Abstract
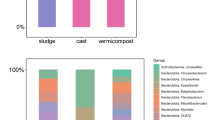
Vermi-composting is considered to be a feasible method for reducing tetracycline resistance genes (TRGs) in the sludge. Nevertheless, the way different gut passages of earthworm might affect the fates of TRGs and whether this process is affected by tetracycline (TC) concentrations need to be further investigated. In this study, we examined the effects of TC concentrations on changes in TRGs and bacterial communities in gut passages of earthworm were determined by using quantitative PCR and Illumina high-throughput sequencing. TRGs and intI1 were mainly reduced in the hindgut under the TC concentrations ranging from 0 to 25 mg/kg, while they were enriched under higher TC stress exposure. Consequently, we suggest the TC limitation of 25 mg/kg in the domestic sludge (DS) for vermi-composting. Although the predominant genera were TC sensitive under TC stress, many bacterial hosts harboring multiple TRGs (especially those in the hindgut) should be paid further attention to. In the foregut, five genera with abundant tetracycline-resistant bacteria (TRB) were specialized taxa. Among these genera, Unclassified_Solirubrobacterales and Pirellulaceae were probably related to the digestion processes. Other unclassified taxa related to the TRGs were probably derived from the DS. Five genera with abundant TRB were shared in the gut passages, and three specialized genera in the hindgut. These genera could spread TRGs and intI1 to the environment. These results suggest that vermi-composting is a feasible approach for TRG control in the DS containing TC concentration that does not exceed 25 mg/kg. Fates of TRGs and intI1 widely differ in the gut passages, showing inevitable connections with bacterial communities.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aira M, Bybee S, Pérez-Losada M, Domínguez J (2015) Feeding on microbiomes: effects of detritivory on the taxonomic and phylogenetic bacterial composition of animal manures. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 91:fiv117
An J, Chen H, Wei S, Gu J (2015) Antibiotic contamination in animal manure, soil, and sewage sludge in Shenyang, northeast China. Environ Earth Sci 74:5077–5086
Berg M, Stenuit B, Ho J, Wang A, Parke C, Knight M, Alvarez-Cohen L, Shapira M (2016) assembly of the Caenorhabditis elegans gut microbiota from diverse soil microbial environments. ISME J 10:1998–2009
Bernard L, Chapuis-Lardy L, Razafimbelo T, Razafindrakoto M, Pablo A-L, Legname E, Poulain J, Brüls T, O’Donohue M, Brauman A, Chotte J-L, Blanchart E (2012) Endogeic earthworms shape bacterial functional communities and affect organic matter mineralization in a tropical soil. ISME J 6:213–222
Bokulich NA, Subramanian S, Faith JJ, Gevers D, Gordon JI, Knight R, Mills DA, Caporaso JG (2013) Quality-filtering vastly improves diversity estimates from Illumina amplicon sequencing. Nat Methods 10:57–59
Cao J, Wang C, Ji D (2016) Improvement of the soil nitrogen content and maize growth by earthworms and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in soils polluted by oxytetracycline. Sci Total Environ 571:926–934
Cao J, Wang C, Dou Z, Liu M, Ji D (2018) Hyphospheric impacts of earthworms and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus on soil bacterial community to promote oxytetracycline degradation. J Hazard Mater 341:346–354
Chao A (1984) Nonparametric estimation of the number of classes in a population. Scand J Stat 11:265–270
Chopra I, Roberts M (2001) Tetracycline antibiotics: mode of action, applications, molecular biology, and epidemiology of bacterial resistance. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 65:232–260
Derrien M, van Hylckama Vlieg JET (2015) Fate, activity, and impact of ingested bacteria within the human gut microbiota. Trends Microbiol 23:354–366
DeSantis TZ, Hugenholtz P, Larsen N, Rojas M, Brodie EL, Keller K, Huber T, Dalevi D, Hu P, Andersen GL (2006) Greengenes, a chimera-checked 16S rRNA gene database and workbench compatible with ARB. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:5069–5072
Ding J, Zhu D, Hong B, Wang HT, Li G, Ma YB, Tang YT, Chen QL (2019) Long-term application of organic fertilization causes the accumulation of antibiotic resistome in earthworm gut microbiota. Environ Int 124:145–152
Drake HL, Horn MA (2007) As the worm turns: the earthworm gut as a transient habitat for soil microbial biomes. Annu Rev Microbiol 61:169–189
Edgar RC (2010) Search and clustering orders of magnitude faster than BLAST. Bioinformatics 26:2460–2461
Fu X, Cui G, Huang K, Chen X, Li F, Zhang X, Li F (2016) Earthworms facilitate the stabilization of pelletized dewatered sludge through shaping microbial biomass and activity and community. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:4522–4530
Gao M, Qi Y, Song W, Zhou Q (2015) Biomarker analysis of combined oxytetracycline and zinc pollution in earthworms (Eisenia fetida). Chemosphere 139:229–234
Gao M, Lv M, Han M, Song W, Wang D (2016) Avoidance behavior of Eisenia fetida in oxytetracycline- and heavymetal-contaminated soils. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 47:119–123
Ghosh S, Ramsden SJ, LaPara TM (2009) The role of anaerobic digestion in controlling the release of tetracycline resistance genes and class 1 integrons from municipal wastewater treatment plants. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 84:791–796
Gihring TM, Green SJ, Schadt CW (2012) Massively parallel rRNA gene sequencing exacerbates the potential for biased community diversity comparisons due to variable library sizes. Environ Microbiol 14:285–290
Girvan MS, Campbell CD, Killham K, Prosser JI, Glover LA (2005) Bacterial diversity promotes community stability and functional resilience after perturbation. Environ Microbiol 7:301–313
Gómez-Brandón M, Aira M, Lores M, Domínguez J (2011) Epigeic earthworms exert a bottleneck effect on microbial communities through gut associated processes. PLoS One 6:e24786
He S, Gall DL, McMahon KD (2007) “Candidatus Accumulibacter” population structure in enhanced biological phosphorus removal sludges as revealed bypolyphosphate kinase genes. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:5865–5874
He X, Xu Y, Chen J, Ling J, Li Y, Huang L, Zhou X, Zheng L, Xie G (2017) Evolution of corresponding resistance genes in the water of fish tanks with multiple stresses of antibiotics and heavy metals. Water Res 124:39–48
Hu Y, Yang X, Qin J, Lu N, Cheng G, Wu N, Pan Y, Li J, Zhu L, Wang X, Meng Z, Zhao F, Liu D, Ma J, Qin N, Xiang C, Xiao Y, Li L, Yang H, Wang J, Yang R, Gao GF, Wang J, Zhu B (2013) Metagenome-wide analysis of antibiotic resistance genes in a large cohort of human gut microbiota. Nat Commun 4:2151
Huang K, Xia H, Wu Y, Chen J, Cui G, Li F, Chen Y, Wu N (2018) Effects of earthworms on the fate of tetracycline and fluoroquinolone resistance genes of sewage sludge during vermicomposting. Bioresour Technol 259:32–39
Ju F, Li B, Ma L, Wang Y, Huang D, Zhang T (2016) Antibiotic resistance genes and human bacterial pathogens: co-occurrence, removal, and enrichment in municipal sewage sludge digesters. Water Res 91:1–10
Juan JJ, Brown GG, Decaëns T, Feijoo A, Lavelle P (2000) Differences in the timing of diapause and patterns of aestivation in tropical earthworms. Pedobiologia 44:677–694
Kang Y, Gu X, Hao Y, Hu J (2016a) Autoclave treatment of pig manure does not reduce the risk of transmission and transfer of tetracycline resistance genes in soil: successive determinations with soil column experiments. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:4551–4560
Kang Y, Hao Y, Shen M, Zhao Q, Li Q, Hu J (2016b) Impacts of supplementing chemical fertilizers with organic fertilizers manufactured using pig manure as a substrate on the spread of tetracycline resistance genes in soil. Ecotox Environ Safe 130:279–288
Khambata SR, Bhat JV (1957) A contribution to the study of the intestinal microflora of Indian earthworms. Arch Mikrobiol 28:69–80
Klindworth A, Pruesse E, Schweer T, Peplies J, Quast C, Horn M, Glöckner FO (2013) Evaluation of general 16S ribosomal RNA gene PCR primers for classical and next-generation sequencing-based diversity studies. Nucleic Acids Res 41:e1
Lepš J, Šmilauer P (2003) Multivariate analysis of ecological data using Canoco 5. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Li D, Qi R, Yang M, Zhang Y, Yu T (2011) Bacterial community characteristics under long-term antibiotic selection pressures. Water Res 45:6063–6073
Li Y, Hu Y, Ai X, Qiu J, Wang X (2015) Acute and sub-acute effects of enrofloxacin on the earthworm species Eisenia fetida in an artificial soil substrate. Eur J Soil Biol 66:19–23
Li Y, Liu Q, Liu F, Zhu P, Zhang L, Zhou X, Sun C, Cheng Y (2016a) Effects of different ratios of sewage sludge and cattle manure on growth and propagation of Eisenia fetida. PLoS One 11:e0156492
Li Y, Tang H, Hu Y, Wang X, Ai X, Tang L, Matthew C, Cavanagh J, Qiu J (2016b) Enrofloxacin at environmentally relevant concentrations enhances uptake and toxicity of cadmium in the earthworm Eisenia fetida infarm soils. J Hazard Mater 308:312–320
Lin Z, Zhen Z, Ren L, Yang J, Luo C, Zhong L, Hu H, Liang Y, Li Y, Zhang D (2018) Effects of two ecological earthworm species on atrazine degradation performance and bacterial community structure in red soil. Chemosphere 196:467–475
Liu D, Lian B, Wu C, Guo P (2018) A comparative study of gut microbiota profiles of earthwormsfed in three different substrates. Symbiosis 74:21–29
Liu K, Sun M, Ye M, Chao H, Zhao Y, Xia B, Jiao W, Feng Y, Zheng X, Liu M, Jiao J, Hu F (2019) Coexistence and association between heavy metals, tetracycline and corresponding resistance genes in vermicomposts originating from different substrates. Environ Pollut 244:28–37
Monroy F, Aira M, Domínguez J (2009) Reduction of total coliform numbers during vermicomposting is caused by short-term direct effects of earthworms on microorganisms and depends on the dose of application of pig slurry. Sci Total Environ 407(20):5411–5416
Mougin C, Cheviron N, Cd R, Hedde M, Hernandez-Raquet G (2013) Earthworms highly increase ciprofloxacin mineralization in soils. Environ Chem Lett 11:127–133
Murray A, Horvath A, Nelson KL (2008) Hybrid life-cycle environmental and cost inventory of sewage sludge treatment and end-use scenarios: a case study from China. Environ Sci Technol 42:3163–3169
Pass DA, Morgan AJ, Read DS, Field D, Weightman AJ, Kille P (2014) The effect of anthropogenic arsenic contamination on the earthworm microbiome. Environ Microbiol 17:1884–1896
Sampedro L, Jeannotte R, Whalen JK (2006) Trophic transfer of fatty acids from gut microbiota to the earthworm Lumbricus terrestris L. Soil Biol Biochem 38:2188–2198
Sengeløv G, Agersø Y, Halling-Sørensen B, Baloda SB, Andersen JS, Jensen LB (2003) Bacterial antibiotic resistance levels in Danish farmland as a result of treatment with pig manure slurry. Environ Int 28:587–595
Shannon CE (1948) A mathematical theory of communication. Bell Labs Tech J 27:379–423
Sinha RK, Bharambe G, Chaudhari U (2008) Sewage treatment by vermifiltration with synchronous treatment of sludge by earthworms: a low-cost sustainable technology over conventional systems with potential for decentralization. Environmentalist 28:409–420
Song K, Harper FW Jr, Hori T, Riya S, Hosomi M, Terada A (2015) Impact of carbon sources on nitrous oxide emission and microbial community structure in an anoxic/oxic activated sludge system. Clean Techn Environ Policy 17:2375–2385
Suleiman H, Rorat A, Grobelak A, Grosser A, Milczarek M, Płytycz B, Kacprzak M, Vandenbulcke F (2017) Determination of the performance of vermicomposting process applied to sewage sludge by monitoring of the compost quality and immune responses in three earthworm species: Eisenia fetida, Eisenia andrei and Dendrobaena veneta. Bioresour Technol 241:103–112
Suthar S, Singh S (2008) Vermicomposting of domestic waste by using two epigeic earthworms (Perionyx excavatus and Perionyx sansibaricus). Int J Environ Sci Te 5:99–106
Tejada M (1992) Use of organic amendment as a strategy for saline soil remediation. Soil Biol Biochem 38:1413–1421
van den Bogaard AE, Stobberingh EE (2000) Epidemiology of resistance to antibiotics: links between animals and humans. Int J Antimicrob Ag 14:327–335
Wang L, Zheng Z, Luo X, Zhang J (2011) Performance and mechanisms of a microbial-earthworm ecofilter for removing organic matter and nitrogen from synthetic domestic wastewater. J Hazard Mater 195:245–253
Wu N, Qiao M, Zhang B, Cheng W-D, Zhu Y-G (2010) Abundance and diversity of tetracycline resistance genes in soils adjacent to representative swine feedlots in China. Environ Sci Technol 44:6933–6939
Wu X, Wei Y, Zheng J, Zhao X, Zhong W (2011) The behavior of tetracyclines and their degradation products during swine manure composting. Bioresour Technol 102:5924–5931
Xia H, Chen J, Chen X, Huang K, Wu Y (2019) Effects of tetracycline residuals on humification, microbial profile and antibiotic resistance genes during vermicomposting of dewatered sludge. Environ Pollut 252:1068–1077
Yang C-W, Tang S-L, Chen L-Y, Chang B-V (2014a) Removal of nonylphenol by earthworms and bacterial community change. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 96:9–17
Yang Y, Li B, Zou S, Fang HHP, Zhang T (2014b) Fate of antibiotic resistance genes in sewage treatment plant revealed by metagenomic approach. Water Res 62:97–106
Yu N, Zhao C, Ma B, Li S, She Z, Guo L, Zhang Q, Zhao Y, Jin C, Gao M (2019) Impact of ampicillin on the nitrogen removal, microbial community and enzymatic activity of activated sludge. Bioresour Technol 272:337–345
Zeng Q, Ding D, Tan X (2018) Pollution status and sources of tetracycline antibiotics in agricultural soil in China: a review. Ecol Environ Sci 27:1774–1782
Zhao L, Wang Y, Yang J, Xing M, Li X, Yi D, Deng D (2010) Earthworm–microorganism interactions: a strategy to stabilize domestic wastewater sludge. Water Res 44:2572–2582
Zhu YG, Johnson TA, Su JQ, Qiao M, Guo GX, Stedtfeld RD, Hashsham SA, Tiedje JM (2013) Diverse and abundant antibiotic resistance genes in Chinese swine farms. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 110:3435–3440
Zhu D, An X-L, Chen Q-L, Yang X-R, Christie P, Ke∥ X, Wu L-H, Zhu Y-G (2018) Antibiotics disturb the microbiome and increase the incidence of resistance genes in the gut of a common soil collembolan. Environ Sci Technol 52:3081–3090
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41977053, 41773103, and 41977112), the National Science-technology Support Plan Projects (2015BAD01B03), the “Qing Lan” Project Foundation of Jiangsu Province, and the 333 Talents Project of Jiangsu Province.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Responsible editor: Chris Lowe
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 16 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y., Yin, Z., Zhao, H. et al. The effects of tetracycline concentrations on tetracycline resistance genes and their bacterial hosts in the gut passages of earthworms (Eisenia fetida) feeding on domestic sludge. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26, 34412–34420 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06495-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06495-y