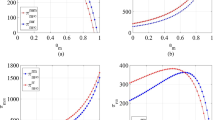
Abstract
Municipal solid waste (MSW) incineration contributes significantly to carbon emissions, and has become a serious problem in China, which has seen an exponential rise in waste over the last twenty years due to rapid urbanization and the associated consumer economy growth. To tackle this issue, this paper develops a leader-follower optimized approach for economic and environmental equilibrium in incineration power plants that includes a carbon allowance allocation scheme (IPP-CAAS) under combustion and pollutant limitations. In the leader-follower (bi-level) game, the regional authority on the upper level determines the carbon allocations and environmental targets and the IPPs on the lower level develop schemes to maximize revenue under the upper-level restrictions. By employing uncertain parameters for the carbon and power conversion fluctuations, the approach is able to more accurately depict the industry characteristics of waste incineration process in this carbon-economy balance problem. The robustness and practicality of the proposed methodology was then validated through a case study. Scenario analysis under different political parameters indicates that the proposed methodology can assist the authorities to achieve carbon-economy trade-off and under serious carbon-control situations, encourage the IPPs to reduce their blended coal ratios, and invest in low-carbon incineration technology. Managerial insights on further industrial developments are also given for the authority and relevant practitioners.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agbor E, Zhang X, Kumar A (2014) A review of biomass co-firing in North America. Renewable & Sustainable Energy Reviews 40:930–943
Andreani R, Martinez JM, Schuverdt ML (2005) On the relation between constant positive linear dependence condition and quasinormality constraint qualification. Journal of Optimization Theory & Applications 125(2):473–483
Boyd S, Vandenberghe L (2004) Convex optimization. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press 244
Chen D, Christensen TH (2010) Life-cycle assessment (EASEWASTE) of two municipal solid waste incineration technologies in China. Waste Management & Research 28(6):508–519
Chen H, Zhang M, Xue K, Xu G, Yang Y, Wang Z, Liu W, Liu T (2020) An innovative waste-to-energy system integrated with a coal-fired power plant. Energy 194:116 893
Cho S, Kim J (2019) Multi-site and multi-period optimization model for strategic planning of a renewable hydrogen energy network from biomass waste and energy crops. Energy 185:527– 540
Choi I (2005) Global climate change and the use of economic approaches: the ideal design features of domestic greenhouse gas emissions trading with an analysis of the European Union’s CO2 Emissions Trading Directive and the Climate Stewardship Act. Nat Resour J 45:865
Chum H, la Vega Navarro AD (2018) Edmonds j. The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC)-energy systems. Cambridge University Press, Faaij A
Cox L (1999) Nitrogen oxides NOx why and how they are controlled. Diane Publishing
Dubois D, Prade H (1987) Properties of measures of information in evidence and possibility theories. Fuzzy sets and systems 24(2):161–182
Durán I, Rubiera F, Pevida C (2017) Separation of CO2 in a solid waste management incineration facility using activated carbon derived from pine sawdust. Energies 10(6):827
Feng Z, Tang W, Niu Z, Wu Q (2018) Bi-level allocation of carbon emission permits based on clustering analysis and weighted voting: a case study in China. Applied Energy 228:1122–1135
Fujii M, Dou Y, Sun L, Ohnishi S, Maki S, Dong H, Dong L, Chandran R (2019) Contribution to a low-carbon society from improving energy of waste-to-energy system by upgrading utilization of waste. Resour Conserv Recycl 149:586–594
Ganesan T, Elamvazuthi I, Shaari KZK, Vasant P (2014) Hopfield differential evolution for multi-objective optimization of a cement-bonded sand mould system. International Journal of Management Science & Engineering Management 9(1):40–47
Grossman SJ, Hart OD (1980) Takeover bids, the free-rider problem, and the theory of the corporation. Bell J Econ 11(1):42–64
Groves T, Ledyard J (1977) Optimal allocation of public goods: a solution to the “free rider” problem. Econometrica 45(4):783–809
Han R, Yu BY, Tang BJ, Liao H, Wei YM (2017) Carbon emissions quotas in the Chinese road transport sector: a carbon trading perspective. Energy Policy 106:298–309
Hanson MA (1981) On sufficiency of the Kuhn-Tucker conditions. Journal of Mathematical Analysis & Applications 80(2):545–550
He J, Lin B (2019) Assessment of waste incineration power with considerations of subsidies and emissions in China. Energy policy 126:190–199
He L, Huang GH, Lu H (2011) Greenhouse gas emissions control in integrated municipal solid waste management through mixed integer bilevel decision-making. J Hazard Mater 193(20):112–119
He PJ (2012) Municipal solid waste in rural areas of developing country: do we need special treatment mode? Waste Manag 32(7):1289–1290
He PJ, Zhang H, Zhang CG, Lee DJ (2004) Characteristics of air pollution control residues of MSW incineration plant in Shanghai. J Hazard Mater 116(3):229–237
Herrmann B, Thöni C, Gächter S (2008) Antisocial punishment across societies. Science 319 (5868):1362–1367
Huang J, Xue F, Song X (2013) Simulation analysis on policy interaction effects between emission trading and renewable energy subsidy. Journal of Modern Power Systems and Clean Energy 1(2):195–201
Ilic DD, Ödlund L (2018) Method for allocation of carbon dioxide emissions from waste incineration which includes energy recovery. Energy Procedia 149:400–409
Isaloo F, Paydar MM (2020) Optimizing a robust bi-objective supply chain network considering environmental aspects: a case study in plastic injection industry. International Journal of Management Science and Engineering Management 15(1):26–38
Jouhara H, Nannou T, Anguilano L, Ghazal H, Spencer N (2017) Heat pipe based municipal waste treatment unit for home energy recovery. Energy 139:1210–1230
Keshari AK, Datta B (2001) A combined use of direct search algorithms and exterior penalty function method for groundwater pollution management. Journal of Porous Media 4(3):259–270
Kuhn AWHW (1951) Tucker nonlinear programming. In: Proceedings of the Second Berkeley Symposium on Mathematical Statistics and Probability, University of California Press, Berkeley California, pp 481–492
Kun L, Li J, Chris H (2017) Bi-level optimization with hybrid algorithms for energy saving and CO2 emissions reduction by wireless sensor networks for transportation management. Journal of Intelligent & Fuzzy Systems 32 (5):3387–3400
Kuo JH, Lin CL, Chen JC, Tseng HH, Wey MY (2011) Emission of carbon dioxide in municipal solid waste incineration in Taiwan: a comparison with thermal power plants. International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control 5(4):889–898
Lee E, Irving B, Martinsen t, Mareckova K (2019) Emissions from waste incineration. Cambridge University Press
Lee J (2019) Operational decision model with carbon cap allocation and carbon trading price. Journal of Open innovation: Technology Market, and Complexity 5(1):11
Li G, Zhang R, Jiang T, Chen H, Bai L, Li X (2017) Security-constrained bi-level economic dispatch model for integrated natural gas and electricity systems considering wind power and power-to-gas process. Applied energy 194:696–704
Li Y (2017) Governing environmental conflicts in urban China: Lessons learned from the case of the Liulitun waste incineration plant in Beijing. Public Policy & Administration 34(2):189–209
Li Y, Homburg V, De Jong M, Koppenjan J (2016) Government responses to environmental conflicts in urban China: the case of the Panyu waste incineration power plant in Guangzhou. J Clean Prod 134:354–361
Li Y, Zhao X, Li Y, Li X (2015) Waste incineration industry and development policies in China. Waste Management 46:234–241
Liqiang H (2019) Chinadaily http://www.chinadaily.com.cn/a/201905/14/WS5cd9fe7ca3104842260bb625.html
Liu X, Liu L, Leng P, Hu Z (2019) Feasible and effective reuse of municipal sludge for vegetation restoration: physiochemical characteristics and microbial diversity. Scientific reports 9(1):879
Liu Z (2016) China’s carbon emissions report 2016. Working Paper Belfer Center for Science and International Affairs Harvard Kennedy School
Lu H, Sun S, Ren L, He L (2015) GHG emission control and solid waste management for megacities with inexact inputs: a case study in Beijing, China. Journal of hazardous materials 284:92–102
Lu JW, Zhang S, Hai J, Lei M (2017) Status and perspectives of municipal solid waste incineration in China: a comparison with developed regions. Waste Manag 69:170–186
Mathews JA, Tan H (2016) Circular economy: lessons from China. Nature News 531(7595):440
Mi Z, Meng J, Green F, Coffman D, Guan D (2018) China’s exported carbon peak: patterns, drivers, and implications. Geophys Res Lett 45(9):4309–4318
Mian MM, Zeng X, Nasry AANB, Al-Hamadani SMZF (2017) Municipal solid waste management in China: a comparative analysis. Journal of Material Cycles & Waste Management 19(3):1127–1135
NBS (2017) National bureau of statistics of China http://www.stats.gov.cn/english/
Parker CF, Karlsson C (2018) The UN climate change negotiations and the role of the United States: assessing American leadership from Copenhagen to Paris. Environmental Politics 27(3):519–540
Quina MJ, Bordado JC, Quinta-Ferreira RM (2011) Air pollution control in municipal solid waste incinerators. The impact of air pollution on health, economy, environment and agricultural sources 331–358
Ramachandra TV, Bharath HA, Kulkarni G, Han SS (2018) Municipal solid waste: generation, composition and GHG emissions in Bangalore, India. Renewable & Sustainable Energy Reviews 82(1):1122–1136
Safaei AS, Farsad S, Paydar MM (2018) Robust bi-level optimization of relief logistics operations. Appl Math Model 56:359–380
Sakawa M, Nishizaki I, Uemura Y, Kubota K (2015) Interactive fuzzy programming for multilevel linear programming problems with fuzzy parameters. Journal of Japan Society for Fuzzy Theory & Systems 83(6):1–9
Sha’Ato R, Aboho S, Oketunde F, Eneji I, Unazi G, Agwa S (2007) Survey of solid waste generation and composition in a rapidly growing urban area in Central Nigeria. Waste management 27(3):352–358
Sichuan N (2018) National bureau of statistics of Sichuan Province http://tjj.sc.gov.cn//
Soltani A, Sadiq R, Hewage K (2016) Selecting sustainable waste-to-energy technologies for municipal solid waste treatment: a game theory approach for group decision-making. J Clean Prod 113:388–399
Song J, Song D, Zhang D (2015) Modeling the concession period and subsidy for BOT waste-to-energy incineration projects. Journal of Construction Engineering and Management 141(10):04015– 033
Srivastava V, Goel G, Thakur VK, Singh RP, de Araujo ASF, Singh P (2020) Analysis and advanced characterization of municipal solid waste vermicompost maturity for a green environment. Journal of Environmental Management 255(109):914
Sun C, Meng X, Peng S (2017) Effects of waste-to-energy plants on china’s urbanization: evidence from a hedonic price analysis in shenzhen. Sustainability 9(3):475
Tolis A, Rentizelas A, Aravossis K, Tatsiopoulos I (2010) Electricity and combined heat and power from municipal solid waste; theoretically optimal investment decision time and emissions trading implications. Waste Management & Research the Journal of the International Solid Wastes & Public Cleansing Association Iswa 28(11):985
Van-Broekhoven E , De Baets B (2006) Fast and accurate center of gravity defuzzification of fuzzy system outputs defined on trapezoidal fuzzy partitions. Fuzzy Sets and Systems 157(7):904–918
Wang G, Deng J, Ma Z, Hao J, Jiang J (2018) Characteristics of filterable and condensable particulate matter emitted from two waste incineration power plants in China. Science of The Total Environment 639:695–704
Wang H, He J, Kim Y, Kamata T (2016) Municipal solid waste management in small towns: an economic analysis conducted in Yunnan, China. Social Science Electronic Publishing 31:151–165
Wang Y, Zhang X, Liao W, Wu J, Yang X, Shui W, Deng S, Zhang Y, Lin L, Xiao Y (2018) Investigating impact of waste reuse on the sustainability of municipal solid waste (MSW) incineration industry using emergy approach: a case study from Sichuan Province, China. Waste Management 77:252–267
Wei J, Lu J, Zhao J (2020) Interactions of competing manufacturers’ leader-follower relationship and sales format on online platforms. Eur J Oper Res 280(2):508–522
Wen L, Zhang Y (2020) A study on carbon transfer and carbon emission critical paths in china: I-O analysis with multidimensional analytical framework. Environmental Science and Pollution Research
Xu J, Zhou X (2011) Fuzzy-like multiple objective decision making. Springer Berlin Heidelberg
Xu J, Hou S, Yao L, Li C (2017) Integrated waste load allocation for river water pollution control under uncertainty: a case study of Tuojiang River, China. Environmental Science and Pollution Research 24 (21):17,741–17,759
Xu X, Zhang W, He P, Xu X (2017) Production and pricing problems in make-to-order supply chain with cap-and-trade regulation. Omega 66:248–257
Zhang G, Lu j, Dillon T (2008) Solution concepts and an approximation Kuhn–Tucker approach for fuzzy multiobjective linear bilevel programming. Springer
Zhang H, Duan M (2020) China’s pilot emissions trading schemes and competitiveness: an empirical analysis of the provincial industrial sub-sectors. Journal of Environmental Management 258(109):997
Zhou X, James G, Liebman A, Dong ZY, Ziser C (2010) Partial carbon permits allocation of potential emission trading scheme in australian electricity market. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems 25(1):543–553
Funding
This research is supported by the China Scholarship Council (Grant No. CSC201906240106) and the Scientific Research Staring Foundation of Sichuan University (Grant No. 2015SCU11034).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Muhammad Shahbaz
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, J., Zhu, M. & Zhao, S. Leader-follower optimized approach for carbon-economy equilibrium in the municipal solid waste (MSW) incineration industry. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27, 32637–32658 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-09076-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-09076-6