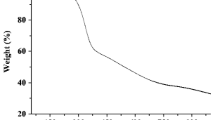
Abstract
Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons are a class of highly toxic and unremitting organic pollutants that are widely distributed in the natural environment. In this work, a metal-organic framework (MOF) designated as HKUST-1 [Cu3(BTC)2] was synthesized, characterized, and applied as a solid-phase extraction sorbent for the determination of a trace polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon, anthracene (Ant) as model compound, in various real samples by spectrofluorimetry. The synthesized MOF exhibited large surface areas and high extraction ability, making it excellent candidate as sorbent for enrichment of trace anthracene. The effects of influential parameters on the performance of the dispersive micro-solid-phase extraction (Dμ-SPE) process, such as the initial anthracene concentration, pH, sorbent dosage, and shaking time, were investigated and optimized by the experiment design method. Under the optimized experimental conditions, good linearity in the range of 3–85 ng mL−1 with correlation coefficient 0.997 and good sensitivity with low detection limit 0.5 ng mL−1 for Ant was achieved. The method has been validated in the analysis of real tap water, soft drink, and vegetable juice samples with recoveries in the range of 86.33–103.00% and relative standard deviations in the range of 1.94–3.77%. The as-prepared HKUST-1 was used for at least four times without any obvious decline of extraction capability. The results of this study show the great potential of MOFs as sorbents in Dμ-SPE procedures for the separation and determination of trace Ant in complicated matrices.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arrebola FJ, Garrido Frenich A, González Rodríguez MJ, Plaza Bolaños P, Martínez Vidal JL (2006) Determination of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in olive oil by a completely automated headspace technique coupled to gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. J Mass Spectrom 41:822–829
Azzouz A, Kailasa SK, Lee SS, Rascón AJ, Ballesteros E, Zhang M, Kim KH (2018) Review of nanomaterials as sorbents in solid-phase extraction for environmental samples. TrAC Trends Anal Chem 108:347–369
Bagheri A, Taghizadeh M, Behbahani M, Asgharinezhad AA, Salarian M, Dehghani A, Ebrahimzadeh H, Amini MM (2012) Synthesis and characterization of magnetic metal-organic framework (MOF) as a novel sorbent, and its optimization by experimental design methodology for determination of palladium in environmental samples. Talanta 99:132–139
Bogusz MJ, El Hajj SA, Ehaideb Z, Hassan H, Al-Tufail M (2004) Rapid determination of benzo(a)pyrene in olive oil samples with solid-phase extraction and low-pressure, wide-bore gas chromatography–mass spectrometry and fast liquid chromatography with fluorescence detection. J Chromatogr A 1026:1–7
Cai Y, Kulkarni AR, Huang YG, Sholl DS, Walton KS (2014) Control of metal–organic framework crystal topology by ligand functionalization: functionalized HKUST-1 derivatives. Cryst Growth Des 14:6122–6128
Chagas PMB, Caetano AA, Rossi MA, Gonçalves MA, Ramalho TC, Corrêa AD, Guimarães IR (2019) Chitosan-iron oxide hybrid composite: mechanism of hexavalent chromium removal by central composite design and theoretical calculations. Environ Sci Pollut R 26:15973–15988
Chisvert A, Cárdenas S, Lucena R (2019) Dispersive micro-solid phase extraction. TrAC Trends Anal Chem 112:226–233
Chui SS-Y, Lo SM-F, Charmant JPH, Orpen AG, Williams ID (1999) A chemically functionalizable nanoporous material [Cu3(TMA)2(H2O)3]n. Science 283:1148–1150
Dyachuk OA, Gubina TI, Melnikov GV (2009) Adsorption preconcentration in the luminescence determination of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. J Anal Chem 64:3–7
Ghasemi JB, Zolfonoun E (2013) Simultaneous spectrophotometric determination of trace amount of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in water samples after magnetic solid-phase extraction by using projection pursuit regression. Environ Monit Assess 185:2297–2305
Habibi MH, Hadjmohammadi MR (2008) Determination of some polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the Caspian seawater by HPLC following preconcentration with solid-phase extraction. Iran J Chem Chem Eng 27:91–96
Hashemi B, Zohrabi P, Raza N, Kim KH (2017) Metal-organic frameworks as advanced sorbents for the extraction and determination of pollutants from environmental, biological, and food media. TrAC Trends Anal Chem 97:65–82
Hu H, Zhang H, Chen Y, Ou H (2019) Enhanced photocatalysis using metal–organic framework MIL-101(Fe) for organophosphate degradation in water. Environ Sci Pollut R 26:24720–24732
Karimi-Maleh H, Shafieizadehd M, Taher MA, Opoku F, Muriithi Kiarii E, Penny Govender P, Ranjbari S, Rezapour M, Orooji Y (2020) The role of magnetite/graphene oxide nano-composite as a high-efficiency adsorbent for removal of phenazopyridine residues from water samples, an experimental/theoretical investigation. J Mol Liq 298:112040
Khani R, Sobhani S, Hossein Beyki M (2016) Highly selective and efficient removal of lead with magnetic nano-adsorbent: multivariate optimization, isotherm and thermodynamic studies. J Colloid Interface Sci 466:198–205
Khani R, Sobhani S, Hossein Beyki M, Miri S (2018) Application of magnetic ionomer for development of very fast and highly efficient uptake of triazo dye Direct Blue 71 form different water samples. Ecotox Environ Safe 150:54–61
Khani R, Sobhani S, Yari T (2019) Magnetic dispersive micro solid-phase extraction of trace Rhodamine B using imino-pyridine immobilized on iron oxide as nanosorbent and optimization by Box–Behnken design. Microchem J 46:71–478
Khezeli T, Daneshfar A (2017) Development of dispersive micro-solid phase extraction based on micro and nano sorbents. TrAC Trends Anal Chem 89:99–118
Kim KH, Jahan SA, Kabir E, Brown RJ (2013) A review of airborne polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) and their human health effects. Environ Int 60:71–80
Liu H, Ran F, Wang X, He N, Guo Y (2018) A chromium (III) oxide-coated steel wire prepared by arc ion plating for use in solid-phase microextraction of aromatic hydrocarbons. Microchim Acta 185:82–89
Marce RM, Borrull F (2000) Solid-phase extraction of polycyclic aromatic compounds. J Chromatogr A 885:273–290
Moja SJ, Mtunzi F, Madlanga X (2013) Determination of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in river water samples from the Vaal Triangle area in South Africa. J Environ Sci Heal A 48:847–854
Nakamoto K (2006) Infrared and Raman spectra of inorganic and coordination compounds. Handbook of Vibrational Spectroscopy. Wiley, Hoboken
Oleszczuk P, Baran S (2004) Application of solid-phase extraction to determination of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in sewage sludge extracts. J Hazard Mater 113:237–245
Pérez-López B, Merkoçi A (2012) Carbon nanotubes and graphene in analytical sciences. Microchim Acta 179:1–16
Plaza-Bolaños P, Garrido Frenich A, Martínez Vidal JL (2010) Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in food and beverages. Analytical methods and trends J Chromatogr A 1217:6303–6326
Prestipino C, Regli L, Vitillo JG, Bonino F, Damin A, Lamberti C, Zecchina A, Solari PL, Kongshaug KO, Bordiga S (2006) Local structure of framework Cu (II) in HKUST-1 metal organic framework: spectroscopic characterization upon activation and interaction with adsorbates. Chem Mater 18:1337–1346
Rocío-Bautista P, Martínez-Benito C, Pino V, Pasán J, Ayala JH, Ruiz-Pérez C, Afonso AM (2015) The metal–organic framework HKUST-1 as efficient sorbent in a vortex-assisted dispersive micro solid-phase extraction of parabens from environmental waters, cosmetic creams and human urine. Talanta 139:13–20
Rosales E, Sanromán MA, Pazos M (2012) Application of central composite face-centered design and response surface methodology for the optimization of electro-Fenton decolorization of azure B dye. Environ Sci Pollut R 19:1738–1746
Sadowska-Rociek A, Surma M, Cieślik E (2015) Determination of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in coffee and coffee substitutes using dispersive SPE and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Food Anal Methods 8:109–121
Sun S, Huang L, Xiao H, Shuai Q, Hu S (2019) In situ self-transformation metal into metal-organic framework membrane for solid phase microextraction of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Talanta 202:145–151
Van der Wat L, Forbes PBC (2019) Comparison of extraction techniques for polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from lichen biomonitors. Environ Sci Pollut R 26:11179–11190
Vichi S, Pizzale L, Conte LS, Buxaderas S, López-Tamames E (2005) Simultaneous determination of volatile and semi-volatile aromatic hydrocarbons in virgin olive oil by headspace solid-phase microextraction coupled to gas chromatography/mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 1090:146–154
Viñas P, Campillo N, Aguinaga N, Pézez-Cánovas E, Hernández-Córdoba M (2007) Use of headspace solid-phase microextraction coupled to liquid chromatography for the analysis of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in tea infusions. J Chromatogr A 1164:10–17
Wang M, Cui S, Yang X, Bi W (2015) Synthesis of g-C3N4/Fe3O4 nanocomposites and application as a new sorbent for solid phase extraction of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in water samples. Talanta 132:922–928
Yaghi OM, Kalmutzki MJ, Diercks CS (2019) Introduction to reticular chemistry: metal-organic frameworks and covalent organic frameworks. Wiley-VCH, Weinheim
Yasini P, Shemirani F, Khani R (2012) Combination of in situ surfactant-based solid phase extraction and central composite design for preconcentration and determination of manganese in food and water samples. Food Anal Methods 5:1303–1310
Yue X, Guo W, Li X, Zhou H, Wang R (2016) Core-shell Fe3O4@MIL-101 (Fe) composites as heterogeneous catalysts of persulfate activation for the removal of Acid Orange 7. Environ Sci Pollut R 23:15218–15226
Zhao L, Azhar M, Li X, Duan X, Sun H, Wang S, Fang X (2019) Adsorption of cerium (III) by HKUST-1 metal-organic framework from aqueous solution. J Colloid Interface Sci 542:421–428
Funding
The financial support from the University of Birjand.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Tito Roberto Cadaval Jr
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khani, R., Ghalibafan, M. & Farrokhi, A. Performance of metal-organic framework as an excellent sorbent for highly efficient and sensitive trace determination of anthracene in water and food samples. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27, 26305–26314 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-09033-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-09033-3