Abstract
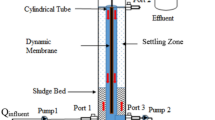
The aim of this study was to develop a laboratory-scale anaerobic dynamic membrane bioreactor (AnDMBR) for the treatment of high-strength synthetic and real cheese whey wastewater. We determined the appropriate pore size for a convenient type of support material (nylon mesh) to optimize cake layer formation. The performance of the AnDMBRs was measured in terms of chemical oxygen demand (COD) and solids removal efficiencies. During high-strength synthetic wastewater treatment, the 70-μm pore size AnDMBR achieved COD removal efficiencies of 78% and 96% with COD loading rates of 4.03 and 2.34 kg m−3 day−1, respectively, while the 10-μm pore size AnDMBR achieved 66% and 92% COD removal efficiencies at COD loading rates of 5.02 and 3.16 kg m−3 day−1. The 10 μm pore size AnDMBR was operated in two periods: first period and second period (before and after physical cleaning) during high-strength synthetic wastewater treatment. The 10-μm pore size AnDMBR removed 83% and 88% of suspended solids during period 1 and period 2, respectively. Furthermore, using a pore size of 10 μm retained 72% of solids (973 mg L−1) in the reactor outlet. The 10-μm pore size AnDMBR performed better than the 70-μm pore size AnDMBR in terms of cake layer formation. The 10-μm pore size AnDMBR was used to treat real cheese whey wastewater, resulting in COD removal efficiencies ranging from 59% (4.32 kg m−3 day−1) to 97% (5.22 kg m−3 day−1). In addition, 85% of suspended solids were removed from real cheese whey wastewater after treatment. The results show that dynamic membrane technology using a pore size of 10 μm can be used to treat real industrial wastewater.








Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AnSBR:
-
Anaerobic sequencing batch reactor
- ASDFA:
-
Anaerobic semicontinuous digester with flocculant addition
- ARBC:
-
Anaerobic rotating biological contact reactor
- AUFFR:
-
Anaerobic upflow fixed film reactor
- AUFFLR:
-
Anaerobic upflow fixed film loop reactor
- CP:
-
Contact process
- DUHR:
-
Downflow-upflow hybrid reactor
- L CH4 g−1 CODremoved :
-
Methane yield per gram of COD removed
- SSeff:
-
Effluent suspended solid
- TSMAMD:
-
Two-stage mixed anaerobic membrane digester
- TSUAD:
-
Two-stage unmixed anaerobic digester
- UAF:
-
Upflow anaerobic filter process
References
Alibardi L, Cossu R, Saleem M, Spagni A (2014) Development and permeability of a dynamic membrane for anaerobic wastewater treatment. Bioresour Technol 161:236–244. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2014.03.045
Alibardi L, Bernava N, Cossu R, Spagni A (2016) Anaerobic dynamic membrane bioreactor for wastewater treatment at ambient temperature. Chem Eng J 284:130–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2015.08.111
An Y, Wang Z, Wu Z, Yang D, Zhou Q (2009) Characterization of membrane foulants in an anaerobic non-woven fabric membrane bioreactor for municipal wastewater treatment. Chem Eng J 155:709–715. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2009.09.003
Andrade LH, Motta GE, Amaral MCS (2013) Treatment of dairy wastewater with a membrane bioreactor. Braz J Chem Eng 30:759–770. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0104-66322013000400008
APHA (2005) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. American Public Health Association/American Water Works Association/Water Environment Federation, Washington DC
Barford JP, Cail RG, Callander IJ, Floyd EJ (1986) Anaerobic digestion of highstrength cheese whey utilizing semicontinuous digesters and chemical flocculant addition. Biotechnol Bioeng 28:1601–1607. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.260281102
Bayrakdar A, Molaey R, Sürmeli RÖ, Sahinkaya E, Çalli B (2017) Biogas production from chicken manure: co-digestion with spent poppy straw. Int Biodeterior Biodegradation 119:205–210. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2016.10.058
Carvalho F, Prazeres AR, Rivas J (2013) Cheese whey wastewater: characterization and treatment. Sci Total Environ 445–446:385–396. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2012.12.038
Casu S, Crispino NA, Farina R, Mattioli D, Ferraris M, Spagni A (2012) Wastewater treatment in submerged anaerobic membrane bioreactor. J Environ Sci Health A Tox Hazard Subst Environ Eng 47:204–209. https://doi.org/10.1080/10934529.2012.640562
Chen C, Guo W, Ngo HH, Lee DJ, Tung KL, Jin P, Wang J, Wu Y (2016) Challenges in biogas production from anaerobic membrane bioreactors. Renew Energy 98:120–134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2016.03.095
Dereli RK, Loverdou L, van der Zee FP, van Lier JB (2015) A systematic study on the effect of substrate acidification degree and acidogenic biomass on sludge filterability. Water Res 82:94–103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2016.03.095
Dereli RK, van der Zee FP, Ozturk İ, van Lier JB (2019) Treatment of cheese whey by a cross-flow anaerobic membrane bioreactor: biological and filtration performance. Environ Res 168:109–117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2018.09.021
Diamantis VI, Kapagiannidis AG, Ntougias S, Tataki V, Melidis P, Aivasidis A (2014) Two-stage CSTR–UASB digestion enables superior and alkali addition-free cheese whey treatment. Biochem Eng J 84:45–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bej.2014.01.001
Ergüder TH, Tezel U, Güven E, Demirer GN (2001) Anaerobic biotransformation and methane generation potential of cheese whey in batch and UASB reactors. Waste Manag 21:643–650. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0956-053X(00)00114-8
Ersahin ME, Ozgun H, Dereli RK, Ozturk I, Roest K, van Lier JB (2012) A review on dynamic membrane filtration: materials, applications and future perspectives. Bioresour Technol 122:196–206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2012.03.086
Ersahin ME, Ozgun H, Tao Y, van Lier JB (2014) Applicability of dynamic membrane technology in anaerobic membrane bioreactors. Water Res 48:420–429. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2013.09.054
Ersahin ME, Tao Y, Ozgun H, Spanjers H, van Lier JB (2016a) Characteristics and role of dynamic membrane layer in anaerobic membrane bioreactors. Biotechnol Bioeng 113:761–771. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.25841
Ersahin ME, Gimenez JB, Ozgun H, Tao Y, Spanjers H, van Lier JB (2016b) Gaslift anaerobic dynamic membrane bioreactors for high strength synthetic wastewater treatment: effect of biogas sparging velocity and HRT on treatment performance. Chem Eng J 305:46–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.02.003
Ersahin ME, Tao Y, Ozgun H, Gimenez JB, Spanjers H, van Lier JB (2017) Impact of anaerobic dynamic membrane bioreactor configuration on treatment and filterability performance. Jo Membr Sci 526:387–394. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2016.12.057
Fernandez C, Cuetos MJ, Martínez EJ, Gomez X (2015) Thermophilic anaerobic digestion of cheese whey: coupling H2 and CH4 production. Biomass Bioenergy 81:55–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biombioe.2015.05.024
Ferraris M, Innella C, Spagni A (2009) Start-up of a pilot-scale membrane bioreactor to treat municipal wastewater. Desalination 237:190–213. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2007.12.032
Gannoun H, Khelifi E, Bouallagui H, Touhami Y, Hamdi M (2008) Ecological clarification of cheese whey prior to anaerobic digestion in upflow anaerobic filter. Bioresour Technol 99:6105–6111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2007.12.037
Ghaly AE (1996) A comparative study of anaerobic digestion of acid cheese whey and dairy manure in a two-stage reactor. Bioresour Technol 58:61–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0960-8524(96)00105-8
Hall ER, Berube PR (2006) Membrane bioreactors for anaerobic treatment of wastewaters: phase II. The International Water Association Publishing, London
Hu Y, Wang CX, Ngo HH, Sun Q, Yang Y (2018a) Anaerobic dynamic membrane bioreactor (AnDMBR) for wastewater treatment: a review. Bioresour Technol 247:1107–1118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.09.101
Hu Y, Yang Y, Yu S, Wang X, Tang J (2018b) Psychrophilic anaerobic dynamic membrane bioreactor for domestic wastewater treatment: effects of organic loading and sludge recycling. Bioresour Technol 270:62–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2018.08.128
Hwang SH, Hansen CL, Stevens DK (1992) Biokinetics of an upflow anaerobic sludge blanket reactor treating whey permeate. Bioresour Technol 41:223–230. https://doi.org/10.1016/0960-8524(92)90006-J
Jeison D, van Lier JB (2008) Feasibility of thermophilic anaerobic submerged membrane bioreactors (AnSMBR) for wastewater treatment. Desalination 231:227–235. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2007.11.048
Judd S (2006) The MBR book: principles and application of membrane bioreactors in water and wastewater treatment. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Katsoni A, Mantzavinos D, Diamadopoulos E (2014) Coupling digestion in a pilot-scale UASB reactor and electrochemical oxidation over BDD anode to treat diluted cheese whey. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21:12170–12181. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-2960-2
Lee J, Ahn WY, Lee CH (2001) Comparison of the filtration characteristics between attached and suspended growth microorganisms in submerged membrane bioreactor. Water Res 35:2435–2445. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1354(00)00524-8
Li W W, Sheng G P, Wang Y K, Liu X W, Xu J, Yu H Q (2011) Filtration behaviors and biocake formation mechanism of mesh filters used in membrane bioreactors.Sep. Purif. Technol 81:472–479. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2011.08.026
Li N, Hu Y, Lu Y, Zeng RJ, Sheng G (2016) In-situ biogas sparging enhances the performance of an anaerobic membrane bioreactor (AnMBR) with mesh filter in low-strength wastewater treatment. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 100:6081–6089. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-016-7455-2
Lin HJ, Xie K, Mahendran B, Bagley DM, Leung KT, Liss SN, Liao BQ (2010) Factors affecting sludge cake formation in a submerged anaerobic membrane bioreactor. J Membrane Sci 361:126–134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2010.05.062
Lin H, Peng W, Zhang M, Chen J, Hong H, Zhang Y (2013) A review on anaerobic membrane bioreactors: applications, membrane fouling and future perspectives. Desalination 314:169–188. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2013.01.019
Loderer C, Gahleitner B, Steinbacher K, Stelzer C, Fuchs W (2013) Dynamic filtration—a novel approach for critical flux determination using different textiles. Sep Purif Technol 120:410–414. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2013.10.013
Malaspina F, Cellamare L, Stante L, Tilche A (1996) Anaerobic treatment of cheese whey with a downflow-upflow hybrid reactor. Bioresour Technol 55:131–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/0960-8524(95)00187-5
Martin-Garcia I, Monsalvo V, Pidou M, Le-Clech P, Judd SJ, McAdam EJ, Jefferson B (2011) Impact of membrane configuration on fouling in anaerobic membrane bioreactors. J Membr Sci 382:41–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2011.07.042
McHugh S, Collins G, O’Flaherty V (2006) Long-term, high-rate anaerobic biological treatment of whey wastewaters at psychrophilic temperatures. Bioresour Technol 97:1669–1678. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2005.07.020
Meng F, Zhang H, Yang F, Liu L (2007) Characterization of cake layer in submerged membrane bioreactor. Environ Sci Technol 41:4065–4070. https://doi.org/10.1021/es062208b
Mockaitis G, Ratusznei SM, Rodrigues JAD, Zaiat M, Foresti E (2006) Anaerobic whey treatment by a stirred sequencing batch reactor (ASBR): effects of organic loading and supplemented alkalinity. J Environ Manag 79:198–206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2005.07.001
Ozgun H, Dereli RK, Ersahin ME, Kinaci C, Spanjers H, van Lier JB (2013) A review of anaerobic membrane bioreactors for municipal wastewater treatment: integration options, limitations and expectations. Sep Purif Technol 118:89–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2013.06.036
Patel C, Madamwar D (1997) Biomethanization of salty cheese whey using anaerobic rotating biological contact reactor. J Ferment Bioeng 83:502–504. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0922-338X(97)83012-7
Patel P, Desai M, Madamwar D (1995) Biomethanation of cheese whey using anaerobic upflow fixed film reactor. J Ferment Bioeng 79:398–399. https://doi.org/10.1016/0922-338X(95)94006-D
Polprasert C, Koottatep T (2017) Organic waste recycling: technology, management and sustainability. IWA Publishing 4th edn. https://doi.org/10.2166/9781780408217_FPxiv. Accessed June 2017
Quek PJ, Yeap TS, Ng HY (2017) Applicability of upflow anaerobic sludge blanket and dynamic membrane-coupled process for the treatment of municipal wastewater. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 101:6531–6540. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-017-8358-6
Saddoud A, Hassairi I, Sayadi S (2007) Anaerobic membrane reactor with phase separation for the treatment of cheese whey. Bioresour Technol 98:2102–2108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2006.08.013
Saleem M, Alibardi L, Lavagnolo MC, Cossu R, Spagni A (2016) Effect of filtration flux on the development and operation of a dynamic membrane for anaerobic wastewater treatment. J Environ Manag 180:459–465. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2016.05.054
Saleem M, Lavagnolo MC, Spagni A (2018) Biological hydrogen production via dark fermentation by using a sidestream dynamic membrane bioreactor: effect of substrate concentration. Chem Eng J 349:719–727. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.05.129
Seghezzo L, Zeeman G, van Lier JB, Hamelers HVM, Lettinga G (1998) A review: the anaerobic treatment of sewage in UASB and EGSB reactors. Bioresour Technol 65:175–190. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0960-8524(98)00046-7
Siso MIG (1996) The biotechnological utilization of cheese whey: a review. Bioresour Technol 57:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/0960-8524(96)00036-3
Skouteris G, Hermosilla D, Lopez P, Negro C, Blanco A (2012) Anaerobic membrane bioreactors for wastewater treatment: a review. Chem Eng J 198–199:138–148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2012.05.070
Smith AL, Stadler LB, Love NG, Skerlos SJ, Raskin L (2012) Perspectives on anaerobic membrane bioreactor treatment of domestic wastewater: a critical review. Bioresour Technol 122:149–159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2012.04.055
Smith AL, Skerlos SJ, Raskin L (2013) Psychrophilic anaerobic membrane bioreactor treatment of domestic wastewater. Water Res 47(4):1655–1665. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2012.12.028
Spagni A, Casu S, Crispino NA, Farina R, Mattioli D (2010) Filterability in a submerged anaerobic membrane bioreactor. Desalination 250:787–792. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2008.11.042
Sun F, Zhang N, Li F, Wang X, Zhang J, Song L, Liang S (2018) Dynamic analysis of self-forming dynamic membrane (SFDM) filtration in submerged anaerobic bioreactor: performance, characteristic, and mechanism. Bioresour Technol 270:383–390. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2018.09.003
Vourch M, Balannec B, Chaufer B, Dorange G (2008) Treatment of dairy industry wastewater by reverse osmosis for water reuse. Desalination 219:190–202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2007.05.013
Wang YK, Sheng GP, Ni BJ, Li WW, Zeng RJ, Wang YQ, Shi BJ, Yu HQ (2013) Simultaneous carbon and nitrogen removals in membrane bioreactor with mesh filter: an experimental and modelling approach. Chem Eng Sci 95:78–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ces.2013.03.025
Wang L, Liu H, Zhang W, Yu T, Jin Q, Fu B, Liu H (2018) Recovery of organic matters in wastewater by self-forming dynamic membrane bioreactor: performance and membrane fouling. Chemosphere 203:123–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.03.171
Wildenauer FX, Winter J (1985) Anaerobic digestion of high-strength acidic whey in a pH-controlled up-flow fixed film loop reactor. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 22(5):367–372. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00582422
Wu B, An Y, Li Y, Wong FS (2009) Effect of adsorption/coagulation on membrane fouling in microfiltration process post-treating anaerobic digestion effluent. Desalination 242:183–192. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2008.04.005
Xie Z, Wang Z, Wang Q, Zhu C (2014) An anaerobic dynamic membrane bioreactor (AnDMBR) for landfill leachate treatment: performance and microbial community identification. Bioresour Technol 14:29–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2014.03.014
Xiong J, Fu D, Singh RP (2014) Self-adaptive dynamic membrane module with a high flux and stable operation for the municipal wastewater treatment. J Membr Sci 471:308–318. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2014.08.001
Yan JQ, Lo KV, Liao PH (1989) Anaerobic digestion of cheese whey using up-flow anaerobic sludge blanket reactor. Biol Waste 27:289–305. https://doi.org/10.1016/0269-7483(89)90010-4
Yan JQ, Lo KV, Liao PH (1990) Anaerobic digestion of cheese whey using an upflow anaerobic sludge blanket reactor: III. Sludge and substrate profiles. Biomass 21:257–271. https://doi.org/10.1016/0144-4565(90)90076-V
Yesil H, Tugtas AE, Bayrakdar A, Calli B (2014) Anaerobic fermentation of organic solid wastes: volatile fatty acid production and separation. Water Sci Technol 69:2132–2138. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2014.132
Yurtsever A, Sahinkaya E, Aktas Ö, Uçar D, Çınar Ö, Wang Z (2015) Performances of anaerobic and aerobic membrane bioreactors for the treatment of synthetic textile wastewater. Bioresour Technol 192:564–573. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2015.06.024
Zhang X, Wang Z, Wu Z, Lu F, Tong J, Zang L (2010) Formation of dynamic membrane in an anaerobic membrane bioreactor for municipal wastewater treatment. Chem Eng J 165:175–183. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2010.09.013
Zhang X, Wang Z, Wu Z, Lu F, Wei T, Lu F, Tong J, Mai S (2011) Membrane fouling in an anaerobic dynamic membrane bioreactor (AnDMBR) for municipal wastewater treatment: characteristics of membrane foulants and bulk sludge. Process Biochem 46:1538–1544. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2011.04.002
Zhang Y, Zhao Y, Chu H, Dong B, Zhou X (2014) Characteristics of dynamic membrane filtration: structure, operation mechanisms, and cost analysis. Chin Sci Bull 59(3):247–260. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-013-0048-x
Funding
The authors gratefully recognize the financial support from The Scientific and Technological Research Council of Turkey (TUBİTAK).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Ta Yeong Wu
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Paçal, M., Semerci, N. & Çallı, B. Treatment of synthetic wastewater and cheese whey by the anaerobic dynamic membrane bioreactor. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26, 32942–32956 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06397-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06397-z