Abstract
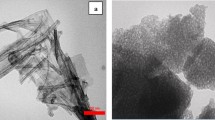
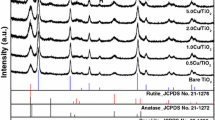
Cu/N-codoped TiO2 nanoparticles were prepared by the modified sol-gel method, to study its efficiency for the removing of polyaromatic hydrocarbon (phenanthrene) from an aqueous solution. Urea and copper sulfate pentahydrate were used as sources of doping element for Cu/N-codoped TiO2, respectively. The characterizations of the nanoparticles were done by X-ray diffraction (XRD), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), and UV-vis diffuse reflectance spectra. XRD revealed that all the nanoparticles were indexed to the anatase phase structure, with crystallite size range from 11 to 30 nm, which decreased with the doping of copper and nitrogen. The photocatalytic activities of Cu/N-codoped TiO2 showed the highest activities than other TiO2 nanoparticles (TiO2 and N-doped TiO2). The photodegradation efficiency of Cu/N-codoped TiO2 on phenanthrene under visible light irradiation was slightly higher (96%) comparing to UV light irradiation (94%). Cu/N-codoped TiO2 was found to be very efficient and economical for phenanthrene removal, because the smallest amount of Cu/N-codoped TiO2 exhibited the best removal efficiency on phenanthrene.







Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
28 October 2019
The article “Cu/N-codoped TiO<Subscript>2</Subscript> prepared by the sol-gel method for phenanthrene removal under visible light irradiation,” written by Zhenhua Zhao, Abduelrahman Adam Omer, Zhirui Qin, Salaheldein Osman, Liling Xia, and Rajendra Prasad Singh
References
Agrawal N, Verma P, Shahi SK (2018) Degradation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons ( phenanthrene and pyrene ) by the ligninolytic fungi Ganoderma lucidum isolated from the hardwood stump. Bioresour Bioprocess. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40643-018-0197-5
Ananpattarachai J, Kajitvichyanukul P, Seraphin S (2009) Visible light absorption ability and photocatalytic oxidation activity of various interstitial N-doped TiO2 prepared from different nitrogen dopants. J Hazard Mater 168:253–261. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.02.036
Asahi R, Morikawa T, Ohwaki T et al (2001) Visible-light photocatalysis in nitrogen-doped titanium oxides. Science 293:269–271. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1061051
Asahi R, Morikawa T, Irie H, Ohwaki T (2014) Nitrogen-doped titanium dioxide as visible-light-sensitive photocatalyst : designs, developments, and prospects
Behnajady MA, Eskandarloo H (2013) Silver and copper co-impregnated onto TiO2 -P25 nanoparticles and its photocatalytic activity. Chem Eng J 228:1207–1213. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2013.04.110
Bellardita M, Addamo M, Di Paola A et al (2009) Preparation of N-doped TiO2: characterization and photocatalytic performance under UV and visible light. Phys Chem Chem Phys 11:4084–4093. https://doi.org/10.1039/b816708g
Binas V, Stefanopoulos V, Kiriakidis G, Papagiannakopoulos P (2018) Photocatalytic oxidation of gaseous benzene, toluene and xylene under UV and visible irradiation over Mn-doped TiO2 nanoparticles. J Mater. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmat.2018.12.003
Bokhimi X, Morales A, Novaro O et al (1997) Effect of copper precursor on the stabilization of titania phases, and the optical properties of Cu/TiO2 prepared with the sol−gel technique. Chem Mater 9:2616–2620. https://doi.org/10.1021/cm970279r
Caratto V, Setti L, Campodonico S et al (2012) Synthesis and characterization of nitrogen-doped TiO2 nanoparticles prepared by sol–gel method. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 63:16–22. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-012-2756-0
Chen Y, Zhang S, Yu Y et al (2008) Synthesis, characterization, and photocatalytic activity of N-doped TiO2 nanotubes. J Dispers Sci Technol 29:245–249. https://doi.org/10.1080/01932690701707456
Chen X, Sun H, Zhang J et al (2019) Cationic S-doped TiO2/SiO2 visible-light photocatalyst synthesized by co-hydrolysis method and its application for organic degradation. J Mol Liq 273:50–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2018.10.021
Chong MN, Jin B, Chow CWK, Saint C (2010) Recent developments in photocatalytic water treatment technology: A review. Water Res 44:2997–3027. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2010.02.039
Dehghani M, Rashidizadeh A, Ghafuri H, Rabbani M (2018) Synthesis and characterization of magnetic nanocomposite Fe3O4/TiO2/Ag,Cu and investigation of photocatalytic activity by degradation of Rhodamine B (RhB) under visible light irradiation. Opt - Int J Light Electron Opt. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2018.10.180
Dong H, Zeng G, Tang L et al (2015) An overview on limitations of TiO2 based particles for photocatalytic degradation of organic pollutants and the corresponding countermeasures. Water Res 79:128–146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2015.04.038
Dung NT, Van Khoa N, Herrmann J-M (2005) ref 33: Photocatalytic degradation of reactive dye RED-3BA in aqueous TiO2 suspension under UV-visible light. Int J Photoenergy 7:11–15. https://doi.org/10.1155/S1110662X05000024
Eesa MT, Juda AM, Ahmed LM (2016) Kinetic and thermodynamic study of the photocatalytic decolourization of light green SF yellowish ( Acid Green 5 ) dye using commercial bulk titania and commercial nanotitania. Int J Sci Res 5:1495–1500. https://doi.org/10.21275/ART20163016
Heena Khan S, R S, Pathak B, Fulekar MH (2015) Photocatalytic degradation of organophosphate pesticides (Chlorpyrifos) using synthesized zinc oxide nanoparticle by membrane filtration reactor under UV irradiation. Front Nanosci Nanotechnol 1:23–27. https://doi.org/10.15761/FNN.1000105
Jagadale TC, Takale SP, Sonawane RS et al (2008) N-doped TiO2 nanoparticle based visible light photocatalyst by modified peroxide sol–gel method N-doped TiO2 nanoparticle based visible light photocatalyst by modified peroxide sol–gel method. J Phys Chem C 112:14595–14602. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp803567f
Jaiswal R, Bharambe J, Patel N et al (2015) Copper and Nitrogen co-doped TiO2 photocatalyst with enhanced optical absorption and catalytic activity. Appl Catal B Environ 168–169:333–341. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2014.12.053
Karafas ES, Romanias MN, Stefanopoulos V, Binas V (2019) Journal of Photochemistry & Photobiology A : Chemistry E ff ect of metal doped and co-doped TiO2 photocatalysts oriented to degrade indoor/outdoor pollutants for air quality improvement . A kinetic and product study using acetaldehyde as probe molecule. J Photochem Photobiol A Chem 371:255–263. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotochem.2018.11.023
Karam FF, Hussein FH, Baqir SJ et al (2014) Photocatalytic degradation of anthracene in closed system reactor. Int J Photoenergy 2014:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/503825
Karunakaran C, Ganapathy A, Paramasivan G et al (2011) NiO/TiO2 nanoparticles for photocatalytic disinfection of bacteria under visible light. J Am Ceram Soc 94:2499–2505. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1551-2916.2011.04403.x
Ke T, Guo H, Zhang Y, Liu Y (2017) Photoreduction of Cr ( VI ) in water using BiVO4-Fe3O4 nano-photocatalyst under visible light irradiation. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 24:28239–28247. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0255-0
Kessler FB (2014) A review on the synthesis of TiO2 nanoparticles by solution route A review on the synthesis of TiO2 nanoparticles by solution route. https://doi.org/10.2478/s11532-011-0155-y
Kitsou I, Panagopoulos P, Maggos T et al (2018) Development of SiO2/TiO2 core-shell nanospheres for catalytic applications. Appl Surf Sci 441:223–231. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.02.008
Le TS, Ngo QB, Nguyen VD et al (2014) Photocatalytic equipment with nitrogen-doped titanium dioxide for air cleaning and disinfecting. Adv Nat Sci Nanosci Nanotechnol 5. https://doi.org/10.1088/2043-6262/5/1/015017
Liu Y, Liang W, Zhang W et al (2013) First principle study of CuN, Cu and N-doped anatase TiO2. Solid State Commun 164:27–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssc.2013.04.005
Liu H, Zou M, Viliam Hakala B et al (2017) Synthesis, characterization of Cu, N co-doped TiO2 microspheres with enhanced photocatalytic activities. Adv Mater Sci 2:1–7. https://doi.org/10.15761/AMS.1000114
López R, Gómez R, Llanos ME (2010) Photophysical and photocatalytic properties of nanosized copper-doped titania sol-gel catalysts. Catal Today 148:103–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cattod.2009.04.001
Mahammed BA, Ahmed LM (2017) Enhanced photocatalytic properties of pure and Cr-modified ZnS powders synthesized by precipitation method. J Geosci Environ Prot 05:101–111. https://doi.org/10.4236/gep.2017.510009
Maicu M, Hidalgo MC, Navı JA (2006) Cu-doped TiO2 systems with improved photocatalytic activity. Appl Catal B Environ 67:41–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2006.03.019
Mrowetz M, Balcerski W, Colussi AJ, Hoffmann MR (2004) Oxidative power of nitrogen-doped TiO2 photocatalysts under visible illumination. J Phys Chem B 108:17269–17273. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp0467090
Patel YM, Park SL, Carmella SG et al (2016) Metabolites of the polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon phenanthrene in the urine of cigarette smokers from five ethnic groups with differing risks for lung cancer. PLoS One:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0156203
Patil P, Sawant D, Rn D (2012) Physico-chemical parameters for testing of water–a review. Int J Environ Sci 3:1194–1207
Perrin C (2005) Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons ( PAHs ) in urban waters. North Carolina Coop Extention Serv:1–8
Qian Y, Du J, Kang DJ (2019) Enhanced electrochemical performance of porous Co-doped TiO2 nanomaterials prepared by a solvothermal method. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 273:148–155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2018.06.056
Rajoriya S, Bargole S, George S et al (2019) Synthesis and characterization of samarium and nitrogen doped TiO2 photocatalysts for photo-degradation of 4-acetamidophenol in combination with hydrodynamic and acoustic cavitation. Sep Purif Technol 209:254–269. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2018.07.036
Reza M, Khaki D, Saleh M et al (2017) Application of doped photocatalysts for organic pollutant degradation - A review. J Environ Manag 198:78–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2017.04.099
Romão J (2015) Photocatalytic water treatment: substrate-specific activity of titanium dioxide [Thesis], University of Twente, Enschede, The Netherlands. https://doi.org/10.3990/1.9789036539609
Sathish M, Viswanathan B, Viswanath RP (2007) Characterization and photocatalytic activity of N-doped TiO2 prepared by thermal decomposition of Ti-melamine complex. Appl Catal B Environ 74:307–312. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2007.03.003
Sekhar M et al (2018) Synthesis, characterization, and analysis of enhanced photocatalytic activity of Zr-doped TiO2 nanostructured powders under UV light. Mater Res Express. https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/aaa21e
Society E, Monographs E (2011) Comparisons of treatments after an analysis of variance in ecology author (s): Day RW, Quinn GP. Published by: Ecological Society of America Stable. 59:433–463. http://www.jstor.org/stable/1943075, https://doi.org/10.2307/1943075
Song K, Zhou J et al (2008) Photocatalytic activity of (copper, nitrogen)-codoped titanium dioxide nanoparticles. J Am Ceram Soc 1371:1369–1371. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1551-2916.2008.02291.x
Song J, Wang X, Bu Y et al (2016) Preparation , characterization , and photocatalytic activity evaluation of Fe – N-codoped TiO2/fly ash cenospheres floating photocatalyst. Environ Sci Pollut Res:22793–22802. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7353-2
Sun C, He P, Pan G et al (2018) Study on preparation and visible-light activity of Ag–TiO2 supported by artificial zeolite. Res Chem Intermed 44:2607–2620. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11164-017-3249-0
Tan YN, Wong CL, Mohamed AR (2011) An overview on the photocatalytic activity of nano-doped-TiO2 in the degradation of organic pollutants. ISRN Mater Sci 2011:1–18. https://doi.org/10.5402/2011/261219
Taylor P, Behnajady MA, Alizade B (2013) Desalination and water treatment enhancement of TiO2 -UV100 nanoparticles photocatalytic activity by Mg impregnation in the removal of a model organic pollutant, pp 37–41. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2013.846509
Taylor P, Talat-mehrabad J, Khosravi M, et al (2015) Desalination and water treatment synthesis , characterization , and photocatalytic activity of co-doped Ag –, Mg – TiO2 -P25 by photodeposition and impregnation methods, pp 37–41. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2015.1036780
Tseng IH, Wu JCS, Chou HY (2004) Effects of sol-gel procedures on the photocatalysis of Cu/TiO2 in CO2 photoreduction. J Catal 221:432–440. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcat.2003.09.002
Varma R, Tiwari K, Makani N, et al (2018) Roles of Vanadium and nitrogen in photocatalytic activity of VN-codoped TiO2 photocatalyst, pp 0–2. https://doi.org/10.1111/php.12942
Vasanth Kumar K, Porkodi K, Selvaganapathi A (2007) Constrain in solving Langmuir-Hinshelwood kinetic expression for the photocatalytic degradation of Auramine O aqueous solutions by ZnO catalyst. Dyes Pigments 75:246–249. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dyepig.2006.05.035
Wang S, Yang XJ, Jiang Q, Lian JS (2014) Enhanced optical absorption and photocatalytic activity of Cu/N-codoped TiO2 nanocrystals. Mater Sci Semicond Process 24:247–253. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mssp.2014.03.029
Xin B, Wang P, Ding D et al (2008) Effect of surface species on Cu-TiO2 photocatalytic activity. Appl Surf Sci 254:2569–2574. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2007.09.002
Yang G, Jiang Z, Shi H et al (2010) Preparation of highly visible-light active N-doped TiO2 photocatalyst. J Mater Chem 20:5301–5309. https://doi.org/10.1039/c0jm00376j
Yang X, Cai H, Bao M et al (2018) Insight into the highly efficient degradation of PAHs in water over graphene oxide/Ag3PO4 composites under visible light irradiation. Chem Eng J 334:355–376. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.09.104
Yoong LS, Chong FK, Dutta BK (2009) Development of copper-doped TiO2 photocatalyst for hydrogen production under visible light. Energy 34:1652–1661. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2009.07.024
Zaleska A (2008) Doped-TiO2: a review. Recent Patents Eng 2:157–164. https://doi.org/10.2174/187221208786306289
Zhang Y, Wong JWC, Liu P, Yuan M (2011) Heterogeneous photocatalytic degradation of phenanthrene in surfactant solution containing TiO2 particles. J Hazard Mater 191:136–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.04.059
Zhao X, Cai Z, Wang T et al (2016) A new type of cobalt-deposited titanate nanotubes for enhanced photocatalytic degradation of phenanthrene. Appl Catal B Environ 187:134–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2016.01.010
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 51879080, 51509129, and 41371307); Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province, China (BK20171435); the Open Foundation of State Key Laboratory of Pollution Control and Resource Reuse (Grant No. PCRRF12010); the State Key Laboratory of Soil and Sustainable Agriculture (Institute of Soil Science, Chinese Academy of Sciences) foundation (Grant No. 0812201228), a project funded by the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions (PAPD), and the Top-notch Academic Programs Project (TAPP) of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Suresh Pillai
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
The original version of this article was revised due to a retrospective open access cancellation.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, Z., Omer, A.A., Qin, Z. et al. Cu/N-codoped TiO2 prepared by the sol-gel method for phenanthrene removal under visible light irradiation. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27, 17530–17540 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05787-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05787-7