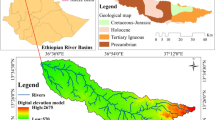
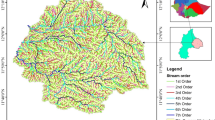
Abstract
This study explores the opportunities for irrigated agriculture in Khyber District of Former Federally Administered Tribal Area (FATA). Agriculture continues to be most important economic activity in Pakistan and former FATA is no exception. However, agriculture in the semi-arid Khyber District continues to suffer a decline due to excessive reliance on rainfall, which is drastically insufficient. Khyber District have large expanses of fertile land; however, farmers depend on unpredictable rain-fed agriculture, which has low productivity and food insecurity. There are a number of rivers in the region where great prospects exist for irrigated farming. Geographical information systems (GIS)-based multi-criteria analysis can be used to map areas with irrigation potential. The current study focused on different variables including soil texture, perennial rivers, land cover, topography, and dams. For this study, data was collected from diverse sources which include Google earth images, top sheets, land use land cover, soil texture map of FATA, and SRTM 30 Meter. The collected data was analyzed by using multi-criteria analysis in Arc GIS 10.2.2 by using MIF technique. The results of this research indicate that there is great potential for irrigated farming in the study area. Potential land for this purpose were divided into three categories, i.e., highly suitable which consisted of 678 km2, or 26% of the total area; 1044 km2 representing 40% were moderately suitable to irrigation; while the remaining 698 km2 representing 27% were considered least suitable for irrigation. Likewise, 204 km2 representing 7% were deemed unsuitable for irrigated agriculture mostly consisting of barren rocks. The results also illustrate how GIS as a tool can be used in the exploration of water resources in a scientific approach, thus making decision-making easier and more accurate.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ammar A, Riksen M, Ouessar M, Ritsema C (2016) Identification of suitable sites for rainwater harvesting structures in arid and semi-arid regions: a review. International Soil and Water Conservation Research 4(2):108–120
Anane M, Bouziri L, Limam A, Jellali S (2012) Ranking suitable sites for irrigation with reclaimed water in the Nabeul-Hammamet region (Tunisia) using GIS and AHP-multicriteria decision analysis. Resour Conserv Recycl 65:36–46
Butt MJ, Mahmood R, Waqas A (2011) Sediments deposition due to soil erosion in the watershed region of Mangla dam. Environ Monit Assess 181(1–4):419–429
Ceballos-Silva A, Lopez-Blanco J (2003) Delineation of suitable areas for crops using a multi-criteria evaluation approach and land use/cover mapping: a case study in Central Mexico. Agric Syst 77(2):117–136
Chen, Y., Yu, J., Shahbaz, K., & Xevi, E. (2009). A GIS-based sensitivity analysis of multi-criteria weights. In proceedings of the 18th world IMACS/MODSIM congressCairns Australia (pp. 13-17)
Chenini I, Mammou AB, El May M (2010) Groundwater recharge zone mapping using GIS-based multi-criteria analysis: a case study in Central Tunisia (Maknassy Basin). Water Resour Manag 24(5):921–939
FATA Secretariat (2017) Digest of mega projects. Planning and Development Department, FATA Secretariat, Warsak Road, Peshawar
Feizizadeh B, Blaschke T (2013) Land suitability analysis for Tabriz County, Iran: a multi-criteria evaluation approach using GIS. J Environ Plan Manag 56(1):1–23
Hill, D. (2013). A history of engineering in classical and medieval times
Hossain MS, Chowdhury SR, Das NG, Sharifuzzaman SM, Sultana A (2009) Integration of GIS and multicriteria decision analysis for urban aquaculture development in Bangladesh. Landsc Urban Plan 90(3–4):119–133
Jha MK, Chowdary VM, Kulkarni Y, Mal BC (2014) Rainwater harvesting planning using geospatial techniques and multicriteria decision analysis. Resour Conserv Recycl 83:96–111
Kallali H, Anane M, Jellali S, Tarhouni J (2007) GIS-based multi-criteria analysis for potential wastewater aquifer recharge sites. Desalination 215(1–3):111–119
Khan FK (2010) Pakistan - Geography, Economy and People. Oxford University Press, New York
Krois J, Schulte A (2014) GIS-based multi-criteria evaluation to identify potential sites for soil and water conservation techniques in the Ronquillo watershed, northern Peru. Appl Geogr 51:131–142
Malczewski J (2004) GIS-based land-use suitability analysis: a critical overview. Progress in Planning 62(1):3–65
Malczewski J (2006) GIS based multicriteria decision analysis: a survey of the literature. International Journal of Geographical Information Science 20(7):703–726
Mishra AK, Deep S, Choudhary A (2015) Identification of suitable sites for organic farming using AHP & GIS. Egypt J Remote Sens Space Sci 18(2):181–193
Mbilinyi BP, Tumbo SD, Mahoo H, Mkiramwinyi FO (2007) GIS-based decision support system for identifying potential sites for rainwater harvesting. Physics and Chemistry of the Earth, Parts A/B/C 32(15–18):1074–1081
Pandey A, Chowdary VM, Mal BC, Dabral PP (2011) Remote sensing and GIS for identification of suitable sites for soil and water conservation structures. Land Degrad Dev 22(3):359–372
Pedrero F, Albuquerque A, do Monte HM, Cavaleiro V, Alarcón JJ (2011) Application of GIS-based multi-criteria analysis for site selection of aquifer recharge with reclaimed water. Resour Conserv Recycl 56(1):105–116
Patel DP, Srivastava PK, Gupta M, Nandhakumar N (2015) Decision support system integrated with geographic information system to target restoration actions in watersheds of arid environment: a case study of Hathmati watershed, Sabarkantha district, Gujarat. Journal of earth system science 124(1):71–86
Singh LK, Jha MK, Chowdary VM (2017) Multi-criteria analysis and GIS modeling for identifying prospective water harvesting and artificial recharge sites for sustainable water supply. J Clean Prod 142:1436–1456
Snyder RL, de Melo-Abreu JP (2005) Frost protection: fundamentals, practice and economics
Victor MW (2014) F56/74904/2014 (Doctoral dissertation, University of Nairobi)
Victor MW (2016) F56/74904/2014 (Doctoral dissertation, University of Nairobi)
Zolekar RB, Bhagat VS (2015) Multi-criteria land suitability analysis for agriculture in hilly zone: remote sensing and GIS approach. Comput Electron Agric 118:300–321
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Waleed, M., Ahmad, S.R., Javed, M.A. et al. Identification of irrigation potential areas, using multi-criteria analysis in Khyber District, Pakistan. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27, 39832–39840 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-08967-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-08967-y