities of heavy metal contaminated soils with various soil properties. Chemosphere 139:604–608
Zhang HY, Xue QH, Shen GH, Wang DS (2013) Effects of actinomycetes agent on ginseng growth and rhizosphere soil microflora. Yingyong Shengtai Xuebao 24:2287–2293
Zhang J, Bei S, Li B, Zhang J, Christie P, Li X (2019a) Organic fertilizer, but not heavy liming, enhances banana biomass, increases soil organic carbon and modifies soil microbiota. Appl Soil Ecol 136:67–79
Zhang X, Li Z, Nie X, Huang M, Wang D, Xiao H, Liu C, Peng H, Jiang J, Zeng G (2019b) The role of dissolved organic matter in soil organic carbon stability under water erosion. Ecol Indic 102:724–733
Zhao J, Xue QH, Wang LN, Duan CM, Xue L, Mao N (2011) Antagonistic effect of multifunctional actinomycete strain Act12 on soil-borne pathogenic fungi and its identification. Chin J Eco-Agric 19:394–398
Zhu GX, Xiao HY, Guo QJ, Song B, Zheng GD, Zhang ZY, Zhao JJ, Okoli CP (2018) Heavy metal contents and enrichment characteristics of dominant plants in wasteland of the downstream of a lead-zinc mining area in Guangxi, Southwest China. Ecotox Environ Safe 151:266–271
Acknowledgments
Our special gratitude also goes to the anonymous constructive suggestions on this work.
Funding
This work was supported in part by the Science and Technology Program of Yangling Demonstration Zone (China) (2017NY-24) and the R&D Project of Shaanxi Province (2018ZDCXL-NY-02-02).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Elena Maestri
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Highlights
• Soil fertility and enzymatic activities were improved by compost treatment.
• Compost + Act12 improved the soil quality and PTEs solubility.
• Compost + Act12 facilitated PTEs uptake in Brassica juncea.
• Microbial-assisted phytoremediation is a potential strategy for soil PTEs reclaim.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, X., Guo, D., Ren, C. et al. Performance of Streptomyces pactum–assisted phytoextraction of Cd and Pb: in view of soil properties, element bioavailability, and phytoextraction indices. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27, 43514–43525 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-09842-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-09842-6