Abstract
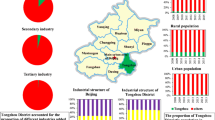
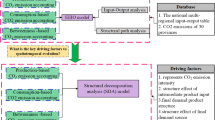
Forecasting CO2 emissions is the bases of making environmental planning and ecological strategy decisions. This paper constructed a multi-sector intertemporal optimization model to forecast the CO2 emission trends of 14 industrial departments in 31 provinces of China from 2012 to 2050. The results indicate that (1) the energy efficiency level of each province will be improved continuously under the influence of technology progress, and CO2 emissions in most provinces will reach the peak during the forecast period. (2) CO2 emissions of metal-manufacturing industries are the highest in all provinces, and the emissions of transportation service industries, construction industries, and other service industries show a trend of gradual increase from west to east. (3) Under the influence of the capital and technology, CO2 emissions caused by transportation service industries in eastern provinces will reach the peak earlier than those in central and western regions. (4) Combined with the industrial structure and the technical input level, the chemical industries in the western provinces have a great potential for emission reduction. Moreover, construction and transportation industries in the eastern and central provinces have a great potential for emission reduction.
















Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Notes
Until the year of 2017, the recent year for the input-output table of provinces in China that we can obtain is 2012. The data come from: http://bbs.pinggu.org/thread-4886478-1-1.html.
World Population Prospects: The 2017 Revision.
Except Hebei which is located in eastern China.
The proportion of agriculture in Jiangsu: 7.86% in 2005, 5.36% in 2016. Data sources: Jiangsu statistical yearbook.
The proportion of the tertiary industry in Beijing and Shanghai was 80.2% and 70.0% in 2016. Data sources: statistical yearbook of Beijing and Shanghai.
Data Source: CEIC Global Database.
Data source: statistical yearbook of each province in 2013. Accounting method: energy consumption of the oil industry/total output of the oil industry.
Data source: China statistical year book in 2017.
References
Adebola Solarin S, Al-Mulali U, Ozturk I (2017) Validating the environmental Kuznets curve hypothesis in India and China: the role of hydroelectricity consumption. Renew Sust Energ Rev 80:1578–1587. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2017.07.028
Ahmad F, Draz M, Su L, Ozturk I, Rauf A (2018) Tourism and environmental pollution: evidence from the One Belt One Road provinces of Western China. Sustainability 10:3520. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10103520
Ahmed K, Rehman MU, Ozturk I (2017) What drives carbon dioxide emissions in the long-run? Evidence from selected South Asian countries. Renew Sust Energ Rev 70:1142–1153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2016.12.018
Alcántara V, Duarte R (2004) Comparison of energy intensities in European Union countries. Results of a structural decomposition analysis. Energy Policy 32:177–189. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0301-4215(02)00263-x
Ang BW (1995) Multilevel decomposition of industrial energy-consumption. Energy Econ 17:39–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/0140-9883(95)98905-J
Baareh AK (2013) Solving the carbon dioxide emission estimation problem: an artificial neural network model. J Softw Eng Appl 06:338–342. https://doi.org/10.4236/jsea.2013.67042
Chen J, Wang P, Cui L, Huang S, Song M (2018) Decomposition and decoupling analysis of CO2 emissions in OECD. Appl Energy 231:937–950. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2018.09.179
Chen J, Xu C, Cui L, Huang S, Song M (2019) Driving factors of CO2 emissions and inequality characteristics in China: a combined decomposition approach. Energy Econ 78:589–597. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eneco.2018.12.011
Dell M, Jones BF, Olken BA (2012) Temperature shocks and economic growth: evidence from the last half century. Am Econ J-Macroecon 4:66–95. https://doi.org/10.1257/mac.4.3.66
Dou X (2017) Low carbon technology innovation, carbon emissions trading and relevant policy support for China8.12.011". 179" uest.JZD031), the Nationalional. J Energy Econ Policy 7:172-184
Fang D, Zhang X, Yu Q, Jin TC, Tian L (2018) A novel method for carbon dioxide emission forecasting based on improved Gaussian processes regression. J Clean Prod 173:143–150. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.05.102
Feng SZ, Krueger AB, Oppenheimer M (2010) Linkages among climate change, crop yields and Mexico-US cross-border migration. P Natl Acad Sci USA 107:14257–14262. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1002632107
He J, Richard P (2010) Environmental Kuznets curve for CO2 in Canada. Ecol Econ 69:1083–1093. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolecon.2009.11.030
Hong T, Jeong K, Koo C (2018) An optimized gene expression programming model for forecasting the national CO2 emissions in 2030 using the metaheuristic algorithms. Appl Energy 228:808–820. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2018.06.106
Huw M, Ligang S (2010) China as a global manufacturing powerhouse: strategic considerations and structural adjustment. China World Econ 18:1–32. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1749-124X.2010.01178.x
Işik C, Ongan S, Özdemir D (2019) Testing the EKC hypothesis for ten US states: an application of heterogeneous panel estimation method. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 26:10846–10853. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-04514-6
Kavoosi H, Kavoosi M, Saidi MH, Rekati KK (2012) Forecast global carbon dioxide emission by use of genetic algorithm (GA). International Journal of Computer Science Issues 9:418–427
Mendelsohn R, Nordhaus WD, Shaw D (1994) The impact of global warming on agriculture - a Ricardian analysis. Am Econ Rev 84:753–771
Meng M, Niu D, Shang W (2014) A small-sample hybrid model for forecasting energy-related CO 2 emissions. Energy 64:673–677. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2013.10.017
Mi Z-F, Pan S-Y, Yu H, Wei Y-M (2015) Potential impacts of industrial structure on energy consumption and CO2 emission: a case study of Beijing. J Clean Prod 103:455–462. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2014.06.011
Mikiko K, Yuzuru M, Tsuneyuki M (2000) The AIM/end-use model and its application to forecast Japanese carbon dioxide emissions European. J Oper Res 122:416–425. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0377-2217(99)00243-X
Proops JLR (1984) Modeling the energy-output ratio. Energy Econ 6:47–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/0140-9883(84)90043-4
Raggad B (2018) Carbon dioxide emissions, economic growth, energy use, and urbanization in Saudi Arabia: evidence from the ARDL approach and impulse saturation break tests. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 25:14882–14898. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-1698-7
Rauf A, Liu X, Amin W, Ozturk I, Rehman OU, Hafeez M (2018) Testing EKC hypothesis with energy and sustainable development challenges: a fresh evidence from belt and road initiative economies. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 25:32066–32080. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-3052-5
Saboori B, Sulaiman J, Mohd S (2012) Economic growth and CO2 emissions in Malaysia: a cointegration analysis of the Environmental Kuznets curve. Energy Policy 51:184–191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2012.08.065
Schmalensee R, Stoker TM, Judson RA (1998) World carbon dioxide emissions: 1950-2050. Rev Econ Stat 80:15–27. https://doi.org/10.1162/003465398557294
Shahbaz M, Farhani S, Ozturk I (2015) Do coal consumption and industrial development increase environmental degradation in China and India? Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 22:3895–3907. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-3613-1
Song M, Zheng W (2016) Computational analysis of thermoelectric enterprises’ environmental efficiency and Bayesian estimation of influence factors. Soc Sci J 53:88–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soscij.2015.10.002
Song M, Wang S, Cen L (2015) Comprehensive efficiency evaluation of coal enterprises from production and pollution treatment process. J Clean Prod 104:374–379. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2014.02.028
Sun W, Wang J, Chang H (2013) Forecasting carbon dioxide emissions in China using optimization grey model. J Comput 8:97–101. https://doi.org/10.4304/jcp.8.1.97-101
Usman O, Iorember PT, Olanipekun IO (2019) Revisiting the environmental Kuznets curve (EKC) hypothesis in India: the effects of energy consumption and democracy. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 26:13390–13400. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-04696-z
Wang Z-X, Ye D-J (2017) Forecasting Chinese carbon emissions from fossil energy consumption using non-linear grey multivariable models. J Clean Prod 142:600–612. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.08.067
Wang K, Wang C, Lu X, Chen J (2007) Scenario analysis on CO2 emissions reduction potential in China’s iron and steel industry. Energy Policy 35:2320–2335. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2006.08.007
Wang Z, Zhu Y, Peng Y (2013) Carbon emissions trends with optimal balanced economic growth of China and the USA and some abatement options for China. J Geogr Sci 23:991–1004. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11442-013-1058-y
Wiltshire A, Kay G, Gornall J, Betts R (2013) The impact of climate, CO2 and population on regional food and water resources in the 2050s. Sustainability 5:2129–2151. https://doi.org/10.3390/su5052129
Yao X, Huang R, Song M (2019) How to reduce carbon emissions of small and medium enterprises (SMEs) by knowledge sharing in China. Prod Plan Control 30:881–892. https://doi.org/10.1080/09537287.2019.1582096
Funding
This work is partially funded by the Major Projects in Philosophy and Social Science Research from the Ministry of Education of China (No. 14JZD031), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 71303029, 71471001), and the National Social Science Foundation Project (No. 17BGL266).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pan, X., Xu, H. & Lu, Y. Long-term forecasting of industrial CO2 emissions in 31 provinces of China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27, 5168–5191 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-07092-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-07092-9