Abstract
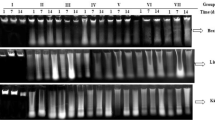
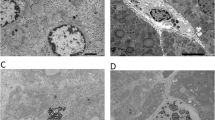
The rapidly growing interest in using graphene-based nanoparticles in a wide range of applications increases human exposure and risk. However, very few studies have investigated the genotoxicity and mutagenicity of the widely used graphene oxide (GO) nanoparticles in vivo. Consequently, this study estimated the possible genotoxicity and mutagenicity of GO nanoparticles as well as possible oxidative stress induction in the mice liver and brain tissues. Nano-GO particles administration at the dose levels of 10, 20, or 40 mg/kg for one or five consecutive days significantly increased the DNA breakages in a dose-dependent manner that disrupts the genetic material and causes genomic instability. GO nanoparticles also induced mutations in the p53 (exons 6&7) and presenilin (exon 5) genes as well as increasing the expression of p53 protein. Positive p53 reaction in the liver (hepatic parenchyma) and brain (cerebrum, cerebellum, and hippocampus) sections showed significant increase of p53 immunostaining. Additionally, induction of oxidative stress was proven by the significant dose-dependent increases in the malondialdehyde level and reductions in both the level of reduced glutathione and activity of glutathione peroxidase observed in GO nanoparticles administered groups. Acute and subacute oral administration of GO nanoparticles induced genomic instability and mutagenicity by induction of oxidative stress in the mice liver and brain tissues.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Afzali M, Parivar K, Roodbari Nand Badiei A (2015) Study of Nano-Graphene oxide effects on the number of Kupffer cells and megakaryocytes in liver of NMRI strain mouse embryo in vivo. Current World Environment 10(1):713–718
Athan ES, Williamson J, Ciappa A, Santana V, Romas SN, Lee JH, Rondon H, Lantigua RA, Medrano M, Torres M, Arawaka S, Rogaeva E, Song YQ, Sato C, Kawarai T, Fafel KC, Boss MA, Seltzer WK, Stern Y, St George-Hyslop P, Tycko B, Mayeux R (2001) A founder mutation in presenilin 1 causing early-onset Alzheimer disease in unrelated Caribbean Hispanic families. JAMA. 286(18):2257–2263. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.286.18.2257
Beutler E, Duron O, Kelly BM (1963) Improved method for the determination of blood glutathione. J Lab Clin Med 61:882–888
Bjelland, Seeberg E (2003) Mutagenicity, toxicity and repair of DNA base damage induced by oxidation. MutatRes-Fundam Mol Mech Mutagen 531:37–80
Chaenyung C, Ryon SS, Xiguang G, Nasim A, Dokmeci MR, Xiaowu Shirley T et al (2014) Controlling mechanical properties of cell-laden hydrogels by covalent incorporation of graphene oxide. Small 10(3):514–523. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.201302182
Chen M, Yin J, Liang Y, Yuan S, Wang F, Song M, Wang H (2016) Oxidative stress and immunotoxicity induced by graphene oxide in zebrafish. Aquat Toxicol 174(1879–1514 (electronic)):54–60
Crews L, Masliah E (2010) Molecular mechanisms of neurodegeneration in Alzheimer’s disease. Hum Mol Genet 19(1):R12–R20
De Marzi L, Ottaviano L, Perrozzi F, Nardone M, Santucci S, De Lapuente J, Borras M, Treossi E, Palermo V, Poma A (2014) Flake size-dependent cyto and genotoxic evaluation of graphene oxide on in vitro A549, CaCo2 and vero cell lines. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents 28(2):281–289
Ding Z, Zhang Z, Ma H, Chen Y (2014) In vitro hemocompatibility and toxic mechanism of graphene oxide on human peripheral blood T lymphocytes and serum albumin. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 6(22):19797–19807 18
Dorszewska J, Oczkowska A, Suwalska M, Rozycka A, Florczak-Wyspianska J, Dezor M, Lianeri M, Jagodzinski P, Kowalczyk MJ, Prendecki M, Kozubski W (2014) Mutations in the exon 7 of Trp53 gene and the level of p53 protein in double transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Folia Neuropathol 52(1):30–40
El-Yamanya AN, Mohamed FF, Salaheldin TA, Tohamya AA, Abd El-Mohsena WN, Amine AS (2017) Graphene oxide nanosheets induced genotoxicity and pulmonary injury in mice. Exp Toxicol Pathol 69:383–392
Ferraro D, Anselmi-Tamburini U, Tredici IG, Ricci V, Sommi P (2016) Overestimation of nanoparticles-induced DNA damage determined by the comet assay. Nanotoxicology 10(7):861–870
Gautheron V, Auffret A, Mattson MP, Mariani J, Garabedian B V-d (2009) A new and simple approach forgenotyping Alzheimer’s disease presenilin-1 mutant knock-inmice. J Neurosci Methods 181(2):235–240
Guo X, Mei N (2014) Review Article:Assessment of the toxic potential of grapheme family nanomaterials. J Food Drug Anal 2 2:1 0 5–1 1 5
Gurunathan S, Han JW, Dayem AA, Eppakayala V, Kim JH (2012) Oxidative stress-mediated antibacterial activity of graphene oxide and reduced graphene oxide in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Int J Nanomedicine 7:5901–5914. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S37397
Gutierrez MI, Bhatia K, Siwarski D, Wolff L, Magrath IT, Mushinski JF, Huppi K (1992) Infrequent p53 Mutation in Mouse Tumors with Deregulated myc. Cancer Res 52:1032–1035
Hsu SM, Raine L, Fanger H (1981) Use of avidin-biotin-peroxidase complex (ABC) in immunoperoxidase techniques: a comparison between ABC and unlabeled antibody (PAP) procedures. J HistochemCytochem 29(4):577–580
Jarosz A, Skoda M, Dudek I, Szukiewicz D (2016) Oxidative stress and mitochondrial activation as the main mechanisms underlying graphene toxicity against human cancer cells. Oxidative Med Cell Longev 2016:5851035
Jasim DA, M’enard-Moyon C, B’egin D, Bianco A, Kostarelos K (2015) Tissue distribution and urinary excretion of intravenously administered chemically functionalized graphene oxide sheets. Chem Sci 6:3952–3964
Jaworski S, Sawosz E, Grodzik M, Winnicka A, Prasek M, Wierzbicki M, Chwalibog A (2013) In vitro evaluation of the effects of graphene platelets on glioblastoma multiforme cells. Int J Nanomedicine 8:413–420
Kelleher RJ, Shen J (2010) γ -Secretase and human disease. Science. 33(6007):1055–1056
Kurantowicz N, Strojny B, Sawosz E, Jaworski S, Kutwin M, Grodzik M, Chwalibog A (2015) Biodistribution of a high dose of diamond, graphite, and Graphene oxide nanoparticles after multiple Intraperitoneal injections in rats. Nanoscale Res Lett 10(1):398. https://doi.org/10.1186/s11671-015-1107-9
Lanoiselée HM, Nicolas G, Wallon D, Rovelet-Lecrux A, Lacour M, Rousseau S (2017) APP, PSEN1, and PSEN2 mutations in early-onset Alzheimer disease: a genetic screening study of familial and sporadic cases. PLoS Med 14(3):e1002270. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.1002270
Liu S, Zeng TH, Hofmann M, Burcombe E, Wei J, Jiang R, Chen Y (2011) Antibacterial activity of graphite, graphite oxide, grapheme oxide, and reduced graphene oxide: membrane and oxidative stress. ACS Nano 5:6971–6980
Liu Y, Luo Y, Wu J, Wang Y, Yang X, Yang R, Wang B, Yang J, Zhang N (2013) Graphene oxide can induce in vitro and in vivo mutagenesis. Sci Rep 3:3469
Liu Z, Choi SW, Crott JW, Smith DE, Mason JB (2008) Multiple B-vitamin inadequacy amplifies alterations induced by folate depletion in p53 expression and its downstream effector MDM2. Int J Cancer 123(3):519–525
Lockman PR, Koziara JM, Mumper RJ, Allen DD (2004) Nanoparticle surface charges alter blood-brain barrier integrity and permeability. J Drug Target 12(9–10):635–641
Mendonça MC, Soares ES, de Jesus MB, Ceragioli HJ, Ferreira MS, Catharino RR, da Cruz-Höfling MA (2015) Reduced graphene oxide induces transient blood-brain barrier opening: an in vivo study. Journal of nanobiotechnology 13:78. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12951-015-0143-z
Nezakati T, Cousins BG, Seifalian AM (2014) REVIEW ARTICLE: Toxicology of chemically modified graphene-based materials for medical application. Arch Toxicol 88:1987–2012
Ohkawa H, Ohishi W, Yagi K (1979) Assay for lipid peroxides in animal tissues by thiobarbituric acid reactionAnal. Biochem 95:351–358
Paglia DE, Valentine WN (1967) Studies on the quantitativeand qualitative characterization of erythrocyte glutathioneperoxidase. J Lab Clin Med 70:158–169
Pan Y, Sahoo NG, Li L (2012) The application of graphene oxide in drug delivery. Expert Opin Drug Deliv 9(11):1365–1376. https://doi.org/10.1517/17425247.2012.729575
Recio L, Hobbs C, Caspary W, Witt KL (2010) Dose-response assessment of four genotoxic chemicals in a combined mouse and rat micronucleus (MN) and comet assay protocol. J Toxicol Sci 35(2):149–162
Ren H, Wang C, Zhang J, Zhou X, Xu D, Zheng J, Guo S, Zhang J (2010) DNA cleavage system of nanosized graphene oxide sheets and copper ions. ACS Nano 4(12):7169–7174
Sanchez VC, Jachak A, Hurt RH, Kane AB (2012) Biological interactions of graphene-family nanomaterials: an interdisciplinary review. Chem Res Toxicol 25:15–34
Seabra AB, Paula AJ, de Lima R, Alves OL, Duran N (2014) Nanotoxicity of graphene and graphene oxide. Chem Res Toxicol 27(2):159–168
Shen H, Zhang L, Liu M, Zhang Z (2012) Biomedical applications of Graphene. Theranostics 2(3):283–294
Tice RR, Agurell E, Anderson V, Burlinson B, Hartmann A, Kobayashi H, Miyamae Y, Rojas E, Ryu JC, Sasaki YF (2000) Single cell gel/comet assay: guidelines for in vitro and in vivo genetic toxicology testing. Environ Mol Mutagen 35:206–221
Valko M, Morris H, Cronin MT (2005) Metals, toxicity and oxidative stress. Curr Med Chem 12(10):1161–1208
Waiwijit U, Kandhavivorn W, Oonkhanond B, Lomas T, Phokaratkul D, Wisitsoraat A, Tuantranont A (2014) Cytotoxicity assessment of MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells on screen-printed graphene-carbon paste substrate. Colloids Surf B: Biointerfaces 113:190–197
Wang A, Pu K, Dong B, Liu Y, Zhang L, Zhang Z, Duan W, Zhu Y (2013) Role of surface charge and oxidative stress in cytotoxicity and genotoxicity of graphene oxide towards human lung fibroblast cells. J Appl Toxicol 33:1156–1164
Yang K, Wan J, Zhang S, Zhang Y, Lee S-T, Liu Z (2011) In vivo pharmacokinetics, long-term biodistribution, and toxicology of PEGylated Graphene in mice. ACS Nano 5(1):516–522. https://doi.org/10.1021/nn1024303
Zhang S, Yang K, Feng L, Liu Z (2011) In vitro and in vivo behaviors of dextran functionalized graphene. Carbon 49:4040–4049
Acknowledgments
Thanks and great appreciation to the Department of Zoology, Faculty of Science, Cairo University, for providing us with the necessary equipment to conduct experiments of this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mohamed, H.R.H., Welson, M., Yaseen, A.E. et al. Estimation of genomic instability and mutation induction by graphene oxide nanoparticles in mice liver and brain tissues. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27, 264–278 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06930-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06930-0