Abstract
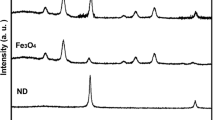
The modified Fe3O4 nanoparticles were used as a support for the immobilization of horseradish peroxidase (HRP). The immobilized enzyme (HRP@Fe3O4) was characterized by transmission electron microscopy (TEM), X-ray diffraction (XRD), Fourier-transform infrared spectrometer (FTIR), and vibration sample magnetometer (VSM). According to the results, the optimum concentration of glutaraldehyde (GA) and agitation time were 300 μL and 7 h. HRP was well loaded on the surface of the Fe3O4. There was no change in the crystal structure of HRP@Fe3O4 compared with Fe3O4. The removals of bisphenol A (BPA) and 17α-ethinylestradiol (EE2) using HRP@Fe3O4 had been investigated. The degradation efficiencies of BPA and EE2 catalyzed by HRP@Fe3O4 were higher than that of soluble HRP. In addition, HRP@Fe3O4 can be reused through magnetic separation. After the fifth repeated use, the removal efficiencies of BPA and EE2 were up to 56% and 48%, respectively. Batch studies of catalyzed oxidation and coagulation on the degradation of BPA and EE2 in the presence of humic acid (HA) were also investigated. The order of the removal efficiencies was HRP+PACl (polyaluminum chloride)+SDS (lauryl sodium sulfate)>HRP+PACl>HRP>HRP+PAM (Polyacrylamide)>HRP+PAM+SDS. The coagulation effect of HRP@Fe3O4 and PACl was better than that of HRP@Fe3O4 and PAM. The removals of BPA and EE2 were 90.3% and 64.5% by use HRP@Fe3O4 and PACl as coagulant, while the removals were 78.7% and 57.6% by use HRP@Fe3O4 and PAM as coagulant. SDS had a positive effect on PACl, while a negative effect on PAM. Moreover, the products generated by enzymatic oxidation reaction can be effectively removed after coagulation.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adeel M, Song XM, Wang YY, Francis D, Yang YS (2017) Environmental impact of estrogens on human, animal and plant life: a critical review. Environ Int 99:107–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2016.12.010
Ai J, Zhang W, Liao G, Xia H, Wang DS (2016) Immobilization of horseradish peroxidase enzymes on hydrous-titanium and application for phenol removal. RSC Adv 6:38117–38123. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6RA02397E
Alemzadeh I, Nejati S (2009) Phenols removal by immobilized horseradish peroxidase. J Hazard Mater 166:1082–1086. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.12.026
Alharbi OML, Basheer AA, Khattab RA, Ali I (2018) Health and environmental effects of persistent organic pollutants. J Mol Liq 263:442–453. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2018.05.029
Ali I, Alharbi OML, Alothman ZA, Alwarthan A (2018) Facile and eco-friendly synthesis of functionalized iron nanoparticles for cyanazine removal in water. Colloid Surface B 171:606–613. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2018.07.071
Ali I, Alothman ZA, Alwarthan A (2017) Supra molecular mechanism of the removal of 17-β-estradiol endocrine disturbing pollutant from water on functionalized iron nano particles. J Mol Liq 241:123–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2017.06.005
Al-Shaalan NH, Ali I, ZA ALO, Al-Wahaibi LH, Alabdulmonem H (2019) High performance removal and simulation studies of diuron pesticide in water on MWCNTs. J Mol Liq 289:111039. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2019.111039
Bai XL, Acharya K (2019) Removal of seven endocrine disrupting chemicals (EDCs) from municipal wastewater effluents by a freshwater green alga. Environ Pollut 247:534–540. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2019.01.075
Basheer AA (2017) Chemical chiral pollution: impact on the society and science and need of the regulations in the 21st century. Chirality 30:402–406. https://doi.org/10.1002/chir.22808
Basheer AA (2018) New generation nano-adsorbents for the removal of emerging contaminants in water. J Mol Liq 261:583–593. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2018.04.021
Bilal M, Iqbal HMN, Hu HB, Wang W, Zhang HX (2017) Development of horseradish peroxidase-based cross-linked enzyme aggregates and their environmental exploitation for bioremediation purposes. J Environ Manag 188:137–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2016.12.015
Boyd GR, Zhang SR, Grimm DA (2005) Naproxen removal from water by chlorination and biofilm processes. Water Res 39:668–676. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2004.11.013
Caliman FA, Gavrilescu M (2009) Pharmaceuticals, personal care products and endocrine disrupting agents in the environment-a review. Clean-Soil Air Water 37:277–303. https://doi.org/10.1002/clen.200900038
Chang Q, Jiang GD, Tang HQ, Li N, Huang J, Wu LY (2015) Enzymatic removal of chlorophenols using horseradish peroxidase immobilized on superparamagnetic Fe3O4/graphene oxide nanocomposite. Chinese J Catal 36:961–968. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1872-2067(15)60856-7
Chen J, LeBoeuf EJ, Dai S, Gu BH (2003) Fluorescence spectroscopic studies of natural organic matter fractions. Chemosphere 50:639–647. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0045-6535(02)00616-1
Cwiertny DM, Snyder SA, Schlenk D, Kolodziej EP (2014) Environmental designer drugs: when transformation may not eliminate risk. Environ Sci Technol 48:11737–11745. https://doi.org/10.1021/es503425w
Gao J, Gu H, Xu B (2009) Multifunctional magnetic nanoparticles: design, synthesis, and biomedical applications. Acc Chem Res 42:1097–1207. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-803581-8.10462-X
Grzybowski W, Szydlowski J (2014) The impact of chromophoric dissolved organic matter on the photo degradation of 17alpha-ethinylestradiol (EE2) in natural waters. Chemosphere 111:13–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2014.03.062
He J, Yang XF, Men B, Pu YB, Wang DS (2014) Heterogeneous Fenton oxidation of catechol and 4-chlorocatechol catalyzed by nano-Fe3O4: role of the interface. Chem Eng J 258:433–441. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2014.07.063
Jiang D, Chen WQ, Zeng Z, Tang L (2018) Dynamic stocks and flows analysis of bisphenol A (BPA) in China: 2000-2014. Environ Sci Technol 52:3706–3715. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.7b05709
Jiang W, Li WT, Xiao F, Wang DS, Wang ZC (2017) Influence of NOM and SS on the BPA removal via peroxidase catalyzed reactions: kinetics and pathways. Sep Purif Technol 173:244–249. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2016.09.029
Kümmerer K, Alexy R, Hüttig J, Scholl A (2004) Standardized tests fail to assess the effects of antibiotics on environmental bacteria. Water Res 38:2111–2116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2004.02.004
Li JL, Chen XY, Xu DF, Pan K (2019) Immobilization of horseradish peroxidase on electrospun magnetic nanofibers for phenol removal. Ecotox Environ Safe 179:716–721. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.12.043
Lin QC, Zi ZF, Zhang M (2013) Enhanced microwave absorption properties of carbonyl iron/ Fe3O4 composites synthesized by a simple hydrothermal method. J Alloy Compd 561:65–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2013.02.007
Liu Y, Jia S, Wu Q, Ran J, Zhang W, Wu S (2011) Studies of Fe3O4-chitosan nanoparticles prepared by co-precipitation under the magnetic field for lipase immobilization. Catal Commun 12:717–720. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catcom.2010.12.032
Liu ZZ, Wei H, Li AM, Yang H (2019) Enhanced coagulation of low-turbidity micro-polluted surface water: properties and optimization. J Environm Manage 233:739–747. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2018.08.101
Ma Y, Liu HH, Wu JX, Yuan L, Wang YQ, Du XD, Wang R, Marwa PW, Petlulu P, Chen XH, Zhang HZ (2019) The adverse health effects of bisphenol A and related toxicity mechanisms. Environ Res 176:108575. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2019.108575
Mohamed SA, Al-Harbi MH, Almulaiky YQ, Ibrahim IH, El-Shishtawy RM (2017) Immobilization of horseradish peroxidase on Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles. Electron J Biotechnol 27:84–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejbt.2017.03.010
Na SY, Lee YL (2017) Elimination of trace organic contaminants during enhanced wastewater treatment with horseradish peroxidase/hydrogen peroxide (HRP/H2O2) catalytic process. Catal Today 282:86–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cattod.2016.03.049
Qiu WH, Zhan HY, Hu JQ, Zhang T, Xu H, Wong MH, Bentuo Xu BT, Zheng CM (2019) The occurrence, potential toxicity, and toxicity mechanism of bisphenol S, a substitute of bisphenol A: a critical review of recent progress. Ecotox Environ Safe 17:192–202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv2019.01.114
Richter D, Massmann G, Dünnbier U (2008) Behaviour and biodegradation of sulfonamides (p-TSA, o-TSA, BSA) during drinking water treatment. Chemosphere 71:1574–1581. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2007.11.026
Schwertmann U, Cornell RM (2000) Iron oxides in the laboratory: preparation and characterization, Second edn. Wiley, New York
Sumpter JP, Johnson AC (2005) Lessons from endocrine disruption and their application to other issues concerning trace organics in the aquatic environment. Environ Sci Technol 39:4321–4332. https://doi.org/10.1021/es0523082
Tang QH, Haung J, Chang Q (2014a) Catalytic oxidation of phenolic wastewater by using horseradish peroxidase immobilized on graphene oxide/Fe3O4. J South-central Univ Nat (Nat Sci Edition) 33:19–22. https://doi.org/10.12130/znmdzk.20140105
Tang WW, Zeng GM, Gong JL, Liang J, Xu P, Zhang C, Huang BB (2014b) Impact of humic/fulvic acid on removal of heavy metals from aqueous solutions using nanomaterials affected by humic/fulvic acid: a review. Sci Total Environ 468-469:1014–1027. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.09.044
Tapia-Orozco N, Ibarra-Cabrera R, Tecante A, Gimeno M, Garcia-Arrazola R (2016) Removal strategies for endocrine disrupting chemicals using cellulose-based materials as adsorbents: a review. J Environ Chem Eng 4:3122–3142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2016.06.025
Valerio SG, Alves JS, Klein MP, Rodrigues RC, Hertz PF (2013) High operational stability of invertase from Saccharomyces cerevisiae immobilized on chitosan nanoparticles. Carbohydr Polym 92:462–468. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2012.09.001
Veitch NC, Smith AT (2006) Horseradish peroxidase. Adv Inorg Chem 51:107–162. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0898-8838(00)51002-2
Wang S (2016) Immobilization of horseradish peroxidase and its applications on the catalytic oxidation of wastewater containing phenol. Fuzhou University, Fuzhou
Wasak A, Drozd R, Jankowiak D, Rakoczy R (2019) The influence of rotating magnetic field on bio-catalytic dye degradation using the horseradish peroxidase. Biochem Eng J 147:81–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bej.2019.04.007
Wildhaber YS, Mestankova H, Schärer M, Schirmer K, Salhi E, vonGunten U (2015) Novel test procedure to evaluate the treatability of wastewater with ozone. Water Res 75:324–335. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2015.02.030
Wu YZ, Ma YJ, Xu GH, Wei FD, Ma YS, Song Q, Wang W, Tang T, Song YY, Shi ML, Xu XM, Hu Q (2017) Metal-organic framework coated Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles with peroxidase-like activity for colorimetric sensing of cholesterol. Sensors Actuat B-Chem 249:195–202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2017.03.145
Xie XQ, Luo P, Han J, Chen T, Wang Y, Cai YF, Liu Q (2019) Horseradish peroxidase immobilized on the magnetic composite microspheres for high catalytic ability and operational stability. Enzyme Microb Tech 122:26–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enzmictec.2018.12.007
Xu P, Zeng GM, Huang DL, Feng CL, Hu S, Zhao MH, Lai C, Wei Z, Huang C, Xie GX, Liu ZF (2012) Use of iron oxide nanomaterials in wastewater treatment: a review. Sci Total Environ 424:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2012.02.023
ZaharinAris A, Shamsuddin AS, Praveena SM (2014) Occurrence of 17α-ethynylestradiol (EE2) in the environment and effect on exposed biota: a review. Environ Int 69:104–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2014.04.011
Zhou FF, Luo JQ, Qi BK, Chen XR, Wan YH (2019) Horseradish peroxidase immobilized on multifunctional hybrid microspheres for aflatoxin B1 removal: will enzymatic reaction be enhanced by adsorption. Ind Eng Chem Res 58:11710–11719. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.iecr.9b02094
Zhu N (2015) Study of the magnetic functional materials in drug load application research and analysis. Shenyang ligong University, Shenyang
Funding
This research was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 51578529, 51338010, 21507149) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No. 2019MS033).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Tito Roberto Cadaval Jr
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 2407 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xiao, F., Xiao, P., Jiang, W. et al. Immobilization of horseradish peroxidase on Fe3O4 nanoparticles for enzymatic removal of endocrine disrupting chemicals. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27, 24357–24368 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-08824-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-08824-y