Abstract
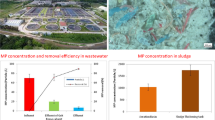
The widespread use of synthetic polymers has made microplastic (MP) a new type of contaminant that has attracted worldwide attention. Studies have shown that wastewater treatment plants (WWTPs) are an important source of MP collection in the natural environment. This study investigated the removal efficiency and migration characteristics of MPs by sampling the sewage from each treatment section of a WWTP in Zhengzhou, China. The results showed that the abundance of MPs in the influent water and primary, secondary, and tertiary treatment discharges was 16.0, 10.3, 4.5, and 2.9 MP/L, respectively, and the total removal rate of MPs from the influent to the final effluent reached 81.9%. The MPs in the WWTP were mainly small-sized (0.08–0.55 mm), followed by medium-sized (0.55–1.7 mm). Fibers were the dominant MP shape in both the water and sediment samples. Black (36%) and red (23%) were the dominant MP colors. Six different polymer types of MPs were detected, which were mainly polypropylene followed by polyethylene. In general, for the MPs in the WWTP, the removal rate of fragments can reach 97.08%, which is better than that of fibers (70.50%); the removal rate of small-sized can reach 95.86%, which is better than that of medium-sized (83.53%) and large-sized (70.00%). In this study, primary treatment has better effects in eliminating fragments and large-sized MPs; secondary treatment has better effects in eliminating fibers and small-sized MPs. Although WWTPs have a very good removal effect on MPs, 870 million MP/d are still discharged into nearby rivers from WWTPs with a treatment scale of 300,000 m3/day.

Graphical Abstract




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alimba CG, Faggio C (2019) Microplastics in the marine environment: current trends in environmental pollution and mechanisms of toxicological profile. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 68:61–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.etap.2019.03.001
Andrady AL (2011) Microplastics in the marine environment. Mar Pollut Bull 62(8):1596–1605. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2011.05.030
Besseling E, Wegner A, Foekema EM, van den Heuvel-Greve MJ, Koelmans AA (2013) Effects of microplastic on fitness and PCB bioaccumulation by the lugworm Arenicola marina (L.). Environ Sci Technol 47(1):593–600. https://doi.org/10.1021/es302763x
Carr SA, Liu J, Tesoro AG (2016) Transport and fate of microplastic particles in wastewater treatment plants. Water Res 91:174–182. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2016.01.002
Cheung PK, Fok L (2017) Characterisation of plastic microbeads in facial scrubs and their estimated emissions in Mainland China. Water Res 122:53–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2017.05.053
Dris R, Gasperi J, Rocher V et al (2015) Microplastic contamination in an urban area: a case study in Greater Paris. Environ Chem 12(5):592–599. https://doi.org/10.1071/EN14167
Eerkes-Medrano D, Thompson RC, Aldridge DC (2015) Microplastics in freshwater systems: a review of the emerging threats, identification of knowledge gaps and prioritisation of research needs. Water Res 75:63–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2015.02.012
Elert AM, Becker R, Duemichen E, Eisentraut P, Falkenhagen J, Sturm H, Braun U (2017) Comparison of different methods for MP detection: what can we learn from them, and why asking the right question before measurements matters? Environ Pollut 231:1256–1264. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2017.08.074
Estahbanati S, Fahrenfeld NL (2016) Influence of wastewater treatment plant discharges on microplastic concentrations in surface water. Chemosphere 162(11):277–284. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.07.083
Fendall LS, Sewell MA (2009) Contributing to marine pollution by washing your face: microplastics in facial cleansers. Mar Pollut Bull 58(8):1225–1228. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2009.04.025
Gao FL, Li JX, Sun CJ et al (2019) Study on the capability and characteristics of heavy metals enriched on microplastics in marine environment. Mar Pollut Bull 144:61–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2019.04.039
Gies EA, LeNoble JL, Noël M, Etemadifar A, Bishay F, Hall ER, Ross PS (2018) Retention of microplastics in a major secondary wastewater treatment plant in Vancouver, Canada. Mar Pollut Bull 133:553–561. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2018.06.006
Hidalgo-Ruz V, Gutow L, Thompson RC, Thiel M (2012) Microplastics in the marine environment: a review of the methods used for identification and quantification. Environ Sci Technol 46(6):3066–3075. https://doi.org/10.1021/es2031505
Holmes LA, Turner A, Thompson RC (2012) Adsorption of trace metals to plastic resin pellets in the marine environment. Environ Pollut 160(1):42–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2011.08.052
Koelmans AA, Besseling E, Wegner A, Foekema EM (2013) Plastic as a carrier of POPs to aquatic organisms: a model analysis. Envrion Sci Technol 47(14):7812–7820. https://doi.org/10.1021/es401169n
Kuptsov A, Zhizhin GN (1998) Handbook of Fourier transform Raman and infrared spectra of polymers, 45. Elsevier. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008198824934
Lares M, Ncibi MC, Sillanpää M, Sillanpää M (2018) Occurrence, identification and removal of microplastic particles and fibers in conventional activated sludge process and advanced MBR technology. Water Res 133:236–246. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2018.01.049
Leslie HA, Brandsma SH, van Velzen MJM, Vethaak AD (2017) Microplastics en route: field measurements in the Dutch river delta and Amsterdam canals, wastewater treatment plants, North Sea sediments and biota. Environ Int 101:133–142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2017.01.018
Li J (2019) The explorer found plastic debris 10927 meters above the mariana trench (In Chinese). China News, http://www.chinanews.com/tp/hd2011/2019/05-14/882363.shtml. Accessed 17 Aug 2019
Li XW, Chen LB, Mei QQ (2018) Microplastics in sewage sludge from the wastewater treatment plants in China. Water Res 142:75–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2018.05.034
Liu K, Wang XH, Fang T et al (2019a) Source and potential risk assessment of suspended atmospheric microplastics in Shanghai. Sci Total Environ 675:462–471. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.04.110
Liu XN, Yuan WK, Di MX, Li Z, Wang J (2019b) Transfer and fate of microplastics during the conventional activated sludge process in one wastewater treatment plant of China. Chem Eng J 362:176–182. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.01.033
Long ZX, Pan Z, Wang Wl et al (2019) Microplastic abundance, characteristics, and removal in wastewater treatment plants in a coastal city of China. Water Res 155:255–265. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2019.02.028
Lusher AL, Burke A, O'Connor I, Officer R (2014) Microplastic pollution in the Northeast Atlantic ocean: validated and opportunistic sampling. Mar Pollut Bull 88(1–2):325–333. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2014.08.023
Magnusson K, Norén F (2014) Screening of microplastic particles in and down-stream a wastewater treatment plant. IVL Swedish Environmental Research Institute, C55
Mahon AM, O’Connell B, Healy MG et al (2017) Microplastics in sewage sludge: effects of treatment. Environ Sci Technol 51(2):810–818. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.6b04048
Mason SA, Garneau D, Sutton R, Chu Y et al (2016) Microplastic pollution is widely detected in US municipal wastewater treatment plant effluent. Environ Pollut 218(11):1045–1054. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2016.08.056
McCormick A, Hoellein TJ, Mason SA, Schluep J, Kelly JJ (2014) Microplastic is an abundant and distinct microbial habitat in an urban river. Environ Sci Technol 48(20):11862–11871. https://doi.org/10.1021/es503610r
Michielssen MR, Michielssen ER, Ni J, Duhaime MB (2016) Fate of microplastics and other small anthropogenic litter (SAL) in wastewater treatment plants depends on unit processes employed. Enviro Sci-Wat Res 2(6):1064–1073. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6ew00207b
Murphy F, Ewins C, Carbonnier F, Quinn B (2016) Wastewater treatment works (WWTW) as a source of microplastics in the aquatic environment. Environ Sci Technol 50(11):5800–5808. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.5b05416
Napper IE, Bakir A, Rowland SJ, Thompson RC (2015) Characterisation, quantity and sorptive properties of microplastics extracted from cosmetics. Mar Pollut Bull 99(1):178–185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2015.07.029
Plastic Europe (2018) Plastics – The Facts 2017: an analysis of European plastics production, demand and waste data. https://www.plasticseurope.org/download_file/view/477/179. Accessed 1 Sept 2019
Qiu Y, Shi HC, He M (2010) Nitrogen and phosphorous removal in municipal wastewater treatment plants in China: a review. Int J Chem Eng 10:1155–1165. https://doi.org/10.1155/2010/914159
Simon M, VanAlst N, Vollertsen J (2018) Quantification of microplastic mass and removal rates at wastewater treatment plants applying focal plane array (FPA)-based Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR) imaging. Water Res 142:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2018.05.019
Sun J, Dai XH, Wang QL et al (2019) Microplastics in wastewater treatment plants: detection, occurrence and removal. Water Res 152:21–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2018.12.050
Talvitie J, Heinonen M, Paakkonen JP et al (2015) Do wastewater treatment plants act as a potential point source of microplastics? Preliminary study in in the coastal Gulf of Finland Baltic Sea. Environ Sci Technol 72(9):1495–1504. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2015.360
Talvitie J, Mikola A, Koistinen A, Setälä O (2017) Solutions to microplastic pollution – removal of microplastics from wastewater effluent with advanced wastewater treatment technologies. Water Res 123:401–407. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2017.07.005
Tao H, Zhu JA (2019) Comparative analysis of fashion color preferences of Chinese resident in past ten years based on questionnaires. Journal of Zhejiang Fashion Institute of Technology 03:1–6 http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/33.1351.Z.20190612.0918.010.html. Accessed 13 Oct 2019
Thompson RC, Olsen Y, Mitchell RP et al (2004) Lost at sea: where is all the plastic. Science 304(5672):838–838. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1094559
Thompson RC, Moore CJ, Saal FSV, Swan SH (2009) Plastics, the environment and human health: current consensus and future trends. Philos T R Soc B 364(1526):2153–2166 https://doi.org/10.1098/rstb.2009.0053
Underwood AJ, Chapman MG, Browne MA (2017) Some problems and practicalities in design and interpretation of samples of microplastic waste. Anal Methods 9:1322–1345. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6AY02641A
Van Cauwenberghe L, Vanreusel A, Mees J, Janssen CR (2013) Microplastic pollution in deep-sea sediments. Environ Pollut 182:495–499. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2013.08.013
Van Wezel A, Caris I, Kools SAE (2016) Release of primary microplastics from consumer products to wastewater in The Netherlands. Environ Toxicol Chem 35(7):1627–1631 https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.3316
Wagner M, Scherer C, Alvarez-Muñoz D et al (2014) Microplastics in freshwater ecosystems: what we know and what we need to know. Environ Sci Eur 26:12. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12302-014-0012-7
Wright LS, Kelly FJ (2017) Plastic and human health: a micro issue? Environ Sci Technol 51(12):6634–6647. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.7b00423
Wright LS, Thompson RC, Galloway TS (2013) The physical impacts of microplastics on marine organisms: a review. Environ Pollut 178:483–492. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2013.02.031
Yang G, Zhang GM, Wang HC (2015) Current state of sludge production, management, treatment and disposal in China. Water Res 78:60–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2015.04.002
Zhang FW (2018) Research progress on harnessing technical equipment of white pollution. Inner Mongolia Environmental Sciences 30(4):93–94. https://doi.org/10.16647/j.cnki.cn15-1369/X.2018.04.054
Zhao SY, Zhu LX, Wang T et al (2014) Suspended microplastics in the surface water of the Yangtze Estuary System,China:First observations on occurrence, distribution. Mar Pollut Bull 86(1-2):562–568. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2014.06.032
Ziajahromi S, Neale PA, Rintoul L, Leusch FDL (2017) Wastewater treatment plants as a pathway for microplastics: development of a new approach to sample wastewater-based microplastics. Water Res 112:93–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2017.01.042
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant numbers 51679218, 51709238, 51879239); the Program for Science & Technology Innovation Talents in Universities of Henan Province (grant number 17HASTIT031); and the Outstanding Young Talent Research Fund of Zhengzhou University (grant numbers 1521323001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 14077 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ren, P., Dou, M., Wang, C. et al. Abundance and removal characteristics of microplastics at a wastewater treatment plant in Zhengzhou. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27, 36295–36305 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-09611-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-09611-5