Abstract
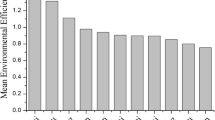
Industrial wastewater is the largest contributor of toxic pollutants and third-largest contributor of nutrients to bodies of water in China, and understanding the characteristics of such pollution is important for water pollution control. In this study, the industrial gray water footprint (GWF) of each industry sector in China’s 31 provinces in 2015 was calculated to identify the pollution characteristics of industrial wastewater discharge and determine how to efficiently allocate investment to pollution reduction. We show that the total industrial GWF of China was 300 billion m3 in 2015 and that the major pollutants were petroleum pollutant (PP), ammonia nitrogen (NH3-N), volatile phenol (VP), and chemical oxygen demand (COD). The water pollution level (WPL) was higher than 1 in Ningxia, Shanxi, Hebei, Tianjin, Shanghai, Henan, and Shandong, indicating that industrial pollution exceeded the carrying capacity of local water bodies in these seven regions. Given equivalent total investment, a scenario that takes the total reduction of the industrial GWF weighted by the WPL in each region as the investment target can better allocate funds to control industrial wastewater pollution in regions with high WPLs relative to a scenario in which investment targets the reduction of the unweighted total industrial GWF. For further industrial GWF reduction in regions with high WPLs, it is crucial to adjust the industrial structure and to upgrade relevant technologies.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amadi CN, Offor SJ, Frazzoli C, Orisakwe OE (2019) Natural antidotes and management of metal toxicity. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:18032–18052. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05104-2
Bazrafshan O, Zamani H, Etedali HR, Dehghanpir S (2019) Assessment of citrus water footprint components and impact of climatic and non-climatic factors on them. Sci Hortic 250:344–351. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2019.02.069
Cai B, Liu B, Zhang B (2019) Evolution of Chinese urban household’s water footprint. J Clean Prod 208:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.10.074
Chen B et al (2019) In search of key: protecting human health and the ecosystem from water pollution in China. J Clean Prod 228:101–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.04.228
Franke NA, Boyacioglu H, Hoekstra AY (2013) Grey water footprint accounting: tier 1 supporting guidelines. UNESCO-IHE, Delft, the Netherlands
General Bureau of China National Environmental Protection (2002) Environmental quality standards for surface water. vol GB 3838–2002
Geng Q, Ren Q, Nolan RH, Wu P, Yu Q (2019) Assessing China’s agricultural water use efficiency in a green-blue water perspective: a study based on data envelopment analysis. Ecol Indic 96:329–335. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2018.09.011
Hauschild MZ, Huijbregts M, Jolliet O, MacLeod M, Margni M, van de Meent D, Rosenbaum RK, McKone T (2008) Building a model based on scientific consensus for life cycle impact assessment of chemicals: the search for harmony and parsimony. Environmental Science & Technology 42:7032–7037. https://doi.org/10.1021/es703145t
Hoekstra AY (2003) Virtual water trade: proceedings of the international expert meeting on virtual water trade, Delft, the Netherlands, 12-13 December 2002, value of water research report series no. 12. UNESCO-IHE, Delft, the Netherlands
Hoekstra AY, Chapagain A, Martinez-Aldaya M, Mekonnen M (2009) Water footprint manual: state of the art 2009. Enschede, the Netherlands
Hoekstra AY, Chapagain AK, Mekonnen MM, Aldaya MM (2011) The water footprint assessment manual: setting the global standard. Routledge, London
Hu Y, Huang Y, Tang J, Gao B, Yang M, Meng F, Cui S (2018) Evaluating agricultural grey water footprint with modeled nitrogen emission data. Resour Conserv Recycl 138:64–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2018.04.020
Huijbregts MAJ et al (2017) ReCiPe2016: a harmonised life cycle impact assessment method at midpoint and endpoint level. Int J Life Cycle Assess 22:138–147
Jeong S, Yeon K, Hur Y, Oh K (2010) Salinity intrusion characteristics analysis using EFDC model in the downstream of Geum River. J Environ Sci 22:934–939. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1001-0742(09)60201-1
Li J (2013) China gears up to tackle tainted water. Nat News 499:14
Li H, Qin L, He H (2018) Characteristics of the water footprint of rice production under different rainfall years in Jilin Province, China. J Sci Food Agric 98:3001–3013. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.8799
Liao X, Chai L, Xu X, Lu Q, Ji J (2019) Grey water footprint and interprovincial virtual grey water transfers for China’s final electricity demands. J Clean Prod 227:111–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.04.179
Liu C, Kroeze C, Hoekstra AY, Gerbens-Leenes W (2012) Past and future trends in grey water footprints of anthropogenic nitrogen and phosphorus inputs to major world rivers. Ecol Indic 18:42–49
Ma L, Zhao S, Shi L (2016) Industrial metabolism of chlorine in a chemical industrial park: the Chinese case. Journal of Cleaner Production 112:4367–4376
Ma L, Chen Z, Xu C, Li F, Jin H, Shi L, Hu HY (2018) Water Meta-cycle model and indicators for industrial processes- the pulp & paper case in China. Resources, Conservation and Recycling 139:228–236
Ma L, Jin C, An L, Huang L, Li L, Jin H, Liang B, Wei H, Sun C (2019) Preliminary investigation of the degradation mechanism of o, m and p-cresol using sludge-derived carbon nanosheets by catalytic oxidation based on quantum chemistry. Catalysis Communications 120:59–65
MEE (Ministry of Ecology and Environment of China) (2015) Annual statistic report on environment in China. China Environment Press, Beijing
Mekonnen MM, Hoekstra AY (2018) Global anthropogenic phosphorus loads to freshwater and associated grey water footprints and water pollution levels: a high-resolution global study. Water Resour Res 54:345–358. https://doi.org/10.1002/2017wr020448
MWR (Ministry of Water Resources of China) (2015) China water resources report in 2015. Ministry of Water Resources of China. http://www.mwr.gov.cn/sj/tjgb/szygb/201612/t20161229_783348.html
NBS (National Bureau of Statistics of China) (2016a) China environmental yearbook. China Environmental Yearbook Press, Beijing
NBS (National Bureau of Statistics of China) (2016b) China statistical yearbook. China Statistics Press, Beijing
NBS (National Bureau of Statistics of China) (2016c) China statistical yearbook on environmental. China Statistics Press, Beijing
Qian Y, Dong H, Geng Y, Zhong S, Tian X, Yu Y, Chen Y, Moss DA (2018) Water footprint characteristic of less developed water-rich regions: case of Yunnan, China. Water Res 141:208–216. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2018.03.075
Smedt FD (1997) A time-dependent flow model for heavy metals in the scheldt estuary. Hydrobiologia 366:143–155. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1003184529504
Sun S, Fang C (2019) Factors governing variations of provincial consumption-based water footprints in China: An analysis based on comparison with national average. Sci Total Environ 654:914–923. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.11.114
Symeonidou S, Vagiona D (2018) The role of the water footprint in the context of green marketing. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:26837–26849. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-1838-0
Teodosiu C, Barjoveanu G, Sluser BR, Popa SAE, Trofin O (2016) Environmental assessment of municipal wastewater discharges: a comparative study of evaluation methods. Int J Life Cycle Assess 21:395–411. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11367-016-1029-5
Tugrul S, Ozhan K, Akcay I (2019) Assessment of trophic status of the northeastern Mediterranean coastal waters: eutrophication classification tools revisited. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:14742–14754. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-2529-6
Wang YB, Wu PT, Engel BA, Sun SK (2015) Comparison of volumetric and stress-weighted water footprint of grain products in China. Ecol Indic 48:324–333. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2014.08.014
Wu B, Zeng W, Chen H, Zhao Y (2016) Grey water footprint combined with ecological network analysis for assessing regional water quality metabolism. J Clean Prod 112:3138–3151. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2015.11.009
Wu Q, Liu Z, Liang J, Kuo DTF, Chen S, Hu X, Deng M, Zhang H, Lu YH (2019) Assessing pollution and risk of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in sewage sludge from wastewater treatment plants in China’s top coal-producing region. Environ Monit Assess 191:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-019-7225-6
Xie X, Jiang X, Zhang T, Huang Z (2019a) Regional water footprints assessment for hydroelectricity generation in China. Renew Energy 138:316–325. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2019.01.089
Xie X, Zhang T, Wang M, Huang Z (2019b) Impact of shale gas development on regional water resources in China from water footprint assessment view. Sci Total Environ 679:317–327. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.05.069
Xu Z, Long A (2004) The primary study on assessing social water scarcity in China. Acta geographica sinica/Dili Xuebao 59:982–988
Xu Y, Wu Y, Han J, Li P (2017) The current status of heavy metal in lake sediments from China: pollution and ecological risk assessment. Ecol Evol 7:5454–5466
Yousefi M, Khoramivafa M, Damghani AM (2017) Water footprint and carbon footprint of the energy consumption in sunflower agroecosystems. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:19827–19834. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-9582-4
Zhai Y, Tan X, Ma X, An M, Zhao Q, Shen X, Hong J (2019) Water footprint analysis of wheat production. Ecol Indic 102:95–102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2019.02.036
Zhang N, Li C, Yang Z, Yin Xa (2017) Water resources assessment of Hebei Province by grey water footprint. J Beijing Norm Univ Nat Sci (China) 53:75–79 doi:https://doi.org/10.16360/j.cnki.jbnuns.2017.01.013
Zhang L, Dong H, Geng Y, Francisco M-J (2019a) China’s provincial grey water footprint characteristic and driving forces. Sci Total Environ 677:427–435
Zhang S, Taiebat M, Liu Y, Qu S, Liang S, Xu M (2019b) Regional water footprints and interregional virtual water transfers in China. J Clean Prod 228:1401–1412. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.04.298
Zhao L, Li C, Huang R, Si S, Xue J, Huang W, Hu Y (2013) Harmonizing model with transfer tax on water pollution across regional boundaries in a China’s lake basin. Eur J Oper Res 225:377–382. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejor.2012.10.002
Zhao J-L, Jiang Y-X, Yan B, Wei C, Zhang L-J, Ying G-G (2014) Multispecies acute toxicity evaluation of wastewaters from different treatment stages in a coking wastewater-treatment plant. Environ Toxicol Chem 33:1967–1975. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.2638
Zhi Y, Yang Z, Yin X, Hamilton PB, Zhang L (2015) Using gray water footprint to verify economic sectors’ consumption of assimilative capacity in a river basin: model and a case study in the Haihe River basin, China. J Clean Prod 92:267–273. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2014.12.058
Zhi Y, Hamilton PB, Wang X, Liang L (2019) Water footprint assessment considering intermediate products: model and a 2016 case study of China. Water Environ J 33:230–240. https://doi.org/10.1111/wej.12394
Zhou W, Chen L, Feng L (2019) Effectiveness evaluation on third-party governance model for environmental pollution in China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:17305–17320. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05106-0
Funding
This work is supported by the Major Science and Technology Program for Water Pollution Control and Treatment (2014ZX07510-001-004).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Loubet
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(XLSX 265 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, Y., Zhou, B., Han, R. et al. China’s industrial gray water footprint assessment and implications for investment in industrial wastewater treatment. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27, 7188–7198 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-07405-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-07405-y