Abstract
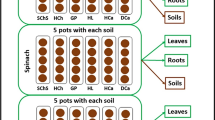
Biosolids are regarded as a major source of pharmaceutically active compounds (PhACs) in soil and may lead to their accumulation in plants and potential human risks through dietary intake. Using 14C labeling, we explored the effect of biosolids on the uptake and tissue distribution of carbamazepine (CAB) by three ready-to-eat vegetables (i.e., carrot, celery, and pak choi) under greenhouse conditions. The 14C-CAB was consistently detected in vegetables and plant tissues with bioconcentration factors in a range of 1.28–37.69, and it was easily translocated from root to leaf and/or stem with translocation factors > 1. The inhibition on the uptake and accumulation of 14C-labeled carbamazepine from soil by the addition of biosolids was consistently observed, and such inhibitory effect was related to the biosolid amendment rates, the category of vegetable, and the plant growth stages. The influence of biosolids on behavior of CAB and other emerging pollutants in the soil-plant system should be considered in their environmental risk assessment.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Rajab AJ, Sabourin L, Scott A, Lapen DR, Topp E (2009) Impact of biosolids on the persistence and dissipation pathways of triclosan and triclocarban in an agricultural soil. Sci Total Environ 407:5978–5985
Álvarez-Muñoz D, Rodríguez-Mozaz S, Maulvault AL, Tediosi A, Fernández-Tejedor M, Van den Heuvel F, Kotterman M, Marques A, Barceló D (2015) Occurrence of pharmaceuticals and endocrine disrupting compounds in macroalgaes, bivalves, and fish from coastal areas in Europe. Environ Res 143:56–64
Carter LJ, Harris E, Williams M, Ryan JJ, Kookana RS, Boxall AB (2014) Fate and uptake of pharmaceuticals in soil-plant systems. J Agric Food Chem 62:816–825
Carter LJ, Williams M, Bottcher C, Kookana RS (2015) Uptake of pharmaceuticals influences plant development and affects nutrient and hormone homeostases. Environ Sci Technol 49:12509–12518
Chefetz B, Mualem T, Ben-Ari J (2008) Sorption and mobility of pharmaceutical compounds in soil irrigated with reclaimed wastewater. Chemosphere 73:1335–1343
Contardo-Jara V, Lorenz C, Pflugmacher S, Nutzmann G, Kloas W, Wiegand C (2011) Exposure to human pharmaceuticals carbamazepine, ibuprofen and Bezafibrate causes molecular effects in Dreissena polymorpha. Aquat Toxicol 105:428–437
Dodgen LK, Li J, Parker D, Gan JJ (2013) Uptake and accumulation of four PPCP/EDCs in two leafy vegetables. Environ Pollut 182:150–156
Durán-Álvarez JC, Prado B, González D, Sánchez Y, Jiménez-Cisneros B (2015) Environmental fate of naproxen, carbamazepine and triclosan in wastewater, surface water and wastewater irrigated soil—results of laboratory scale experiments. Sci Total Environ 538:350–362
Ferrari B, Mons R, Vollat B, Fraysse B, Paxeus N, Lo GR, Pollio A, Garric J (2004) Environmental risk assessment of six human pharmaceuticals: are the current environmental risk assessment procedures sufficient for the protection of the aquatic environment? Environ Toxicol Chem 23:1344–1354
Fu Q, Wu X, Ye Q, Ernst F, Gan J (2016) Biosolids inhibit bioavailability and plant uptake of triclosan and triclocarban. Water Res 102:117–124
Goldstein M, Shenker M, Chefetz B (2014) Insights into the uptake processes of wastewater-borne pharmaceuticals by vegetables. Environ Sci Technol 48:5593–5600
He Y, Nie E, Li C, Ye Q, Wang H (2016) Uptake and subcellular distribution of triclosan in typical hydrophytes under hydroponic conditions. Environ Pollut 200:400–406
Herklotz PA, Gurung P, Vanden HB, Kinney CA (2010) Uptake of human pharmaceuticals by plants grown under hydroponic conditions. Chemosphere 78:1416–1421
Hirpassa WD, Codling EE (2018) Growth and metal uptake of edamame [Glycine max (L.) Merr.] on soil amended with biosolids and gypsum. Commun Soil Sci Plan 49:2793–2801
Holling CS, Bailey JL, Vanden HB, Kinney CA (2012) Uptake of human pharmaceuticals and personal care products by cabbage (Brassica campestris) from fortified and biosolids-amended soils. J Environ Monit 14:3029–3036
Hossain A, Nakamichi S, Habibullah-Al-Mamun M, Tani K, Masunaga S, Matsuda H (2018) Occurrence and ecological risk of pharmaceuticals in river surface water of Bangladesh. Environ Res 165:258–266
Hurtado C, Trapp S, Bayona JM (2016) Inverse modeling of the biodegradation of emerging organic contaminants in the soil-plant system. Chemosphere 156:236–244
Jarvis AL, Bernot MJ, Bernot RJ (2014a) The effects of the psychiatric drug carbamazepine on freshwater invertebrate communities and ecosystem dynamics. Sci Total Environ 496:461–470
Jarvis AL, Bernot MJ, Bernot RJ (2014b) Relationships between the psychiatric drug carbamazepine and freshwater macroinvertebrate community structure. Sci Total Environ 496:499–509
Kaneko S, Otani K, Kondo T, Fukushima Y, Nakamura Y, Ogawa Y, Kan R, Takeda A, Nakane Y, Teranishi T (1992) Malformation in infants of mothers with epilepsy receiving antiepileptic drugs. Neurology 42:68–74
Kinney CA, Furlong ET, Zaugg SD, Burkhard MR, Werner SL, Cahill JD, Jorgensen GR (2006) Survey of organic wastewater contaminants in biosolids destined for land application. Environ Sci Technol 40:7207–7215
Langenkamp H, Marmo L (2000) Proceedings of the workshop on “Problems around sludge”. European Commission Joint Research Centre, Stresa
Li ZH, Zlabek V, Velisek J, Grabic R, Machova J, Kolarova J, Li P, Randak T (2011) Acute toxicity of carbamazepine to juvenile rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss): effects on antioxidant responses, hematological parameters and hepatic EROD. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 74:319–327
Li JY, Dodgen L, Ye Q, Gan J (2013) Degradation kinetics and metabolites of carbamazepine in soil. Environ Sci Technol 47:3678–3684
Li J, Zhang JB, Li C, Wang W, Yang Z, Wang HY, Gan J, Ye QF, Xu XY, Li Z (2013b) Stereoisomeric isolation and stereoselective fate of insecticide Paichongding in flooded paddy soils. Environ Sci Technol 47:12768–12774
Ma R, Wang B, Yin L, Zhang Y, Deng S, Huang J, Wang Y, Yu G (2017) Characterization of pharmaceutically active compounds in Beijing, China: occurrence pattern, spatiotemporal distribution and its environmental implication. J Hazard Mater 323:147–155
Malchi T, Maor Y, Tadmor G, Shenker M, Chefetz B (2014) Irrigation of root vegetables with treated wastewater: evaluating uptake of pharmaceuticals and the associated human health risks. Environ Sci Technol 48:9325–9333
Martin-Diaz L, Franzellitti S, Buratti S, Valbonesi P, Capuzzo A, Fabbri E (2009) Effects of environmental concentrations of the antiepilectic drug carbamazepine on biomarkers and cAMP-mediated cell signaling in the mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis. Aquat Toxicol 94:177–185
McClellan K, Halden RU (2010) Pharmaceuticals and personal care products in archived U.S. biosolids from the 2001 EPA National Sewage Sludge Survey. Water Res 44:658–668
Mordechay EB, Tarchitzky J, Chen Y, Shenker M, Chefetz B (2018) Composted biosolids and treated wastewater as sources of pharmaceuticals and personal care products for plant uptake: a case study with carbamazepine. Environ Pollut 232:164–172
Moreno GR, Rodriguez MS, Huerta B, Barcelo D, Leon VM (2016) Do pharmaceuticals bioaccumulate in marine molluscs and fish from a coastal lagoon? Environ Res 146:282–298
Paz A, Tadmor G, Malchi T, Blotevogel J, Borch T, Polubesova T, Chefetz B (2016) Fate of carbamazepine, its metabolites, and lamotrigine in soils irrigated with reclaimed wastewater: sorption, leaching and plant uptake. Chemosphere 160:22–29
Shenker M, Harush D, Ben-Ari J, Chefetz B (2011) Uptake of carbamazepine by cucumber plants—a case study related to irrigation with reclaimed wastewater. Chemosphere 82:905–910
Sopper WE (1993) Municipal sludge use in land reclamation. CRC Press LLC, Boca Raton
Tanoue R, Sato Y, Motoyama M, Nakagawa S, Shinohara R, Nomiyama K (2012) Plant uptake of pharmaceutical chemicals detected in recycled organic manure and reclaimed wastewater. J Agric Food Chem 60:10203–10211
Ternes TA (1998) Occurrence of drugs in German sewage treatment plants and rivers. Water Res 32:3245–3260
U.S. EPA (1999) Biosolids generation, use, and disposal in the United States. Washington, D.C.
U.S. EPA (2000) Biosolids technology fact sheet: land application of biosolids. Washington, D.C.
U.S. EPA (2009) Targeted national sewage sludge survey. Washington, D.C.
Williams M, Kookana R (2010) Isotopic exchangeability as a measure of the available fraction of the human pharmaceutical carbamazepine in river sediment. Sci Total Environ 408:3689–3695
Williams CF, Williams CF, Adamsen FJ (2006) Sorption-desorption of carbamazepine from irrigated soils. J Environ Qual 35:1779–1783
Winker M, Clemens J, Reich M, Gulyas H, Otterpohl R (2010) Ryegrass uptake of carbamazepine and ibuprofen applied by urine fertilization. Sci Total Environ 408:1902–1908
Wu C, Spongberg AL, Witter JD (2009) Adsorption and degradation of triclosan and triclocarban in soils and biosolids-amended soils. J Agric Food Chem 57:4900–4905
Wu C, Spongberg AL, Witter JD, Fang M, Ames A, Czajkowski KP (2010a) Detection of pharmaceuticals and personal care products in agricultural soils receiving biosolids application. Clean Soil Air Water 38:230–237
Wu C, Spongberg AL, Witter JD, Fang M, Czajkowski KP (2010b) Uptake of pharmaceutical and personal care products by soybean plants from soils applied with biosolids and irrigated with contaminated water. Environ Sci Technol 44:6157–6161
Wu C, Spongberg AL, Witter JD, Sridhar BB (2012) Transfer of wastewater associated pharmaceuticals and personal care products to crop plants from biosolids treated soil. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 85:104–109
Wu X, Ernst F, Conkle JL, Gan J (2013) Comparative uptake and translocation of pharmaceutical and personal care products (PPCPs) by common vegetables. Environ Int 60:15–22
Wu X, Conkle JL, Ernst F, Gan J (2014) Treated wastewater irrigation: uptake of pharmaceutical and personal care products by common vegetables under field conditions. Environ Sci Technol 48:11286–11293
Wu X, Dodgen LK, Conkle JL, Gan J (2015) Plant uptake of pharmaceutical and personal care products from recycled water and biosolids: a review. Sci Total Environ 536:655–666
Funding
This study was financially supported from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grants Nos. 21777104 and 21477105), the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province (No. 2017A030313226), and the Shenzhen Science and Technology Project (Grant No. JCYJ20170818142823471).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Elena Maestri
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM1
(DOC 526 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, M., Ding, T., Wang, H. et al. Biosolids inhibit uptake and translocation of 14C-carbamazepine by edible vegetables in soil. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27, 8323–8333 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-07429-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-07429-4