Abstract
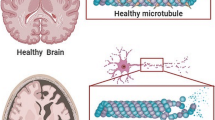
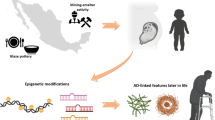
Neurodegenerative disorders are typically sporadic in nature in addition to usually influenced through an extensive range of environmental factors, lifestyle, and genetic elements. Latest observations have hypothesized that exposure of environmental factors may increase the prospective risk of Alzheimer’s diseases (AD). However, the role of environmental factors as a possible dangerous issue has extended importance concerned in AD pathology, although actual etiology of the disorder is still not yet clear. Thus, the aim of this review is to highlight the possible correlation between environmental factors and AD, based on the present literature view. Environmental risk factors might play an important role in decelerating or accelerating AD progression. Among well-known environmental risk factors, prolonged exposure to several heavy metals, for example, aluminum, arsenic, cadmium, lead, and mercury; particulate air, and some pesticides as well as metal-containing nanoparticles have been participated to cause AD. These heavy metals have the capacity to enhance amyloid β (Aβ) peptide along with tau phosphorylation, initiating amyloid/senile plaques, as well as neurofibrillary tangle formation; therefore, neuronal cell death has been observed. Furthermore, particulate air, pesticides, and heavy metal exposure have been recommended to lead AD susceptibility and phenotypic diversity though epigenetic mechanisms. Therefore, this review deliberates recent findings detailing the mechanisms for a better understanding the relationship between AD and environmental risk factors along with their mechanisms of action on the brain functions.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alam Q, Alam MZ, Mushtaq G, Damanhouri GA, Rasool M, Kamal MA, Haque A (2016) Inflammatory process in Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases: central role of cytokines. Curr Pharm Design 22:541–548
Alghamdi BSA (2018) Possible prophylactic anti-excitotoxic and anti-oxidant effects of virgin coconut oil on aluminium chloride-induced Alzheimer’s in rat models. J Integr Neurosci 17:593–607
An L, Liu SC, Yang Z, Zhang T (2012) Cognitive impairment in rats induced by nano-CuO and its possible mechanisms. Toxicol Lett 213:220–227
Andersen HR, Schmidt IM, Grandjean P, Jensen TK, Budtz-Jorgensen E, Kjaerstad MB, Baelum J, Nielsen JB, Skakkebaek NE, Main KM (2008) Impaired reproductive development in sons of women occupationally exposed to pesticides during pregnancy. Environ Health Perspect 116:566–572
Anstey KJ, Cherbuin N, Budge M, Young J (2011) Body mass index in midlife and late-life as a risk factor for dementia: a meta-analysis of prospective studies. Obes Rev 12:e426–e437
Anway MD, Cupp AS, Uzumcu M, Skinner MK (2005) Epigenetic transgenerational actions of endocrine disruptors and male fertility. Science 308:1466–1469
Baillon S, Gasper A, Wilson-Morkeh F, Pritchard M, Jesu A, Velayudhan L (2019) Prevalence and severity of neuropsychiatric symptoms in early- versus late-onset Alzheimer’s disease. Am J Alzheimers Dis Other Dement 34(7-8):433–438 1533317519841191
Bakulski KM, Rozek LS, Dolinoy DC, Paulson HL, Hu H (2012) Alzheimer's disease and environmental exposure to lead: the epidemiologic evidence and potential role of epigenetics. Curr Alzheimer Res 9:563–573
Bangen KJ, Nation DA, Delano-Wood L, Weissberger GH, Hansen LA, Galasko DR, Salmon DP, Bondi MW (2015) Aggregate effects of vascular risk factors on cerebrovascular changes in autopsy-confirmed Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement 11:394–403
Basha MR, Wei W, Bakheet SA, Benitez N, Siddiqi HK, Ge YW, Lahiri DK, Zawia NH (2005) The fetal basis of amyloidogenesis: exposure to lead and latent overexpression of amyloid precursor protein and beta-amyloid in the aging brain. J Neurosci 25:823–829
Behl M, Zhang Y, Shi Y, Cheng J, Du Y, Zheng W (2010) Lead-induced accumulation of beta-amyloid in the choroid plexus: role of low density lipoprotein receptor protein-1 and protein kinase C. Neurotoxicology 31:524–532
Bertram L (2009) Alzheimer's disease genetics current status and future perspectives. Int Rev Neurobiol 84:167–184
Bhat AH, Dar KB, Anees S, Zargar MA, Masood A, Sofi MA, Ganie SA (2015) Oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction and neurodegenerative diseases; a mechanistic insight. Biomed Pharmacother 74:101–110
Bhatt DP, Puig KL, Gorr MW, Wold LE, Combs CK (2015) A pilot study to assess effects of long-term inhalation of airborne particulate matter on early Alzheimer-like changes in the mouse brain. PLoS One 10:e0127102
Bian H, Bian W, Lin X, Ma Z, Chen W, Pu Y (2016) RNA interference silencing of glycogen synthase kinase 3beta inhibits tau phosphorylation in mice with Alzheimer disease. Neurochem Res 41:2470–2480
Bihaqi SW (2019) Early life exposure to lead (Pb) and changes in DNA methylation: relevance to Alzheimer's disease. Rev Environ Health 34:187–195
Bihaqi SW, Zawia NH (2012) Alzheimer’s disease biomarkers and epigenetic intermediates following exposure to Pb in vitro. Curr Alzheimer Res 9:555–562
Bihaqi SW, Zawia NH (2013) Enhanced taupathy and AD-like pathology in aged primate brains decades after infantile exposure to lead (Pb). Neurotoxicology 39:95–101
Bird A (2002) DNA methylation patterns and epigenetic memory. Genes Dev 16:6–21
Bjorklund G, Tinkov AA, Dadar M, Rahman MM, Chirumbolo S, Skalny AV, Skalnaya MG, Haley BE, Ajsuvakova OP, Aaseth J (2019) Insights into the potential role of mercury in Alzheimer’s disease. J Mol Neurosci 67:511–533
Block ML, Calderon-Garciduenas L (2009) Air pollution: mechanisms of neuroinflammation and CNS disease. Trends Neurosci 32:506–516
Boal HL, Christensen BK, Goodhew SC (2018) Social anxiety and attentional biases: A top-down contribution? Atten Percept Psychophysiol 80:42–53
Bu G (2009) Apolipoprotein E and its receptors in Alzheimer's disease: pathways, pathogenesis and therapy. Nat Rev Neurosci 10:333–344
Cacciottolo, M., Wang, X., Driscoll, I., Woodward, N., Saffari, A., Reyes, J., Serre, M.L., Vizuete, W., Sioutas, C., Morgan, T.E., et al. (2017). Particulate air pollutants, APOE alleles and their contributions to cognitive impairment in older women and to amyloidogenesis in experimental models, Transl Psychiat 7:e1022.
Calderon-Garciduenas L, Reed W, Maronpot RR, Henriquez-Roldan C, Delgado-Chavez R, Calderon-Garciduenas A, Dragustinovis I, Franco-Lira M, Aragon-Flores M, Solt AC et al (2004) Brain inflammation and Alzheimer’s-like pathology in individuals exposed to severe air pollution. Toxicol Pathol 32:650–658
Calvanese V, Lara E, Kahn A, Fraga MF (2009) The role of epigenetics in aging and age-related diseases. Ageing Res Rev 8:268–276
Castro-Chavira SA, Fernandez T, Nicolini H, Diaz-Cintra S, Prado-Alcala RA (2015) Genetic markers in biological fluids for aging-related major neurocognitive disorder. Curr Alzheimer Res 12:200–209
Champagne FA, Weaver IC, Diorio J, Dymov S, Szyf M, Meaney MJ (2006) Maternal care associated with methylation of the estrogen receptor-alpha1b promoter and estrogen receptor-alpha expression in the medial preoptic area of female offspring. Endocrinology 147:2909–2915
Chang JW, Pai MC, Chen HL, Guo HR, Su HJ, Lee CC (2008) Cognitive function and blood methylmercury in adults living near a deserted chloralkali factory. Environ Res 108:334–339
Chen JC, Schwartz J (2009) Neurobehavioral effects of ambient air pollution on cognitive performance in US adults. Neurotoxicology 30:231–239
Chen NN, Luo DJ, Yao XQ, Yu C, Wang Y, Wang Q, Wang JZ, Liu GP (2012) Pesticides induce spatial memory deficits with synaptic impairments and an imbalanced tau phosphorylation in rats. J Alzheimers Dis 30:585–594
Chin-Chan M, Navarro-Yepes J, Quintanilla-Vega B (2015) Environmental pollutants as risk factors for neurodegenerative disorders: Alzheimer and Parkinson diseases. Front Cell Neurosci 9:124
Cinzia N, Manuel C, Donatella F, Rosita G, Antonio DS, Cerasa LS, Isabel S, Valentina D, Roberto C (2013) Effects of early life permethrin exposure on spatial working memory and on monoamine levels in different brain areas of pre-senescent rats. Toxicology 303:162–168
Coimbra JRM, Marques DFF, Baptista SJ, Pereira CMF, Moreira PI, Dinis TCP, Santos AE, Salvador JAR (2018) Highlights in BACE1 inhibitors for Alzheimer’s disease treatment. Front Chem 6:178
Colomina MT, Peris-Sampedro F (2017) Aluminum and Alzheimer's disease. Adv Neurobiol 18:183–197
Corder EH, Saunders AM, Strittmatter WJ, Schmechel DE, Gaskell PC, Small GW, Roses AD, Haines JL, Pericak-Vance MA (1993) Gene dose of apolipoprotein E type 4 allele and the risk of Alzheimer’s disease in late onset families. Science 261:921–923
Coupland KG, Kim WS, Halliday GM, Hallupp M, Dobson-Stone C, Kwok JB (2016) Role of the long non-coding RNA MAPT-AS1 in regulation of microtubule associated protein tau (MAPT) expression in Parkinson’s disease. PLoS One 11:e0157924
Cropley JE, Suter CM, Beckman KB, Martin DI (2006) Germ-line epigenetic modification of the murine A vy allele by nutritional supplementation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103:17308–17312
Dai MH, Zheng H, Zeng LD, Zhang Y (2018) The genes associated with early-onset Alzheimer’s disease. Oncotarget 9:15132–15143
Dansokho C, Heneka MT (2018) Neuroinflammatory responses in Alzheimer’s disease. J Neural Transm (Vienna) 125:771–779
Denis PA (2013) Alzheimer’s disease: a gas model. The NADPH oxidase-nitric oxide system as an antibubble biomachinery. Med Hypotheses 81:976–987
Dolinoy DC, Huang D, Jirtle RL (2007) Maternal nutrient supplementation counteracts bisphenol A-induced DNA hypomethylation in early development. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104:13056–13061
Dorsey CD, Lee BK, Bolla KI, Weaver VM, Lee SS, Lee GS, Todd AC, Shi WP, Schwartz BS (2006) Comparison of patella lead with blood lead and tibia lead and their associations with neurobehavioral test scores. J Occup Environ Med 48:489–496
Durga M, Devasena T, Rajasekar A (2015) Determination of LC50 and sub-chronic neurotoxicity of diesel exhaust nanoparticles. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 40:615–625
Dzamba D, Harantova L, Butenko O, Anderova M (2016) Glial cells - the key elements of Alzheimer’s disease. Curr Alzheimer Res 13:894–911
Faulk C, Dolinoy DC (2011) Timing is everything. The when and how of environmentally induced changes in the epigenome of animals. Epigenetics-Us 6:791–797
Feng Y, Wang X (2012) Antioxidant therapies for Alzheimer’s disease. Oxidative Med Cell Longev 2012:472932
Ferrari C, Nacmias B, Bagnoli S, Piaceri I, Lombardi G, Pradella S, Tedde A, Sorbi S (2014) Imaging and cognitive reserve studies predict dementia in presymptomatic Alzheimer’s disease subjects. Neurodegener Dis 13:157–159
Fratiglioni L, Wang HX (2007) Brain reserve hypothesis in dementia. J Alzheimers Dis 12:11–22
Fratiglioni L, Paillard-Borg S, Winblad B (2004) An active and socially integrated lifestyle in late life might protect against dementia. Lancet Neurol 3:343–353
Fujimura M, Usuki F, Sawada M, Takashima A (2009) Methylmercury induces neuropathological changes with tau hyperphosphorylation mainly through the activation of the c-Jun-N-terminal kinase pathway in the cerebral cortex, but not in the hippocampus of the mouse brain. Neurotoxicology 30:1000–1007
Gomez-Gomez ME, Zapico SC (2019) Frailty, cognitive decline, Neurodegenerative Diseases and Nutrition Interventions. Int J Mol Sci 20:E2842
Gong G, O'Bryant SE (2010) The arsenic exposure hypothesis for Alzheimer disease. Alzheimer Dis Assoc Disord 24:311–316
Gu H, Wei X, Monnot AD, Fontanilla CV, Behl M, Farlow MR, Zheng W, Du Y (2011) Lead exposure increases levels of beta-amyloid in the brain and CSF and inhibits LRP1 expression in APP transgenic mice. Neurosci Lett 490:16–20
Guerrero-Bosagna CM, Sabat P, Valdovinos FS, Valladares LE, Clark SJ (2008) Epigenetic and phenotypic changes result from a continuous pre and post natal dietary exposure to phytoestrogens in an experimental population of mice. BMC Physiol 8:17
Heijmans BT, Tobi EW, Stein AD, Putter H, Blauw GJ, Susser ES, Slagboom PE, Lumey LH (2008) Persistent epigenetic differences associated with prenatal exposure to famine in humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105:17046–17049
Heppner FL, Ransohoff RM, Becher B (2015) Immune attack: the role of inflammation in Alzheimer disease. Nat Rev Neurosci 16:358–372
Holliday R (2006) Epigenetics A historical overview. Epigenetics-Us 1:76–80
Hu K, Li Y, Yu H, Hu Y (2019) CTBP1 confers protection for hippocampal and cortical neurons in rat models of Alzheimer’s disease. Neuroimmunomodulation 26(3):139–152 1–14
Huang CL, Hsiao IL, Lin HC, Wang CF, Huang YJ, Chuang CY (2015) Silver nanoparticles affect on gene expression of inflammatory and neurodegenerative responses in mouse brain neural cells. Environ Res 136:253–263
Huang D, Yu M, Yang S, Lou D, Zhou W, Zheng L, Wang Z, Cai F, Zhou W, Li T et al (2018) Ethanol alters APP processing and aggravates Alzheimer-associated phenotypes. Mol Neurobiol 55:5006–5018
Huat TJ, Camats-Perna J, Newcombe EA, Valmas N, Kitazawa M, Medeiros R (2019) Metal toxicity links to Alzheimer’s disease and neuroinflammation. J Mol Biol 431:1843–1868
Huber CM, Yee C, May T, Dhanala A, Mitchell CS (2018) Cognitive decline in preclinical Alzheimer’s disease: amyloid-beta versus tauopathy. J Alzheimers Disease 61:265–281
Ito S, Kuraoka I (2015) Epigenetic modifications in DNA could mimic oxidative DNA damage: a double-edged sword. DNA Repair 32:52–57
Jalilian H, Teshnizi SH, Roosli M, Neghab M (2018) Occupational exposure to extremely low frequency magnetic fields and risk of Alzheimer disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurotoxicology 69:242–252
Jiang LF, Yao TM, Zhu ZL, Wang C, Ji LN (2007) Impacts of Cd (II) on the conformation and self-aggregation of Alzheimer’s tau fragment corresponding to the third repeat of microtubule-binding domain. Bba-Proteins Proteom 1774:1414–1421
Johansson C, Castoldi AF, Onishchenko N, Manzo L, Vahter M, Ceccatelli S (2007) Neurobehavioural and molecular changes induced by methylmercury exposure during development. Neurotox Res 11:241–260
Jouanne M, Rault S, Voisin-Chiret AS (2017) Tau protein aggregation in Alzheimer’s disease: an attractive target for the development of novel therapeutic agents. Eur J Med Chem 139:153–167
Karri V, Schuhmacher M, Kumar V (2016) Heavy metals (Pb, Cd, As and MeHg) as risk factors for cognitive dysfunction: a general review of metal mixture mechanism in brain. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 48:203–213
Kilian J, Kitazawa M (2018) The emerging risk of exposure to air pollution on cognitive decline and Alzheimer’s disease - evidence from epidemiological and animal studies. Biom J 41:141–162
Kim DK, Park JD, Choi BS (2014) Mercury-induced amyloid-beta (Abeta) accumulation in the brain is mediated by disruption of Abeta transport. J Toxicol Sci 39:625–635
Kleinman MT, Araujo JA, Nel A, Sioutas C, Campbell A, Cong PQ, Lia H, Bondy SC (2008) Inhaled ultrafine particulate matter affects CNS inflammatory processes and may act via MAP kinase signaling pathways. Toxicol Lett 178:127–130
Larsson SC, Orsini N (2018) Coffee consumption and risk of dementia and Alzheimer’s disease: a dose-response meta-analysis of prospective studies. Nutrients 10:E1501
Li N, Sioutas C, Cho A, Schmitz D, Misra C, Sempf J, Wang MY, Oberley T, Froines J, Nel A (2003) Ultrafine particulate pollutants induce oxidative stress and mitochondrial damage. Environ Health Perspect 111:455–460
Li N, Yu ZL, Wang L, Zheng YT, Jia JX, Wang Q, Zhu MJ, Liu XH, Xia X, Li WJ (2010) Increased tau phosphorylation and beta amyloid in the hippocampus of mouse pups by early life Lead exposure. Acta Biol Hung 61:123–134
Li J, Wang YJ, Zhang M, Xu ZQ, Gao CY, Fang CQ, Yan JC, Zhou HD, Chongqing Ageing Study, G (2011) Vascular risk factors promote conversion from mild cognitive impairment to Alzheimer disease. Neurology 76:1485–1491
Li FJ, Shen L, Ji HF (2012a) Dietary intakes of vitamin E, vitamin C, and beta-carotene and risk of Alzheimer’s disease: a meta-analysis. J Alzheimers Dis 31:253–258
Li X, Lv Y, Yu S, Zhao H, Yao L (2012b) The effect of cadmium on Abeta levels in APP/PS1 transgenic mice. Exp Ther Med 4:125–130
Li G, Kim C, Kim J, Yoon H, Zhou H, Kim J (2015) Common pesticide, dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane (DDT), increases amyloid-beta levels by impairing the function of ABCA1 and IDE: implication for Alzheimer’s disease. J Alzheimers Dis 46:109–122
Li K, Cheng X, Jiang J, Wang J, Xie J, Hu X, Huang Y, Song L, Liu M, Cai L, Chen L, Zhao S (2017) The toxic influence of paraquat on hippocampal neurogenesis in adult mice. Food Chem Toxicol 106:356–366
Liang RF (2018) Cross talk between aluminum and genetic susceptibility and epigenetic modification in Alzheimer’s disease. Adv Exp Med Biol 1091:173–191
Lindsay J, Laurin D, Verreault R, Hebert R, Helliwell B, Hill GB, McDowell I (2002) Risk factors for Alzheimer’s disease: a prospective analysis from the Canadian Study of Health and Aging. Am J Epidemiol 156:445–453
Liu PD, Huang ZH, Gu N (2013) Exposure to silver nanoparticles does not affect cognitive outcome or hippocampal neurogenesis in adult mice. Ecotox Environ Safe 87:124–130
Lobo V, Patil A, Phatak A, Chandra N (2010) Free radicals, antioxidants and functional foods: impact on human health. Pharmacogn Rev 4:118–126
Luo Y, Niu F, Sun Z, Cao W, Zhang X, Guan D, Lv Z, Zhang B, Xu Y (2009) Altered expression of Abeta metabolism-associated molecules from D-galactose/AlCl(3) induced mouse brain. Mech Ageing Dev 130:248–252
Marques SCF, Oliveira CR, Pereira CMF, Outeiro TF (2011) Epigenetics in neurodegeneration: a new layer of complexity. Prog Neuro-Psychoph 35:348–355
Martinez L, Jimenez V, Garcia-Sepulveda C, Ceballos F, Delgado JM, Nino-Moreno P, Doniz L, Saavedra-Alanis V, Castillo CG, Santoyo ME et al (2011) Impact of early developmental arsenic exposure on promotor CpG-island methylation of genes involved in neuronal plasticity. Neurochem Int 58:574–581
Masoud AM, Bihaqi SW, Machan JT, Zawia NH, Renehan WE (2016) Early-life exposure to lead (Pb) alters the expression of microRNA that target proteins associated with Alzheimer’s disease. Journal of Alzheimers Disease 51:1257–1264
Mawuenyega KG, Sigurdson W, Ovod V, Munsell L, Kasten T, Morris JC, Yarasheski KE, Bateman RJ (2010) Decreased clearance of CNS beta-amyloid in Alzheimer's disease. Science 330:1774
Mendez MF (2017) Early-onset Alzheimer disease. Neurol Clin 35:263–281
Mezzaroba L, Alfieri DF, Colado Simao AN, Vissoci Reiche EM (2019) The role of zinc, copper, manganese and iron in neurodegenerative diseases. Neurotoxicology 74:230–241
Miguel-Alvarez M, Santos-Lozano A, Sanchis-Gomar F, Fiuza-Luces C, Pareja-Galeano H, Garatachea N, Lucia A (2015) Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs as a treatment for Alzheimer’s disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis of treatment effect. Drugs Aging 32:139–147
Monnet-Tschudi F, Zurich MG, Boschat C, Corbaz A, Honegger P (2006) Involvement of environmental mercury and lead in the etiology of neurodegenerative diseases. Rev Environ Health 21:105–117
Mourao RJ, Mansur G, Malloy-Diniz LF, Castro Costa E, Diniz BS (2016) Depressive symptoms increase the risk of progression to dementia in subjects with mild cognitive impairment: systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry 31:905–911
Murugadoss S, Lison D, Godderis L, Van den Brule S, Mast J, Brassinne F, Sebaihi N, Hoet PH (2017) Toxicology of silica nanoparticles: an update. Arch Toxicol 91:2967–3010
Mushtaq G, Khan JA, Joseph E, Kamal MA (2015) Nanoparticles, neurotoxicity and neurodegenerative diseases. Curr Drug Metab 16:676–684
Novikova SI, He F, Bai J, Cutrufello NJ, Lidow MS, Undieh AS (2008) Maternal cocaine administration in mice alters DNA methylation and gene expression in hippocampal neurons of neonatal and prepubertal offspring. PLoS One 3:e1919
Oberlander TF, Weinberg J, Papsdorf M, Grunau R, Misri S, Devlin AM (2008) Prenatal exposure to maternal depression, neonatal methylation of human glucocorticoid receptor gene (NR3C1) and infant cortisol stress responses. Epigenetics-Us 3:97–106
Okuda M, Hijikuro I, Fujita Y, Wu X, Nakayama S, Sakata Y, Noguchi Y, Ogo M, Akasofu S, Ito Y et al (2015) PE859, a novel tau aggregation inhibitor, reduces aggregated tau and prevents onset and progression of neural dysfunction in vivo. PLoS One 10:e0117511
Olivieri G, Brack C, Muller-Spahn F, Stahelin HB, Herrmann M, Renard P, Brockhaus M, Hock C (2000) Mercury induces cell cytotoxicity and oxidative stress and increases beta-amyloid secretion and tau phosphorylation in SHSY5Y neuroblastoma cells. J Neurochem 74:231–236
Park HS, Park SS, Kim CJ, Shin MS, Kim TW (2019) Exercise alleviates cognitive functions by enhancing hippocampal insulin signaling and neuroplasticity in high-fat diet-induced obesity. Nutrients 11:E1603
Perera F, Tang WY, Herbstman J, Tang D, Levin L, Miller R, Ho SM (2009) Relation of DNA methylation of 5'-CpG island of ACSL3 to transplacental exposure to airborne polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and childhood asthma. PLoS One 4:e4488
Peris-Sampedro F, Salazar JG, Cabre M, Reverte I, Domingo JL, Sanchez-Santed F, Colomina MT (2014) Impaired retention in AbetaPP Swedish mice six months after oral exposure to chlorpyrifos. Food Chem Toxicol 72:289–294
Piaceri I, Nacmias B, Sorbi S (2013) Genetics of familial and sporadic Alzheimer's disease. Front Biosci (Elite Ed) 5:167–177
Plassman BL, Havlik RJ, Steffens DC, Helms MJ, Newman TN, Drosdick D, Phillips C, Gau BA, Welsh-Bohmer KA, Burke JR, Guralnik JM, Breitner JC (2000) Documented head injury in early adulthood and risk of Alzheimer's disease and other dementias. Neurology 55:1158–1166
Poirier LA, Vlasova TI (2002) The prospective role of abnormal methyl metabolism in cadmium toxicity. Environ Health Perspect 110:793–795
Pratico D, Uryu K, Sung S, Tang S, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VMY (2002) Aluminum modulates brain amyloidosis through oxidative stress in APP transgenic mice. FASEB J 16:1138
Qi S, Feng Z, Li Q, Qi Z, Zhang Y (2018) Inhibition of ROS-mediated activation Src-MAPK/AKT signaling by orientin alleviates H2O2-induced apoptosis in PC12 cells. Drug Des Devel Ther 12:3973–3984
Rahman MA, Rhim H (2017) Therapeutic implication of autophagy in neurodegenerative diseases. BMB Rep 50:345–354
Ramos-Chavez LA, Rendon-Lopez CR, Zepeda A, Silva-Adaya D, Del Razo LM, Gonsebatt ME (2015) Neurological effects of inorganic arsenic exposure: altered cysteine/glutamate transport, NMDA expression and spatial memory impairment. Front Cell Neurosci 9:21
Reuben A (2018) Childhood lead exposure and adult neurodegenerative disease. J Alzheimers Dis 64:17–42
Richardson JR, Roy A, Shalat SL, von Stein RT, Hossain MM, Buckley B, Gearing M, Levey AI, German DC (2014) Elevated serum pesticide levels and risk for Alzheimer disease. Jama Neurology 71:284–290
Rusanen M, Kivipelto M, Quesenberry CP Jr, Zhou J, Whitmer RA (2011) Heavy smoking in midlife and long-term risk of Alzheimer disease and vascular dementia. Arch Intern Med 171:333–339
Sadakierska-Chudy A, Filip M (2015) A comprehensive view of the epigenetic landscape. Part II: histone post-translational modification, nucleosome level, and chromatin regulation by ncRNAs. Neurotox Res 27:172–197
Sakamoto T, Saito H, Ishii K, Takahashi H, Tanabe S, Ogasawara Y (2006) Aluminum inhibits proteolytic degradation of amyloid beta peptide by cathepsin D: A potential link between aluminum accumulation and neuritic plaque deposition. FEBS Lett 580:6543–6549
Salazar JG, Ribes D, Cabre M, Domingo JL, Sanchez-Santed F, Colomina MT (2011) Amyloid beta peptide levels increase in brain of AbetaPP Swedish mice after exposure to chlorpyrifos. Curr Alzheimer Res 8:732–740
Sananbenesi F, Fischer A (2009) The epigenetic bottleneck of neurodegenerative and psychiatric diseases. Biol Chem 390:1145–1153
Savva GM, Stephan BC, Alzheimer's Society Vascular Dementia Systematic Review, G (2010) Epidemiological studies of the effect of stroke on incident dementia: a systematic review. Stroke 41:e41–e46
Schlosser Covell GE, Hoffman-Snyder CR, Wellik KE, Woodruff BK, Geda YE, Caselli RJ, Demaerschalk BM, Wingerchuk DM (2015) Physical activity level and future risk of mild cognitive impairment or dementia: a critically appraised topic. Neurologist 19:89–91
Sharma HS, Sharma A (2012) Neurotoxicity of engineered nanoparticles from metals. Cns Neurol Disord-Dr 11:65–80
Sharma HS, Ali SF, Hussain SM, Schlager JJ, Sharma A (2009) Influence of engineered nanoparticles from metals on the blood-brain barrier permeability, cerebral blood flow, brain edema and neurotoxicity An Experimental Study in the Rat and Mice Using Biochemical and Morphological Approaches. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 9:5055–5072
Sharp SI, Aarsland D, Day S, Sonnesyn H, Ballard C, Alzheimer's Society Vascular Dementia Systematic Review Group, B (2011) Hypertension is a potential risk factor for vascular dementia: systematic review. Int J Geriatr Psychopharmacol 26:661–669
Shin RW, Kruck TP, Murayama H, Kitamoto T (2003) A novel trivalent cation chelator Feralex dissociates binding of aluminum and iron associated with hyperphosphorylated tau of Alzheimer’s disease. Brain Res 961:139–146
Singh KP, DuMond JW Jr (2007) Genetic and epigenetic changes induced by chronic low dose exposure to arsenic of mouse testicular Leydig cells. Int J Oncol 30:253–260
Smith MA, Harris PLR, Sayre LM, Perry G (1997) Iron accumulation in Alzheimer disease is a source of redox-generated free radicals. P Natl Acad Sci USA 94:9866–9868
Son SM, Kang S, Choi H, Mook-Jung I (2015) Statins induce insulin-degrading enzyme secretion from astrocytes via an autophagy-based unconventional secretory pathway. Mol Neurodegener 10:56
Song JW, Choi BS (2013) Mercury induced the accumulation of amyloid beta (Abeta) in PC12 cells: the role of production and degradation of Abeta. Toxicol Res 29:235–240
Sorgdrager FJH, Vermeiren Y, Van Faassen HJR, Van Der Ley CP, Nollen EAA, Kema IP, De Deyn PP (2019) Age- and disease-specific changes of the kynurenine pathway in Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurochem 151(5):656–668
Souza AD, Couto-Lima CA, Catalao CHR, Santos NN, dos Santos JF, da Rocha MJA, Alberici LC (2019) Neuroprotective action of eicosapentaenoic (EPA) and docosahexaenoic (DHA) acids on Paraquat intoxication in Drosophila melanogaster. Neurotoxicology 70:154–160
Suelves M, Carrio E, Nunez-Alvarez Y, Peinado MA (2016) DNA methylation dynamics in cellular commitment and differentiation. Brief Funct Genomics 15:443–453
Takahashi RH, Nagao T, Gouras GK (2017) Plaque formation and the intraneuronal accumulation of beta-amyloid in Alzheimer’s disease. Pathol Int 67:185–193
Tyler CR, Allan AM (2014) The effects of arsenic exposure on neurological and cognitive dysfunction in human and rodent studies: a review. Curr Environ Health Rep 1:132–147
Uddin MS, Stachowiak A, Al Mamun A, Tzvetkov NT, Takeda S, Atanasov AG, Bergantin LB, Abdel-Daim MM, Stankiewicz AM (2018) Autophagy and Alzheimer’s disease: from molecular mechanisms to therapeutic implications. Front Aging Neurosci 10:4
Uddin MS, Mamun AA, Labu ZK, Hidalgo-Lanussa O, Barreto GE, Ashraf GM (2019) Autophagic dysfunction in Alzheimer’s disease: cellular and molecular mechanistic approaches to halt Alzheimer’s pathogenesis. J Cell Physiol 234:8094–8112
Urdinguio RG, Sanchez-Mut JV, Esteller M (2009) Epigenetic mechanisms in neurological diseases: genes, syndromes, and therapies. Lancet Neurol 8:1056–1072
Vahidnia A, Romijn F, van der Voet GB, de Wolff FA (2008) Arsenic-induced neurotoxicity in relation to toxicokinetics: effects on sciatic nerve proteins. Chem Biol Interact 176:188–195
Ventriglia M, Brewer GJ, Simonelli I, Mariani S, Siotto M, Bucossi S, Squitti R (2015) Zinc in Alzheimer’s disease: A meta-analysis of serum, plasma, and cerebrospinal fluid studies. J Alzheimers Dis 46:75–87
Verreault R, Laurin D, Lindsay J, De Serres G (2001) Past exposure to vaccines and subsequent risk of Alzheimer’s disease. CMAJ 165:1495–1498
Vickers MH (2014) Early life nutrition, epigenetics and programming of later life disease. Nutrients 6:2165–2178
Walton JR, Wang MX (2009) APP expression, distribution and accumulation are altered by aluminum in a rodent model for Alzheimer’s disease. J Inorg Biochem 103:1548–1554
Wang WY, Tan MS, Yu JT, Tan L (2015) Role of pro-inflammatory cytokines released from microglia in Alzheimer’s disease. Ann Transl Med 3:136
Weaver CM, Teegarden D, Welch A, Hwalla N, Lelievre S (2014) International breast Cancer and nutrition: A model for research, training and policy in diet, epigenetics, and chronic disease prevention. Adv Nutr 5:566–567
Wichmann MA, Cruickshanks KJ, Carlsson CM, Chappell R, Fischer ME, Klein BEK, Klein R, Schubert CR (2016) NSAID use and incident cognitive impairment in a population-based cohort. Alzheimer Dis Assoc Disord 30:105–112
Wills J, Credle J, Oaks AW, Duka V, Lee JH, Jones J, Sidhu A (2012) Paraquat, but not Maneb, induces synucleinopathy and tauopathy in striata of mice through inhibition of proteasomal and autophagic pathways. PLoS One 7:e30745
Wingo TS, Cutler DJ, Wingo AP, Le NA, Rabinovici GD, Miller BL, Lah JJ, Levey AI (2019) Association of early-onset Alzheimer disease with elevated low-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels and rare genetic coding variants of APOB. JAMA Neurol 76:809–817
Wirths O, Multhaup G, Czech C, Blanchard V, Moussaoui S, Tremp G, Pradier L, Beyreuther K, Bayer TA (2001) Intraneuronal Abeta accumulation precedes plaque formation in beta-amyloid precursor protein and presenilin-1 double-transgenic mice. Neurosci Lett 306:116–120
Wong P, Appadurai K, Kanagarajah S (2016) Alcohol and the risk of behavioural and psychological symptoms of dementia in men and women. Australas J Ageing 35:29–29
Wu J, Basha MR, Brock B, Cox DP, Cardozo-Pelaez F, McPherson CA, Harry J, Rice DC, Maloney B, Chen D et al (2008) Alzheimer’s disease (AD)-like pathology in aged monkeys after infantile exposure to environmental metal lead (Pb): evidence for a developmental origin and environmental link for AD. J Neurosci 28:3–9
Xu W, Wang HF, Wan Y, Tan CC, Li JQ, Tan L, Yu JT (2017) Alcohol consumption and dementia risk: a dose-response meta-analysis of prospective studies. Eur J Epidemiol 32:31–42
Xu L, Zhang WC, Liu XC, Zhang CL, Wang P, Zhao XL (2018) Circulatory levels of toxic metals (aluminum, cadmium, mercury, lead) in patients with Alzheimer’s disease: A quantitative meta-analysis and systematic review. Journal of Alzheimers Disease 62:361–372
Yamamoto H, Saitoh Y, Yasugawa S, Miyamoto E (1990) Dephosphorylation of tau-factor by protein phosphatase-2a in synaptosomal cytosol fractions, and inhibition by aluminum. J Neurochem 55:683–690
Yan D, Zhang Y, Liu L, Yan H (2016) Pesticide exposure and risk of Alzheimer’s disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci Rep 6:32222
Yang DJ, Shi SO, Zheng LF, Yao TM, Ji LN (2010) Mercury (II) promotes the in vitro aggregation of tau fragment corresponding to the second repeat of microtubule-binding domain: coordination and conformational transition. Biopolymers 93:1100–1107
Yang XF, He CE, Li J, Chen HB, Ma Q, Sui XJ, Tian SL, Ying M, Zhang Q, Luo YG et al (2014) Uptake of silica nanoparticles: neurotoxicity and Alzheimer-like pathology in human SK-N-SH and mouse neuro2a neuroblastoma cells. Toxicol Lett 229:240–249
Yang MH, Chen SC, Lin YF, Lee YC, Huang MY, Chen KC, Wu HY, Lin PC, Gozes I, Tyan YC (2019) Reduction of aluminum ion neurotoxicity through a small peptide application - NAP treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. J Food Drug Anal 27:551–564
Yao D, Jing T, Niu L, Huang XX, Wang Y, Deng XQ, Wang MG (2018) Amyloidogenesis induced by diet cholesterol and copper in a model mouse for Alzheimer's disease and protection effects of zinc and fluvastatin. Brain Res Bull 143:1–8
Yaoi T, Itoh K, Nakamura K, Ogi H, Fujiwara Y, Fushiki S (2008) Genome-wide analysis of epigenomic alterations in fetal mouse forebrain after exposure to low doses of bisphenol A. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 376:563–567
Zarazua S, Burger S, Delgado JM, Jimenez-Capdeville ME, Schliebs R (2011) Arsenic affects expression and processing of amyloid precursor protein (APP) in primary neuronal cells overexpressing the Swedish mutation of human APP. Int J Dev Neurosci 29:389–396
Zawia NH, Lahiri DK, Cardozo-Pelaez F (2009) Epigenetics, oxidative stress, and Alzheimer disease. Free Radical Bio Med 46:1241–1249
Ze YG, Hu RP, Wang XC, Sang XZ, Ze X, Li B, Su JJ, Wang Y, Guan N, Zhao XY et al (2014) Neurotoxicity and gene-expressed profile in brain-injured mice caused by exposure to titanium dioxide nanoparticles. J Biomed Mater Res A 102:470–478
Zenaro E, Piacentino G, Constantin G (2017) The blood-brain barrier in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Dis 107:41–56
Zhang QL (2018) Aluminum-induced neural cell death. Adv Exp Med Biol 1091:129–160
Zhang QL, Niu Q, Niu PY, Shi YT, Liu CY, Di Gioacchino M, Zhang L, Zhang C, Braga M (2010) Bax gene silencing: A potential intervention in aluminum-induced neural cell death. J Biol Reg Homeos Agents 24:7–17
Zhang ZY, Miah M, Culbreth M, Aschner M (2016) Autophagy in neurodegenerative diseases and metal neurotoxicity. Neurochem Res 41:409–422
Zong L, Xing J, Liu S, Liu Z, Song F (2018) Cell metabolomics reveals the neurotoxicity mechanism of cadmium in PC12 cells. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 147:26–33
Funding
This work was supported by the Korea Research Fellowship (KRF) Program (2016H1D3A1908615, 2017H1D3A1A02013844, 2015H1D3A1062189) through the National Research Foundation of Korea and the NRF Research Program (2016M3C7A1913845) funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT, Republic of Korea.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
This collaboration work was carried out among all the authors. MAR designed outlines and wrote the draft of the manuscript. MSR prepared the figures of the manuscript. MJU and ANMMR wrote some part of the manuscript. MGP reviewed the manuscript. HR proposed original idea and reviewed the scientific contents of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final submitted version of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rahman, M.A., Rahman, M.S., Uddin, M.J. et al. Emerging risk of environmental factors: insight mechanisms of Alzheimer’s diseases. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27, 44659–44672 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-08243-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-08243-z