Abstract
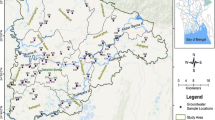
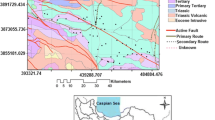
In this study, the quality of groundwater was tested in 95 sampling wells in Shuangliao City. Based on the results, the coefficient of variation method was used to calculate the comprehensively evaluated value F, and the grade of groundwater quality, in accordance with the actual scenario in the study area, was classified according to the results of the evaluation. The spatial distribution of groundwater quality types in the study area was classified. In addition, the influence of human activity on each groundwater subsystem was assessed. Combined with the land use types in the study area, the Circle model was used to extract the land use types in the circular buffer zone with a radius of 500 m, and the Kendall rank correlation test was used to analyze the influence of the land use types on the spatial distribution of groundwater pollution. Based on the coefficient of variation, the groundwater quality standard was divided into four sections considering the actual scenario: ≤ 0.92 (I), 0.92~≤ 1.75 (II), 1.75~≤ 2.40 (III), and > 2.40 (IV). Water from class II was considered the main type for groundwater quality. NO3−, TFe, and Mn were deemed the main indexes of groundwater pollution. Further, land use type was found to have a great influence on the spatial distribution of groundwater pollution; specifically, dry land, paddy field, areas with dense traffic, and residential areas are the main land types that affect the groundwater environment.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed F, Khan MR, Shaheen N, KMU A, Hasan A, Chowdhury IA, Chowdhury R (2018) Anemia and iron deficiency in rural Bangladeshi pregnant women living in areas of high and low iron in groundwater. Nutrition 51-52:46–52
Amiri V, Rezaei M, Sohrabi N (2014) Groundwater quality assessment using entropy weighted Water Quality Index (EWQI) in Lenjanat, Iran. Environ Earth Sci 72:3479–3490
Choi BY, Yun ST, Yu SY, Lee PK, Park SS, Chae GT, Mayer B (2005) Hydrochemistry of urban groundwater in Seoul, South Korea: effects of land-use and pollutant recharge. Environ Geol 48(8):979–990
Dragon K (2016) Impact of human activity on groundwater chemistry (Wielkopolska region, Poland). Baltica 29(2):79–92
Effendi H, Romanto WY (2015) Water quality status of Ciambulawung River, Banten Province, based on pollution index and NSF-WQI. Procedia Environ Sci 24:228–237
Elmahdy SI, Mohamed MM (2016) Land use/land cover change impact on groundwater quantity and quality: a case study of Ajman Emirate, the United Arab Emirates, using remote sensing and GIS. Arab J Geosci 9(19):722
Gorgij AD, Kisi O, Moghaddam AA, Taghipour A (2017) Groundwater quality ranking for drinking purposes, using the entropy method and the spatial autocorrelation index. Environ Earth Sci 76(7):269
He S, Wu J (2019) Relationships of groundwater quality and associated health risks with land use/land cover patterns: a case study in a loess area, northwest China. Hum Ecol Risk Assess 25(1-2):354–373. https://doi.org/10.1080/10807039.2019.1570463
Islam AMT, Ahmed N, Bodrud-Doza M, Chu RH (2017) Characterizing groundwater quality ranks for drinking purposes in Sylhet district, Bangladesh, using entropy method, spatial autocorrelation index, and geostatistics. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 24(2):1–25
Jia Z, Bian J, Wang Y (2018) Impacts of urban land use on the spatial distribution of groundwater pollution, Harbin City, Northeast China. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology 215(2018):19-38
Kaown D, Hyun Y, Bae G-O, Oh CW, Lee K-K (2012) Evaluation of spatio-temporal trends of groundwater quality in different land uses using Kendall test. Geosci J 16(1):65–75
Lambrakis N, Antonakos A, Panagopoulos G (2004) The use of multicomponent statistical analysis in hydrogeological environmental research. Water Res 38(7):1862–1872
Lerner DN, Harris B (2009) The relationship between land use and groundwater resources and quality. Land Use Policy 26(12):S265–S273
Li X, Zuo R, Teng Y, Wang J, Wang B (2015) Development of relative risk model for regional groundwater risk assessment: a case study in the lower Liaohe River Plain, China. PLoS One 10(5):e0128249
Li P, Tian R, Xue C, Wu J (2017) Progress, opportunities, and key fields for groundwater quality research under the impacts of human activities in China with a special focus on western China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24(15):13224–13234
Li Q, Meng XX, Liu YB, Pang LF (2018) Risk assessment of floor water inrush using entropy weight and variation coefficient model. Geotech Geol Eng 37(3):1493–1501
Liu W, Li Q, Zhao J (2018) Application on floor water inrush evaluation based on AHP variation coefficient method with GIS. Geotech Geol Eng 36(5):2799–2808
Lobanov SA (2012) The method of calculating the coefficient of variation of annual runoff. Ecol Syst Devices 10:73–75
Ortmann F, Hannewald K, Bechstedt F (2008) Assessing the impact of changes in landuse and management practices on the diffuse pollution and retention of nitrate in a riparian floodplain. Sci Total Environ 389(1):149–164
Park SS, Kim SO, Yun ST, Chae GT, Yu SY, Kim S, Kim Y (2005) Effects of land use on the spatial distribution of trace metals and volatile organic compounds in urban groundwater, Seoul, Korea. Environ Geol 48(8):1116–1131
Su F, Wu J, He S (2019) Set pair analysis-Markov chain model for groundwater quality assessment and prediction: a case study of Xi’an City, China. Hum Ecol Risk Assess 25(1-2):158–175. https://doi.org/10.1080/10807039.2019.1568860
Sun Y, Sun S, Lu L, Chen G, Wang X (2012) A study on the relationship between the abnormal chemical components of underground water and endemic fluorosis in Shuangliao Area, Jilin Province, China. Adv Mater Res 581-582:1133–1136
Tian R, Wu J (2019) Groundwater quality appraisal by improved set pair analysis with game theory weightage and health risk estimation of contaminants for Xuecha drinking water source in a loess area in Northwest China. Hum Ecol Risk Assess 25(1-2):132–157. https://doi.org/10.1080/10807039.2019.1573035
Wang CL, Zhang MS, Li XB, Wang YN (2017) Early Cretaceous palynological assemblages of the Shuangliao fault depression, Songliao basin and their geological implications. Acta Geologica Sinica (English Edition) 91(06):13–27
Wang D, Wu J, Wang Y, Ji Y (2019) Finding high-quality groundwater resources to reduce the hydatidosis incidence in the Shiqu County of Sichuan Province, China: analysis, assessment, and management. Exposure and Health:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12403-019-00314-y
Wu J, Zhou H, He S, Zhang Y (2019) Comprehensive understanding of groundwater quality for domestic and agricultural purposes in terms of health risks in a coal mine area of the Ordos basin, north of the Chinese Loess Plateau. Environ Earth Sci 78:1–17. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-019-8471-1
Yan B, Xiao C, Liang X, Fang Z (2016) Impacts of urban land use on nitrate contamination in groundwater, Jilin City, Northeast China. Arab J Geosci 9(2):105
Yang W, Shen L, Xiao H, Wang Y (2013) Impact of shallow groundwater quality evolution in Kunming Urban by human activities. Adv Mater Res 788:302–306
Zhao W, Lin J, Wang SF, Liu JL, Chen ZR, Kou WJ (2013) Influence of human activities on groundwater environment based on coefficient variation method. Environ Sci 34(4):1277–1283
Acknowledgments
We thank the anonymous reviewers for their useful comments that helped us improve our manuscript.
Funding
This work is financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41572216), the China Geological Survey Shenyang Geological Survey Center “Changji Economic Circle Geological Environment Survey” project (121201007000150012), the Provincial School Co-construction Project Special–Leading Technology Guide (SXGJQY2017-6), the Jilin Province Key Geological Foundation Project (2014-13), and the Natural Science Funds of Jilin Province (20160520178JH).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, Y., Liang, X. & Xiao, C. Assessing the influence of land use on groundwater pollution based on coefficient of variation weight method: a case study of Shuangliao City. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26, 34964–34976 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06598-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06598-6