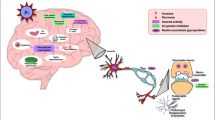
Abstract
The fluoride contamination in water is still a live discussion among the scientific community, because of its beneficial and injurious health effects inflicted on the human population. The magnitude of groundwater fluoride contamination is aggravated by increasing anthropogenic activities. Groundwater is supposedly the main source through which people are highly exposed to fluoride, compared with other sources of exposure. Among human populations, fluoride-related health issues span from mild effects on teeth and bones to severe kidney problems, neurotoxicity, and even cancer. Nowadays, fluoride toxicity is gaining much attention in the endemic areas due to its adverse impact on the children’s cognitive function, since children are more susceptible to fluoride toxicity as compared to adults. The primary mechanism behind the neurotoxicity of fluoride is still not clearly understood. However, knowingly, fluoride disrupts the biochemical mechanism and thus alters the normal functioning of the brain. Several human studies are suggestive of lowering children’s IQ who was exposed to fluoride during their childhood. The conclusive findings of past research suggest that the fluoride concentration in potable water tends to grossly affect the children’s IQ level. However, the body of proof is limited, because most of the studies are concentrated in few countries, and have their own limitations and data gaps. The grave implications of fluoride toxicity, therefore, demand extensive and properly designed research to bridging the data gap in developing countries. Furthermore, spanning research work across all the endemic areas of the world could generate larger database, helping resolve the issue on a large scale.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
An J, Mei S, Liu A (1992) The effects of high fluoride on the level of intelligence of primary and secondary students. Chinese Journal of Control of Endemic Diseases 7:93–94
Brigatti MF, Guggenheim S (2002) Mica crystal chemistry and the influence of pressure, temperature, and solid solution on atomistic models. Rev Mineral Geochem 46:1–97
Browne D, Whelton H, O’Mullane D (2005) Fluoride metabolism and fluorosis. J Dent 33:177–186
Catherine E. Housecroft and Alan G. Sharpe. Inorganic chemistry (3rd edition), Pearson education limited 2008
Chakraborti D, Rahman MM, Chatterjee A, Das D, Das B, Nayak B, Pal A, Chowdhury UK, Ahmed S, Biswas BK, Sengupta MK, Lodh D, Samanta G, Chakraborty S, Roy MM, Dutta RN, Saha KC, Mukherjee SC, Pati S, Kar PB (2016) Fate of over 480 million inhabitants living in arsenic and fluoride endemic Indian districts: magnitude, health, socio-economic effects and mitigation approaches. J Trace Elem Med Biol 38:33–45
Chen Y, Han F, Zhou Z, Zhang H, Jiao X, Zhang S et al (1991) Research on the intellectual development of children in high fluoride areas. Chin J Control Endem Dis 6:99–100
Choi AL, Zhang Y, Sun G, Bellinger DC, Wang K, Yang XJ, Li JS, Zheng Q, Fu Y, Grandjean P (2015) Association of lifetime exposure to fluoride and cognitive functions in Chinese children: a pilot study. Neurotoxicol Teratol 47:96–101
Clarkson JJ, McLoughlin J (2000) Role of fluoride in oral health promotion. Int Dent J 50:119–128
Das K, Mondal NK (2016) Dental fluorosis and urinary fluoride concentration as a reflection of fluoride exposure and its impact on IQ level and BMI of children of Laxmisagar, Simlapal Block of Bankura District, WB. India Environmental monitoring and assessment 188:218
Ding Y, Sun H, Han H, Wang W, Ji X, Liu X et al (2011) The relationships between low levels of urine fluoride on children’s intelligence, dental fluorosis in endemic fluorosis areas in Hulunbuir, Inner Mongolia, China. J Hazard Mater 186:1942–1946
Erdal S, Buchanan SN (2004) A quantitative look at fluorosis, fluoride exposure, and intake in children using a health risk assessment approach. Environ Health Perspect 113:111–117
Eswar P, Nagesh L, Devaraj C (2011) Intelligence quotients of 12-14 year old school children in a high and a low fluoride village in India. Fluoride 44:168
FAN Z, DAI H, BAI A, LI P, RO L, LI G, et al. The effect of high fluoride exposure on the level of intelligence in children significance 2007; 10: 0.01
Gazzano E, Bergandi L, Riganti C, Aldieri E, Doublier S, Costamagna C, Bosia A, Ghigo D (2010a) Fluoride effects: the two faces of janus. Curr Med Chem 17:2431–2441
Gazzano EBL, Riganti C, Aldieri E, Doublier S, ea CC (2010b) Fluoride effects: the two faces of janus. Curr Med Chem 17:2431–2441
Ghosh A, Mukherjee K, Ghosh SK, Saha B (2013) Sources and toxicity of fluoride in the environment. Res Chem Intermed 39:2881–2915
Grandjean P, Landrigan PJ (2006) Developmental neurotoxicity of industrial chemicals. Lancet 368:2167–2178
Green R, Lanphear B, Hornung R, Flora D, Martinez-Mier EA, Neufeld R, Ayotte P, Muckle G, Till C. 2019. Association between maternal fluoride exposure during pregnancy and IQ scores in offspring in Canada. JAMA Pediatr Aug 19. doi: https://doi.org/10.1001/jamapediatrics.2019.1729
Heifetz SB, Horowitz HS (1986) Amounts of fluoride in self-administered dental products: safety considerations for children. Pediatrics 77:876–882
Hoque A, Khaliquzzaman M, Hossain M, Khan A (2003) Fluoride levels in different drinking water sources in Bangladesh. Fluoride 36:38–44
JK. Water quality andtreatment: a handbook on drinking water. 2011a
JK E. Water quality and treatment: a handbook on drinking water. 2011b
Karimzade S, Aghaei M, Mahvi A (2014) Investigation of intelligence quotient in 9-12-year-old children exposed to high-and low-drinking water fluoride in West Azerbaijan Province, Iran. Fluoride 47:9–14
Khan SA, Rahul Kumar Singh SN, Chadha D, Johri N, Navit P, Sharma A, et al. Relationship between dental fluorosis and intelligence quotient of school going children in and around Lucknow District: a cross-sectional study Journal of clinical and diagnostic research: JCDR 2015; 9: ZC10
Kundu H, Basavaraj P, Singla A, Gupta R, Singh K, Jain S (2015) Effect of fluoride in drinking water on children’s intelligence in high and low fluoride areas of Delhi. Journal of Indian Association of Public Health Dentistry 13:116
Li Y, Jing X, Chen D, Lin L, Wang Z (2008) Effects of endemic fluoride poisoning on the intellectual development of children in Baotou. Fluoride 41:161–164
Liu G, Ye Q, Chen W, Zhao Z, Li L, Lin P (2015) Study of the relationship between the lifestyle of residents residing in fluorosis endemic areas and adult skeletal fluorosis. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 40:326–332
Lu Y, Sun Z, Wu L, Wang X, Lu W, Liu S (2000) Effect of high-fluoride water on intelligence in children. Fluoride 33:74–78
Mahboob S, Ashraf S, Al-Misned F, Ahmed Z, Sultana S (2013) Determination of fluoride concentration in underground water from different urban areas of Faisalabad city. Life Sci J 10:60–70
Meija J, Coplen TB, Berglund M, Brand WA, De Bièvre P, Gröning M et al (2016) Atomic weights of the elements 2013 (IUPAC technical report). Pure Appl Chem 88:265–291
Mondal D, Dutta G, Gupta S (2016) Inferring the fluoride hydrogeochemistry and effect of consuming fluoride-contaminated drinking water on human health in some endemic areas of Birbhum district, West Bengal. Environ Geochem Health 38:557–576
Nagarajappa R, Pujara P, Sharda AJ, Asawa K, Tak M, Aapaliya P et al (2013) Comparative assessment of intelligence quotient among children living in high and low fluoride areas of Kutch. India-a pilot study Iranian journal of public health 42:813
Oganessian E, Lencova E, Broukal Z (2007) Is systemic fluoride supplementation for dental caries prevention in children still justifiable. Prague Medical Report 108:306–314
Ozsvath DL (2009) Fluoride and environmental health: a review. Rev Environ Sci Biotechnol 8:59–79
Poureslami H, Horri A, Khoramian S, Garrusi B (2011) Intelligence quotient of 7 to 9 year-old children from an area with high fluoride in drinking water. J Dent Oral Hyg 3:61–64
Prasad B, Narayana T. Subsurface water quality of different sampling stations with some selected parameters at Machilipatnam Town. 2004
Quotient I. 2012
Marquis RE (1990) Diminished acid tolerance of plaque bacteria caused by fluoride. J Dent Res 69:672–675
Repetto R, Baliga SS. Pesticides and the immune system: the public health risks: World Resources Institute, 1996
Rocha-Amador D, Navarro ME, Carrizales L, Morales R, Calderón J (2007) Decreased intelligence in children and exposure to fluoride and arsenic in drinking water. Cadernos de saúde pública 23:S579–S587
Sebastian ST, Sunitha S (2015) A cross-sectional study to assess the intelligence quotient (IQ) of school going children aged 10-12 years in villages of Mysore district. India with different fluoride levels Journal of Indian Society of Pedodontics and Preventive Dentistry 33:307
Seraj B, Shahrabi M, Shadfar M, Ahmadi R, Fallahzadeh M, Eslamlu HF et al (2012) Effect of high water fluoride concentration on the intellectual development of children in makoo/iran. J dent (Tehran, Iran) 9:221
Shivaprakash P, Ohri K, Noorani H (2011) Relation between dental fluorosis and intelligence quotient in school children of Bagalkot district. Journal of Indian Society of Pedodontics and Preventive Dentistry 29:117
Silk H (2014) Diseases of the mouth. Primary care 41:75–90
Singh V, Chauhan D, Tripathi S, Kumar S, Gaur V, Tiwari M et al (2013) A correlation between serum vitamin, acetylcholinesterase activity and IQ in children with excessive endemic fluoride exposure in Rajasthan, India. Int Res J Med Sci 1:12–16
Sudhir K, Chandu GD, Prashant G, Reddy VS (2009) Effect of fluoride exposure on intelligence quotient (IQ) among 13-15 year old school children of known endemic area of fluorosis, Nalgonda District, Andhra Pradesh. Public Health Dentistry: 2009(13)
Susheela A, Bhatnagar M, Vig K, Mondal N (2005) Excess fluoride ingestion and thyroid hormone derangements in children living in Delhi, India. Fluoride 38:98–108
Trivedi M, Sangai N, Patel R, Payak M, Vyas S (2012) Assessment of groundwater quality with special reference to fluoride and its impact on IQ of schoolchildren in six villages of the Mundra region, Kachchh, Gujarat, India. Fluoride 45:377–383
Trivedi M, Verma R, Chinoy N, Patel R, Sathawara N (2007) Effect of high fluoride water on intelligence of school children in India. Fluoride 40:178–183
Vithanage M, Bhattacharya P (2015) Fluoride in the environment: sources, distribution and defluoridation. Environ Chem Lett 13:131–147
WANG XH, WANG LF, PY HU (2001) Effects of high iodine and high fluorine on children’s intelligence and thyroid function [J]. Chinese Jouranl of Endemiology 4:020
Whitford GM (1999) Fluoride metabolism and excretion in children. J Public Health Dent 59:224–228
WHO. Fluoride in drinking-water World Health Organization 2006: 144
Xiang Q, Liang Y, Chen L, Wang C, Chen B, Chen X et al (2003) Effect of fluoride in drinking water on children’s intelligence. Fluoride 36:84–94
Yao L, Zhuo J, Wang X, Cui Q, Lin F. 1996 Analysis on the Correla on Between TSH and Intelligence in Children with Dental Fluorosis from Endemic Fluorosis Regions.Literature and Information on Preventive Medicine.Volume 2(1): 42–43
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saeed, M., Malik, R.N. & Kamal, A. Fluorosis and cognitive development among children (6–14 years of age) in the endemic areas of the world: a review and critical analysis. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27, 2566–2579 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06938-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06938-6