Abstract
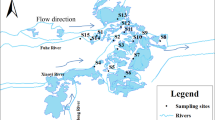
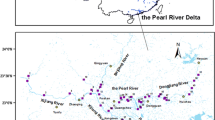
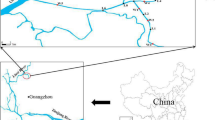
Neutral polyfluoroalkyl and perfluoroalkyl substances (nPFASs) were detected in the surface water and sediment from the Haihe River (HR) and Dagu Drainage Canal (DDC), Tianjin, China. N-methyl perfluorooctane sulfonamide ethanol (MeFOSE) and N-ethyl perfluorooctane sulfonamide ethanol (EtFOSE) were the predominant nPFASs in surface water and sediment, which was different from the composition in air. The concentrations of ΣnPFASs in water from the HR (1.88–8.21 ng/L) were lower than those from the DDC (3.72–11.32 ng/L). Concentrations of ΣnPFASs were higher in the middle of the HR in the Dongli District due to industrial activity, whereas at lower reaches of the DDC, high ΣnPFAS concentrations might be due to effluent from wastewater treatment plants (WWTPs). The detection frequency in sediment (13.5%) was less than that in water (83%). The concentrations in sediment from the DDC (below limit of qualification (LOQ) to 5.58 ng/g) were higher than those from the HR (below LOQ to 2.46 ng/g). The distribution coefficient (log KD) between water and sediment was calculated, and they were highly related to the compound structures. The contribution of nPFASs to nPFASs+PFAAs was up to 52% in sediment in the DDC, suggesting the importance of nPFASs in aquatic systems.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahrens L, Yamashita N, Yeung LW, Taniyasu S, Horii Y, Lam PK, Ebinghaus R (2009) Partitioning behavior of per- and polyfluoroalkyl compounds between pore water and sediment in two sediment cores from Tokyo Bay, Japan. Environ Sci Technol 43:6969–6975
Ahrens L, Taniyasu S, Yeung LW, Yamashita N, Lam PK, Ebinghaus R (2010) Distribution of polyfluoroalkyl compounds in water, suspended particulate matter and sediment from Tokyo Bay, Japan. Chemosphere 79:266–272
Ahrens L, Gashaw H, Sjöholm M, Gebrehiwot SG, Getahun A, Derbe E, Bishop K, Åkerblom S (2016) Poly- and perfluoroalkylated substances (PFASs) in water, sediment and fish muscle tissue from Lake Tana, Ethiopia and implications for human exposure. Chemosphere 165:352–357
Barber JL, Berger U, Chaemfa C, Huber S, Jahnke A, Temme C, Jones KC (2007) Analysis of per- and polyfluorinated alkyl substances in air samples from Northwest Europe. J Environ Monit 9:530–541
Becker AM, Gerstmann S, Frank H (2008) Perfluorooctanoic acid and perfluorooctane sulfonate in the sediment of the Roter Main river, Bayreuth, Germany. Environ Pollut 156:818–820
Benskin JP, Muir DC, Scott BF, Spencer C, De Silva AO, Kylin H, Martin JW, Morris A, Lohmann R, Tomy G (2012) Perfluoroalkyl acids in the Atlantic and Canadian Arctic Oceans. Environ Sci Technol 46:5815–5823
Bossi R, Vorkamp K, Skov H (2016) Concentrations of organochlorine pesticides, polybrominated diphenyl ethers and perfluorinated compounds in the atmosphere of North Greenland. Environ Pollut 217:4–10
David AE, Jonathan WM, Amila ODS, Scott AM, Michael DH, Wallington TJ (2004) Degradation of fluorotelomer alcohols: a likely atmospheric source of perfluorinated carboxylic acids. Environ Sci Technol 38:3316
Dinglasan-Panlilio MJA, Mabury SA (2006) Significant residual fluorinated alcohols present in various fluorinated materials. Environ Sci Technol 40:1447–1453
Fiedler S, Pfister G, Schramm KW (2010) Poly- and perfluorinated compounds in household consumer products. Toxicol Environl Chem Rev 92:1801–1811
Higgins CP, Luthy RG (2006) Sorption of perfluorinated surfactants on sediments. Environ Sci Technol 40:7251–7256
Hoover GM, Chislock MF, Tornabene BJ, Guffey SC, Choi YJ, Perre CD, Hoverman JT, Lee LS, Sepúlveda MS (2017) Uptake and depuration of four per/polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) in northern leopard frog rana pipiens tadpoles. Environl Sci Technol lett 4:399–403
Jahnke A, Ahrens L, Ebinghaus R, Berger U, Barber JL, Temme C (2007) An improved method for the analysis of volatile polyfluorinated alkyl substances in environmental air samples. Anal Bioanal Chem 387:965–975
Keränen J, Ahkola H, Knuutinen J, Herve S, Reinikainen M, Koistinen J (2013) Formation of PFOA from 8:2 FTOH in closed-bottle experiments with brackish water. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 20:8001–8012
Krafft MP, Riess JG (2015) Per- and polyfluorinated substances (PFASs): environmental challenges. Curr Opin Colloid Interface Sci 20:192–212
Li J, Del Vento S, Schuster J, Zhang G, Chakraborty P, Kobara Y, Jones KC (2011a) Perfluorinated Compounds in the Asian Atmosphere. Environmental Sci Technol 45:7241-7248.
Li FS, Sun HW, Hao ZN, He N, Zhao LJ, Zhang T, Sun TH (2011b) Perfluorinated compounds in Haihe River and Dagu Drainage Canal in Tianjin, China. Chemosphere 84:265–271
Li Y, Oliver DP, Kookana RS (2018) A critical analysis of published data to discern the role of soil and sediment properties in determining sorption of per and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs). Sci Total Environ 628:110–120
Liu J, Lee LS (2007) Effect of fluorotelomer alcohol chain length on aqueous solubility and sorption by soils. Environ Sci Technol 41:5357–5362
Lu ZB, Lu R, Zheng HY, Yan J, Song LN, Wang J, Yang HZ, Cai MH (2018) Risk exposure assessment of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) in drinking water and atmosphere in central eastern China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:1–1
Mahmoud MA, Kärrman A, Oono S, Harada KH, Koizumi A (2009) Polyfluorinated telomeres in precipitation and surface water in an urban area of Japan. Chemosphere 74:467–472
Peng H, Wei Q, Wan Y, Giesy JP, Li L, Hu J (2010) Tissue distribution and maternal transfer of poly- and perfluorinated compounds in Chinese sturgeon (Acipenser sinensis): implications for reproductive risk. Environ Sci Technol 44:1868–1874
Piekarz AM, Primbs T, Field JA, Barofsky DF, Simonich S (2007) Semivolatile fluorinated organic compounds in Asian and western U.S. air masses. Environ Sci Technol 41:8248–8255
Prevedouros K, Cousins IT, Buck RC, Korzeniowski SH (2006) Sources, fate and transport of perfluorocarboxylates. Environ Sci Technol 40:32–44
Scheringer M, Trier X, Cousins IT, De VP, Fletcher T, Wang Z, Webster TF (2014) Helsingør statement on poly- and perfluorinated alkyl substances (PFASs). Chemosphere 114:337–339
Schultz MM, Barofsky DF, Field JA (2003) Fluorinated alkyl surfactants. Environ Eng Sci 20:487–501
Stock NL, Lau FK, Ellis DA, Martin JW, Muir DC, Mabury SA (2004) Polyfluorinated telomer alcohols and sulfonamides in the North American troposphere. Environ Sci Technol 38:991–996
Sun H, Zhang X, Wang L, Zhang T, Li F, He N, Alder AC (2012) Perfluoroalkyl compounds in municipal WWTPs in Tianjin, China--concentrations, distribution and mass flow. Environ Sci Pollut Res 19:1405–1415
Sun R, Wu M, Tang L, Li J, Qian Z, Han T, Xu G (2018) Perfluorinated compounds in surface waters of Shanghai, China: source analysis and risk assessment. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 149:88–95
Tianjin Environmental Protection Bureau. 2001. Environmental quality report of Tianjin in 1996–2000 Tianjin, China.
Tianjin Binhai New Area Government. (2016) In 2016, the total value of the Binhai New Area was broken by trillions, http://bhxq.mofcom.gov.cn/article/dongtai/201702/20170202519704.shtml
UNEP. Stockholm convention on persistent organic pollutants, http://chm.pops.int/.
Wang N, Szostek B, Buck RC, Folsom PW, Sulecki LM, Gannon JT (2009) 8-2 Fluorotelomer alcohol aerobic soil biodegradation: pathways, metabolites, and metabolite yields. Chemosphere 75:1089–1096
Wang Z, Xie Z, Möller A, Mi W, Wolschke H, Ebinghaus R (2015) Estimating dry deposition and gas/particle partition coefficients of neutral poly-/perfluoroalkyl substances in northern German coast. Environ Pollut 202:120–125
Wang Z, Cousins IT, Scheringer M, Buck RC, Hungerbühler K (2014) Global emission inventories for C4-C14 perfluoroalkyl carboxylic acid (PFCA) homologues from 1951 to 2030, part II: the remaining pieces of the puzzle. Environ Int 69:166–176
Washington JW, Jenkins TM (2015) Abiotic hydrolysis of fluorotelomer-based polymers as a source of perfluorocarboxylates at the global scale. Environ Sci Technol 49:14129–14135
Xie Z, Zhao Z, Möller A et al (2013) Neutral poly- and perfluoroalkyl substances in air and seawater of the north sea. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20(11):7988–8000
Yao Y, Chang S, Zhao YY, Tang JH, Sun HW, Xie ZY (2017) Per- and poly-fluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) in the urban, industrial, and background atmosphere of Northeastern China coast around the Bohai Sea: occurrence, partitioning, and seasonal variation. Atmos Environ 167:150–158
Yeung LW, Dassuncao C, Mabury SA, Sunderland EM, Zhang X, Lohmann R (2017) Vertical profiles, sources and transport of PFASs in the Arctic Ocean. Environ Sci Technol 51:6735–6744
Zushi Y, Ye F, Motegi M, Nojiri K, Hosono S, Suzuki T, Kosugi Y, Yaguchi K, Masunaga S (2011) Spatially detailed survey on pollution by multiple perfluorinated compounds in the Tokyo Bay basin of Japan. Environ Sci Technol 45:2887–2893
Funding
This study was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 41603101 and No.41573097).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Roland Peter Kallenborn
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hua, X., Luo, J., Zhao, Z. et al. Neutral polyfluoroalkyl and perfluoroalkyl substances in surface water and sediment from the Haihe River and Dagu Drainage Canal deserve more attention. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26, 32911–32918 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06331-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06331-3