Abstract
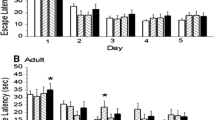
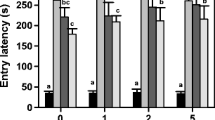
Spirotetramat is a toxic commercially known as Movento used to control pistachio psylla pests. In the present study, the effects of Movento on passive avoidance learning of rats and their ability to explore the novel object in the novel object recognition test were investigated. The changes in the concentration of hippocampal brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) proteins were evaluated, too. Male Wistar rats were gavaged at different dosages of the Movento (50, 100, 250, 500, 1000, 1250, and 1500 mg/kg) or saline for 7 days (administered every 2 days). We showed that Movento caused 50 and 100% mortality at the dose of 1250 and 1500 mg/kg, respectively. At the dose of 1000 mg/kg, Movento significantly decreased locomotor activity (P < 0.05). These rats also displayed a significant decrease in the number of training trials in the shuttle box and the ability to recognize a novel object compared with the control group (P < 0.01). The BDNF protein level of hippocampus also showed a significant decrease in the Movento (1000 mg/kg) compared with the control group (P < 0.01) while the number of pancellular necrosis pyramidal CA1 cells increased significantly in the Movento group (P < 0.001). We concluded that exposure to Movento can decline sensory, motor, and learning in rats.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ambali SF, Idris SB, Onukak C, Shittu M, Ayo JO (2010) Ameliorative effects of vitamin C on short-term sensorimotor and cognitive changes induced by acute chlorpyrifos exposure in Wistar rats. Toxicol Ind Health 26:547–558
Ananth C, Thameem Dheen S, Gopalakrishnakone P, Kaur C (2001) Domoic acid-induced neuronal damage in the rat hippocampus: changes in apoptosis related genes (Bcl-2, Bax, caspase-3) and microglial response. J Neurosci Res 66:177–190
Antunes M, Biala G (2012) The novel object recognition memory: neurobiology, test procedure, and its modifications. Cogn Process 13:93–110
Back S, Peranen J, Galli E, Pulkkila P, Lonka-Nevalaita L, Tamminen T, Voutilainen MH, Raasmaja A, Saarma M, Mannisto PT, Tuominen RK (2013) Gene therapy with AAV2-CDNF provides functional benefits in a rat model of Parkinson’s disease. Brain Behav 3:75–88
Bekinschtein P, Cammarota M, Medina JH (2014) BDNF and memory processing. Neuropharmacology 76:677–683
Broadbent NJ, Gaskin S, Squire LR, Clark RE (2010) Object recognition memory and the rodent hippocampus. Learn Mem 17:5–11
Choi J-S, Cain CK, LeDoux JE (2010) The role of amygdala nuclei in the expression of auditory signaled two-way active avoidance in rats. Learn Mem 17:139–147
Cohen SJ, Stackman RW Jr (2015) Assessing rodent hippocampal involvement in the novel object recognition task. A review. Behav Brain Res 285:105–117
Elfving B, Plougmann PH, Wegener G (2010) Detection of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) in rat blood and brain preparations using ELISA: pitfalls and solutions. J Neurosci Methods 187:73–77
Faraguna U, Vyazovskiy VV, Nelson AB, Tononi G, Cirelli C (2008) A causal role for brain-derived neurotrophic factor in the homeostatic regulation of sleep. J Neurosci 28:4088–4095
Fullwood NJ (2007) Neural stem cells, acetylcholine and Alzheimer’s disease. Nat Chem Biol 3:435
Greenwood BN, Strong PV, Foley TE, Thompson RS, Fleshner M (2007) Learned helplessness is independent of levels of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in the hippocampus. Elsevier, pp 1193-1208
Guzelian PS (1982) Comparative toxicology of chlordecone (Kepone) in humans and experimental animals. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 22:89–113
Kandel ER, Schwartz JH, Jessell TM, Do B, Jessell MBT, Siegelbaum S, Hudspeth A (2000) Principles of neural science, 4. McGraw-hill, New York
Kramar EA, Babayan AH, Gall CM, Lynch G (2013) Estrogen promotes learning-related plasticity by modifying the synaptic cytoskeleton. Neuroscience 239:3–16
Luine V, Frankfurt M (2013) Interactions between estradiol, BDNF and dendritic spines in promoting memory. Neuroscience 239:34–45
Malcangio M, Lessmann V (2003) A common thread for pain and memory synapses? Brain-derived neurotrophic factor and trkB receptors. Trends Pharmacol Sci 24:116–121
Manber R, Armitage RA (1999) Sex, steroids, and sleep: a review. Sleep 22:540–555
Marcic D, Petronijevic S, Drobnjakovic T, Prijovic M, Peric P, Milenkovic S (2012) The effects of spirotetramat on life history traits and population growth of Tetranychus urticae (Acari: Tetranychidae). Exp Appl Acarol 56:113–122
More SV, Kumar H, Cho D-Y, Yun Y-S, Choi D-K (2016) Toxin-induced experimental models of learning and memory impairment. Int J Mol Sci 17:1447
Paxinos G, Watson C (2007): The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates 44-168
Pesticides A, Authority VM (2009) Evaluation of the new active SPIROTETRAMAT in the product MOVENTO 240 SC INSECTICIDE. APVMA, April, p 9-10
Ramos JM (2000) Long-term spatial memory in rats with hippocampal lesions. Eur J Neurosci 12:3375–3384
Ridley R, Timothy C, Maclean C, Baker H (1995) Conditional learning and memory impairments following neurotoxic lesion of the CA1 field of the hippocampus. Neuroscience 67:263–275
Roozendaal B, McGaugh JL (2011) Memory modulation. Behav Neurosci 125:797
Sarter M, Markowitsch HJ (1985) Involvement of the amygdala in learning and memory: a critical review, with emphasis on anatomical relations. Behav Neurosci 99:342
Scharfman HE, MacLusky NJ (2005) Similarities between actions of estrogen and BDNF in the hippocampus: coincidence or clue? Trends Neurosci 28:79–85
Valenzuela A, Nieto S, Sanhueza J, Morgado N, Rojas I, Zañartu P (2010) Supplementing female rats with DHA-lysophosphatidylcholine increases docosahexaenoic acid and acetylcholine contents in the brain and improves the memory and learning capabilities of the pups. Grasas Aceites 61:16–23
Wang T, Zhao L, Liu M, Xie F, Ma X, Zhao P, Liu Y, Li J, Wang M, Yang Z, Zhang Y (2014) Oral intake of hydrogen-rich water ameliorated chlorpyrifos-induced neurotoxicity in rats. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 280:169–176
Zafra F, Castren E, Thoenen H, Lindholm D (1991) Interplay between glutamate and gamma-aminobutyric acid transmitter systems in the physiological regulation of brain-derived neurotrophic factor and nerve growth factor synthesis in hippocampal neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci 88:10037–10041
Acknowledgments
This study is extracted from the dissertation of Mr. Iman Zangiabadi as a submitted proposal under ethical code number of IR.KMU.REC.1397.255. The authors also appreciate collaboration of KNRC.
Funding
This paper received support from the Kerman Neuroscience Research Center (EC/KNRC/95-43).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zangiabadi, I., Afarinesh, M.R., Shamsara, A. et al. Movento effects on learning and hippocampal brain-derived neurotrophic factor protein of adult male rats. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26, 36615–36622 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06809-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06809-0