Abstract
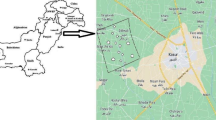
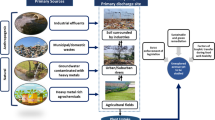
Accretion of heavy metals in forage is a potential risk to grazing animals due to their uptake by plants and its entrance into the food chain. This study aimed to examine the Mn and Cd concentration from different samples. Sampling was done twice after the interval of 6 months during 2018; five different sites from Chakwal (Pidh, Tobar, Ratoccha, Kalar Kahar Road, Choa Saiden Shah and Chakwal Road, Choa Saiden Shah) were selected. Thirty samples of soil, forage (Acacia nilotica, Ziziphus nummularia, and Acacia modesta), and blood were collected. Forage and soil samples were dried, ground very fine, digested by wet digestion method, and analyzed by atomic absorption spectrophotometer. Samples collected from site I and site II had a very high concentration of heavy metals because these sites were very close to the coal mines and receive higher contamination. Manganese concentration in the soil fluctuated from 5.46 to 1.20, in the forage 6.84 to 1.00, and in the blood 5.21 to 1.03 mg/l, and cadmium concentration in the soil fluctuate from 1.85 to 0.03, in the forage 0.57 to 0.16, and in the blood 1.67 to 0.25 mg/l. Manganese concentration was higher as compared to the Cd. Higher concentration of Mn shows that this metal is due to human activities. Pollution load index value of Cd was higher than 1 in some samples, and the value fluctuates from 0.01 to 1.24 mg/kg. The values of a bioconcentration factor for Mn were greater than 1. Daily intake of metal value fluctuates from 0.01 to 1.03 mg/kg. Health risk index value ranges from 0.03 to 1.09 mg/kg. Health risk index of metals showed the risk which is due to the intake of contaminated fodder. From the soil, the metals can enter forage and bioaccumulate in the food chain. The health risk index was highest for Cd. The result obtained from the present research work indicated that there is a biomagnification of both metals in the food chain due to mining activities.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad K, Ashfaq A, Khan ZI, Bashir H, Sohail M, Mehmood N, Dogan Y (2018b) Metal accumulation in Raphanus sativus and Brassica rapa: an assessment of potential health risk for inhabitants in Punjab, Pakistan. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25(8):16676–16685
Ahmad K, Nawaz K, Khan ZI, Nadeem M, Wajid K, Ashfaq A et al (2018a) Effect of diverse regimes of irrigation on metals accumulation in wheat crop: an assessment - dire need of the day. Fresenius Environ Bull 27(2):846–855
Ahmad K, Wajid K, Khan ZI, Ugulu I, Memoona H, Sana M, Nawaz K, Malik IS, Bashir H, Sher M (2019) Evaluation of potential toxic metals accumulation in wheat irrigated with wastewater. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 102(6):822–828
Arora M, Kiran B, Rani S, Rani A, Kaur B, Mittal N (2008) Heavy metal accumulation in vegetables irrigated with water from different sources. Food Chem 111(4):811–815
Baslar S, Kula I, Dogan Y, Yildiz D, Ay G (2009) A study of trace element contents in plants growing at Honaz Dagi-Denizli, Turkey. Ekoloji 18(72):1–7
Campbell CD, Planks CO (1992) An assessment of the hazards of lead in food. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol 16:26
Cui YJ, Zhu YG, Zhai RH, Chen DY, Huang YZ, Qui Y, Liang JZ (2004) Transfer of metals from near a smelter in Nanning, China. Environ Int 30:785–791
Deribachew B, Made M, Nigussie-D AM, Taddesse (2015) Selected heavy metals in some vegetables produced through wastewater irrigation and their toxicological implications in eastern Ethiopia. Afr J Food Agric Nutr Dev 15(3):10013–10032
Dey S, Dwivedi SK, Swarup D (1996) Lead concentration in blood, milk and feed of lactating buffaloes after acute poisoning. Vet Rec 138:336–336
Dogan Y, Unver MC, Ugulu I, Calis M, Durkan N (2014) Heavy metal accumulation in the bark and leaves of Juglans regia planted in Artvin City, Turkey. Biotechnol Biotechnol Equip 28(4):643–649
Ducic T, Polle A (2005) Transport and detoxification of manganese and copper in plants. Braz J Plant Physiol 17:103–112
Durkan N, Ugulu I, Unver MC, Dogan Y, Baslar S (2011) Concentrations of trace elements aluminum, boron, cobalt and tin in various wild edible mushroom species from Buyuk Menderes River Basin of Turkey by ICP-OES. Trace Elem Electrolytes 28(4):242–248
Finkelman RB, Orem W, Castranova V, Tatu C, Belkin HE, Zheng B, Lerch HE, Maharaj S, Bates A (2002) Health impacts of coal and coal use: possible solutions. Int J Coal Geol 50:425–443
Gowda NKS, Malathi VS, Jash S, Roy KS (2003) Status of pollutants and trace elements in water, soil, vegetation and dairy animals in industrial area of Bangalore. Indian J Dairy Sci 56:86–90
Huma ZE, Khan ZI, Noorka IR, Ahmad K, Bayat AR, Wajid K (2019) Bioaccumulation of zinc and copper in tissues of chicken fed corn grain irrigated with different water regimes. Int J Environ Res 13(4):689–703
Jekins KJ, Kraner JKG (1991) Effect of excess dietary manganese on lipid composition of calf blood plasma, heart and liver. J Dairy Sci 74:3944–3948
Kachenko AG, Singh B (2006) Heavy metals contamination in vegetables grown in urban and metal smelter contaminated sites in Australia. Water Air Soil Pollut 169:101–123
Kaplan O, Yildirim NC, Yildirim N, Cimen M (2011) Toxic elements in animal products and environmental health. Asian J Anim Vet Adv 6:228–232
Khan ZI, Ahmad K, Iqbal S, Ashfaq A, Bashir H, Mehmood N, Dogan Y (2018a) Evaluation of heavy metals uptake by wheat growing in sewage water irrigated soil. Hum Ecol Risk Assess 24(5):1409–1420
Khan ZI, Ahmad K, Rehman S, Ashfaq A, Mehmood N, Ugulu I, Dogan Y (2019c) Effect of sewage water on accumulation of metals in soil and wheat in Punjab, Pakistan. Pak J Anal Environ Chem 20(1):60–66
Khan ZI, Ahmad K, Safdar H, Ugulu I, Wajid K, Bashir H, Dogan Y (2018b) Manganese bioaccumulation and translocation of in forages grown in soil irrigated with city effluent: an evaluation on health risk. Res J Pharm Biol Chem Sci 9(5):759–770
Khan ZI, Iqbal S, Ahmad K, Ashfaq A, Bashir H, Dogan Y (2019a) Assessment of heavy metal content of wheat irrigated with wastewater in Sargodha, Pakistan: implications for human health. Trace Elem Electrolytes 36(2):82–92
Khan ZI, Safdar H, Ahmad K, Wajid K, Bashir H, Ugulu I, Dogan Y (2019b) Health risk assessment through determining bioaccumulation of iron in forages grown in soil irrigated with city effluent. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(14):14277–14286
Liu WH, Zhao JZ, Ouyang ZY, Soderlund L, Liu GH (2005) Impacts of sewage irrigation on heavy metals distribution and contamination in Beijing, China. Environ Int 31:805–812
Mcdowell LR (1992) Minerals in animal and human nutrition. Academic Press, Inc., San Diego
Mermut AR, Jain JC, Song L, Kerrich R, Kozak L, Jana S (1996) Trace element concentrations of selected soils and fertilizers in Saskatchewan, Canada. J Environ Qual 25:845–853
Oskarson AL, Jorham L, Sindberg J, Nilson N, Abanus L (1992) Toxicological implication of grazing on forages in Dareta village Zamfara, Nigeria. Sci Total Environ 111:83–94
Paul TK, Ghosh TK, Haldar S (2005) Assessment of trace element status in common goat feeds and in vital body tissues of black Bengal bucks (Capra hircus) with special reference to chromium. Indian J Anim Sci 75:429–432
Pinto AP, Mota AM, de Varennes A, Pinto FC (2004) Influence of organic matter on the uptake of cadmium, zinc, copper and iron by sorghum plants. Sci Total Environ 326:239–247
Raj BG, Patnaik MC, Babu SP, Kalakumar B, Singh MV, Shylaja J (2006) Heavy metal contaminants in water-soil-plant-animal continuum due to pollution of Musi river around Hyderabad in India. Indian J Anim Sci 76:131–133
Rodriguez EMR, Uretra ED, Romero CD (1999) Concentrations of cadmium and lead in different types of milk. Z Lebensm Unters Forsch 208:162–168
Sajjad K, Farooq R, Shahbaz S, Khan MA, Sadique M (2009) Health risk assessment of heavy metals for population via consumption of vegetables. World Appl Sci J 6:1602–1606
Singh A, Sharma RK, Agrawal M, Marshall FM (2010) Health risk assessment of heavy metals via dietary intake of foodstuffs from the wastewater irrigated site of a dry tropical area of India. Food Chem Toxicol 48:611–619
Somasundaram J, Krishnasamy R, Savithri P (2005) Bio transfer of heavy metals in Jersey cows. Indian J Anim Sci 75:1257–1260
Steel RGD, Torrie JH (1980) Principal and procedure of statistics, a biometrical approach (2nd Ed.). Mc Graw Hill Book Co. Inc., New York, pp 336–354
Tyokumbur ET, Okorie T (2011) Bioconcentration of trace metals in tissues of two leafy vegetables widely consumed in South West Nigeria. Biol Trace Elem Res 140:215–224
Ugulu I, Unver MC, Dogan Y (2016) Determination and comparison of heavy metal accumulation level of Ficus carica bark and leaf samples in Artvin, Turkey. Oxid Commun 39(1–2):765–775
Ugulu I, Unver MC, Dogan Y (2019) Potentially toxic metal accumulation and human health risk from consuming wild Urtica urens sold on the open markets of Izmir. Euro-Mediterr J Environ Integr 4:36
Unver MC, Ugulu I, Durkan N, Baslar S, Dogan Y (2015) Heavy metal contents of Malva sylvestris sold as edible greens in the local markets of Izmir. Ekoloji 24(96):13–25
USEPA (1997) Exposure factors handbook. Office of research and development, Washington
USEPA (2010) Risk-based concentration table. United State Environmental Protection Agency, Washington, DC
Voutsa D, Grimanis A, Samara C (1996) Trace elements in vegetables grown in an industrial area in relation to soil and air particulate matter. Environ Pollut 94:325–335
WHO (World Health Organization) (1996) Guidelines for drinking water quality. Health criteria and other supporting information. 94/9960-MastercomlWiener Verlag-800, Australia
Yadav S, Khirwar SS (2005) Inter-relationship of soil micronutrient with feedstuffs in Jind district of Haryana. Indian J Anim Sci 75:531–533
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khan, Z.I., Akhtar, M., Ahmad, K. et al. A study on the seasonal transfer of two metals from pasture to animals: health risk assessment. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27, 16339–16349 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-08140-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-08140-5