Abstract
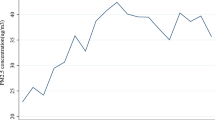
In this paper, the panel data of China’s four municipalities and 223 prefecture-level cities were used to investigate whether the EKC hypothesis for urban PM2.5 concentration was satisfied, considering such factors as urbanization population, electricity consumption, innovation capacity, and foreign direct investment in the cities. Assuming that the level of economic development directly affects the PM2.5 concentration, and the PM2.5 concentration will continue to increase at the early stage. Once the urban economy develops to a certain extent, the PM2.5 concentration will start to decline, and the environmental quality will be improved. Therefore, we attempt to construct the standard EKC by incorporating the quadratic and cubic terms of GDP per capita. The empirical results show that, except for the four municipalities of Beijing, Tianjin, Shanghai, and Chongqing, economic growth has a complex impact on PM2.5 concentration in most cities during the study period, rather than a simple inverted U-shaped pattern. Moreover, only in recent years has smog pollution shown an average decrease. But if the sources of smog are difficult to explore, it is worth considering the possibility of adjusting economic structure to meet environmental targets.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agras J, Chapman D (1999) A dynamic approach to the environmental Kuznets curve hypothesis. Ecol Econ 28(2):267–277
Alshehry AS, Belloumi M (2017) Study of the environmental Kuznets curve for transport carbon dioxide emissions in Saudi Arabia. Renew Sust Energ Rev 75:1339–1347
Al-Mulali U, Saboori B, Ozturk I (2015) Investigating the environmental Kuznets curve hypothesis in Vietnam. Energ Policy 76:123–131
Andreoni J, Levinson A (2001) The simple analytics of the environmental Kuznets curve. J Public Econ 80(2):269–286
Apergis N, Christou C, Gupta R (2017) Are there environmental Kuznets curves for us state-level CO2 emissions? Renew Sust Energ Rev 69:551–558
Arellano M, Bond S (1991) Some tests of specification for panel data: Monte Carlo evidence and an application to employment equations. Rev Econ Stud 58:277–297
Barbier EB, Stern DI, Common MS (1996) Economic growth and environmental degradation: the environmental Kuznets curve and sustainable development. World Dev 24(7):1151–1160
Brajer V, Mead RW, Xiao F (2011) Searching for an environmental Kuznets curve in China’s air pollution. China Econ Rev 22(3):383–397
Churchill SA, Inekwe J, Ivanovski K, Smyth R (2018) The environmental Kuznets curve in the OECD: 1870–2014. Energy Econ 75:389–399
Ding Y, Zhang M, Chen S, Wang W, Nie R (2019) The environmental Kuznets curve for PM2.5 pollution in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region of China: a spatial panel data approach. J Clean Prod 220:984–994
Dinda S (2005) A theoretical basis for the environmental Kuznets curve. Ecol Econ 53(3):403–413
Dong K, Sun R, Dong C, Li H, Zeng X, Ni G (2018) Environmental Kuznets curve for PM2.5 emissions in Beijing, China: what role can natural gas consumption play? Ecol Indic 93:591–601
Du G, Liu S, Lei N, Huang Y (2018) A test of environmental Kuznets curve for haze pollution in China: evidence from the penal data of 27 capital cities. J Clean Prod 205:821–827
Fosten J, Morley B, Taylor T (2012) Dynamic misspecification in the environmental Kuznets curve: evidence from CO2 and SO2 emissions in the United Kingdom. Ecol Econ 76:25–33
Hao Y, Liu Y, Weng JH, Gao Y (2016) Does the environmental Kuznets curve for coal consumption in China exist? New evidence from spatial econometric analysis. Energy 114:1214–1223
Hao Y, Wu Y, Wang L, Huang J (2018) Re-examine environmental Kuznets curve in China: spatial estimations using environmental quality index. Sustain Cities Soc 42:498–511
Hanif I, Gago-De-Santos P (2017) The importance of population control and macroeconomic stability to reducing environmental degradation: an empirical test of the environmental Kuznets curve for developing countries. Environ Dev 23:1–9
Han Y, Zhang Z (2019) Nanostructured membrane materials for CO2 capture: a critical review. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 19(6):3173–3179
Hidemichi F, Kazuyuki I, Andrew C, Shigemi K, Shunsuke M (2018) An analysis of urban environmental Kuznets curve of CO2 emissions: empirical analysis of 276 global metropolitan areas. Appl Energy 228:1561–1568
Hilton FGH, Levinson A (1998) Factoring the environmental Kuznets curve: evidence from automotive lead emissions. J Environ Econ Manag 35(2):126–141
Kaika D, Zervas E (2013) The environmental Kuznets curve (EKC) theory. Part B: critical issues. Energ Policy 62(9):1403–1411
Li H, Zhang Z (2018) Mining the intrinsic trends of CO2 solubility in blended solutions. J CO2 Util 26:496–502
Li H, Dan Yan D, Zhang Z (2019) Prediction of CO2 absorption by physical solvents using a chemoinformatics-based machine learning model. Environ Chem Lett 17(3):1397–1404
Lin B, Omoju OE, Nwakeze NM, Okonkwo JU, Megbowon ET (2016) Is the environmental Kuznets curve hypothesis a sound basis for environmental policy in Africa? J Clean Prod 133:712–724
Maddison D (2006) Environmental Kuznets curves: a spatial econometric approach. J Environ Econ Manag 51(2):218–230
Müller-Fürstenberger G, Wagner M (2007) Exploring the environmental Kuznets hypothesis. Theoretical and econometric problems. Ecol Econ 62(3):648–660
Olale E, Ochuodho TO, Lantz V, El Armali J (2018) The environmental Kuznets curve model for greenhouse gas emissions in Canada. J Clean Prod 184:859–868
Özokcu S, Özdemir Ö (2017) Economic growth, energy, and environmental Kuznets curve. Renew Sust Energ Rev 72:639–647
Roberts JT, Grimes PE (1997) Carbon intensity and economic development 1962-1991: a brief exploration of the environmental Kuznets curve. World Dev 25(2):191–198
Saboori B, Sulaiman J (2013) Environmental degradation, economic growth and energy consumption: evidence of the environmental Kuznets curve in Malaysia. Energ Policy 60:892–905
Sinha A, Bhattacharya J (2017) Environmental Kuznets curve estimation for SO2 emission: a case of Indian cities. Ecol Indic 72:881–894
Sinha A, Shahbaz M (2018) Estimation of environmental Kuznets curve for CO2 emission: role of renewable energy generation in India. Renew Energy 119:703–711
Suri V, Chapman D (1998) Economic growth, trade and energy: implications for the environmental Kuznets curve. Ecol Econ 25(2):195–208
Wang Y, Zhang C, Lu A, Li L, He Y, Tojo J, Zhu X (2017) A disaggregated analysis of the environmental Kuznets curve for industrial CO2 emissions in China. Appl Energy 190:172–180
Wang Y, Han R, Kubota J (2016) Is there an environmental Kuznets curve for SO2 emissions? A semi-parametric panel data analysis for China. Renew Sust Energ Rev 54:1182–1188
Wang SX, Fu YB, Zhang ZG (2015) Population growth and the environmental Kuznets curve. China Econ Rev 36:146–165
Windmeijer F (2005) A finite sample correction for the variance of linear efficient two-step GMM estimators. J Econ 126:25–51
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Eyup Dogan
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y., Komonpipat, S. Revisiting the environmental Kuznets curve of PM2.5 concentration: evidence from prefecture-level and above cities of China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27, 9336–9348 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-07621-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-07621-x