Abstract
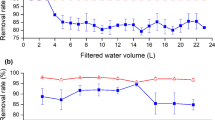
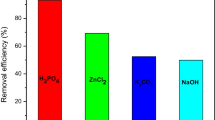
Bisphenol-A is widely used chemical in industry and unfortunately often detected in natural waters. Considered as an emerging pollutant, bisphenol-A represents an environmental problem due to its endocrine-disrupting behavior. The production of activated carbon from alternative precursors has shown to be attractive in the removal of emerging pollutants from the water. Activated carbon was produced from waste coffee by physical and chemical activation and applied in the removal of bisphenol-A. The samples were characterized by elemental analysis, scanning electron microscopy, X-ray diffraction, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, and analysis of textural properties. Bisphenol-A adsorption experiments showed that the chemically activated carbon was more efficient due to its high specific surface area (1039 m2/g) compared to the physically activated carbon (4.0 m2/g). The bisphenol-A adsorption data followed the pseudo-second-order model and Langmuir isotherm, which indicated a maximum adsorption capacity of 123.22 mg/g for chemically activated carbon. The results demonstrated a potential use of the coffee grounds as a sustainable raw material for the production of chemically activated carbon that could be used in water treatment.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arampatzidou AC, Voutsa D, Deliyanni EA, Matis KA (2017) Adsorption of endocrine disruptor bisphenol a by carbonaceous materials: influence of their porosity and specific surface area. Desalin Water Treat 76:1–9. https://doi.org/10.5004/dwt.2017.20706
Asada T, Oikawa K, Kawata K, Ishihara S, Iyobe T, Yamada A (2004) Study of removal effect of bisphenol a and β-estradiol by porous carbon. J Health Sci 50:588–593. https://doi.org/10.1248/jhs.50.588
Aznar JS (2011) Characterization of activated carbon produced from coffee residues by chemical and physical activation. Thesis, KTH Vetenskap Och Konst, Stockolm
Bansal CR, Goyal M (2005) Adsorption, fisrt. CRC Press, New York
Barrett E, Joyner L, Halenda P (1951) The determination of pore volume and area distributions in porous substances. I. Computations from nitrogen isotherms. J Am Chem Soc 73:378–380
Belhachemi M, Addoun F (2011) Comparative adsorption isotherms and modeling of methylene blue onto activated carbons. Appl Water Sci 1:111–117. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-011-0014-1
Blanchard G, Maunaye M, Martin G (1984) Removal of heavy metals from waters by means of natural zeolites. Water Res 18:1501–1507. https://doi.org/10.1016/0043-1354(84)90124-6
Bouchenafa-Saïb N, Mekarzia A, Bouzid B, Mohammedi O, Khelifa A, Benrachedi K, Belhaneche N (2014) Desalination and water treatment removal of malathion from polluted water by adsorption onto chemically activated carbons produced from coffee grounds. Desalin Water Treat 52:4920–4927. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2013.808845
Boudrahem F, Soualah A, Aissani-Benissad F (2011) Pb ( II ) and cd ( II ) removal from aqueous solutions using activated carbon developed from coffee residue activated with phosphoric acid and zinc chloride. J Chem Eng 56:1946–1955. https://doi.org/10.1021/je1009569
Brunauer S, Emmett PH, Teller E (1938) Adsorption of gases in multimolecular layers. J Am Chem Soc 60:309–319. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja01269a023
Castro CS, Abreu AL, Silva CLT, Guerreiro MC (2011) Phenol adsorption by activated carbon produced from spent coffee grounds. Water Sci Technol 64:2059–2065. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2011.786
Djilani C, Zaghdoudi R, Modarressi A, Rogalski M, Djazi F, Lallam A (2012) Elimination of organic micropollutants by adsorption on activated carbon prepared from agricultural waste. Chem Eng J 189–190:203–212. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2012.02.059
Essabir H, Raji M, Laaziz SA, Rodrique D, Bouhfid R, Qaiss A (2018) Thermo-mechanical performances of polypropylene biocomposites based on untreated, treated and compatibilized spent coffee grounds. Compos Part B Eng 149:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2018.05.020
Everett DH (1971) Manual of symbols and terminology for physicochemical quantities and units. Appendix II - definitions, terminology and symbols in colloid and surface chemistry, part I. Int Union Pure Appl Chem
Freundlich H (1906) Über die Adsorption in Lösungen. Z Phys Chem 38:385–471
Gao Y, Li L, Jin Y, Wang Y, Yuan C, Wei Y, Chen G, Ge J, Lu H (2015) Porous carbon made from rice husk as electrode material for electrochemical double layer capacitor. Appl Energy 153:41–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2014.12.070
Giles CH, MacEwan TH, Nakhwa SN, Smith D (1960) Studies in adsorption. Part XI. A system of classification of solution adsorption isotherms, and its use in diagnosis of adsorption mechanisms and in measurement of specific surface areas of solids. J Chem Soc 846:3973–3993
Gwenzi W, Chaukura N, Noubactep C, Mukome FND (2017) Biochar-based water treatment systems as a potential low-cost and sustainable technology for clean water provision. J Environ Manag 197:732–749. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2017.03.087
Hadoun H, Sadaoui Z, Souami N, Sahel D, Toumert I (2013) Characterization of mesoporous carbon prepared from date stems by H3PO4 chemical activation. Appl Surf Sci 280:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2013.04.054
Ho YS, McKay G (1998) A comparison of chemisorption kinetic models applied to pollutant removal on various sorbents. Process Saf Environ Prot 76:332–340. https://doi.org/10.1205/095758298529696
Kamaraj M, Satheesh K, Rajeshwari S (2017) Bioremediation and sustainable Technologies for Cleaner Environment. Bioremediation Sustain Technol Clean Environ Environ Sci Eng 163–176. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-48439-6
Khenniche L, Aissani F (2009) Characterization and utilization of activated carbons prepared from coffee residue for adsorptive removal of salicylic acid and phenol : kinetic and isotherm study. Desalin Water Treat 11:192–203. https://doi.org/10.5004/dwt.2009.801
Koduru RJ, Lingamdinne PL, Singh J, Choo K (2016) Effective removal of bisphenol a ( BPA ) from water using a goethite / activated carbon composite. Process Saf Environ Prot 103:87–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2016.06.038
Lagergren S (1898) About the theory of so-called adsorption of soluble substances. K Sven Vetenskapsakademiens Handl 24:1–39
Laksaci H, Khelifi A, Trari M, Addoun A (2017) Synthesis and characterization of microporous activated carbon from coffee grounds using potassium hydroxides. J Clean Prod 147:254–262. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.01.102
Langmuir I (1916) The constitution and fundamental properties of solids and liquids. Part I. solids. J Am Chem Soc 38:2221–2295
Levenspiel O (2000) Engenharia das reações químicas, 3rd edn. Blucher, São Paulo
Marsh H, Rodriguez-reinoso F (2006) Activated carbon. Elsevier
Moreira M, Aquino S, Coutrim M, Silva J, Afonso R (2011) Determination of endocrine - disrupting compounds in waters from Rio das Velhas , Brazil , by liquid chromatography / high resolution mass spectrometry (ES-LC-IT-TOF/MS). Environ Technol 32:1409–1417. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2010.537829
Nasseri S, Ebrahimi S, Abtahi M, Saeedi R (2018) Synthesis and characterization of polysulfone / graphene oxide nano- composite membranes for removal of bisphenol a from water. J Environ Manag 205:174–182. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2017.09.074
Nowicki P (2016) Effect of heat treatment on the physicochemical properties of nitrogen-enriched activated carbons. J Therm Anal Calorim 125:1017–1024. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-016-5254-8
Ozdemir I, Şahin M, Orhan R, Erdem M (2014) Preparation and characterization of activated carbon from grape stalk by zinc chloride activation. Fuel Process Technol 125:200–206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuproc.2014.04.002
Pamidimukkala PS, Soni H (2018) Efficient removal of organic pollutants with activated carbon derived from palm shell: spectroscopic characterisation and experimental optimisation. J Environ Chem Eng 6:3135–3149. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2018.04.013
Park J, Regalbuto JR (1995) A simple, accurate determination of oxide PZC and the strong buffering effect of oxide surfaces at incipient wetness. J Colloid Interface Sci 175:239–252
Pendleton P, Schumann R, Wong SH (2001) Microcystin-LR adsorption by activated. Carbon. 8:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1006/jcis.2001.7616
Pendleton P, Wu SH, Badalyan A (2002) Activated carbon oxygen content influence on water and surfactant. Adsorption. 240:235–240. https://doi.org/10.1006/jcis.2001.8052
Prauchner MJ, Sapag K, Rodríguez-Reinoso F (2016) Tailoring biomass-based activated carbon for CH4storage by combining chemical activation with H3PO4or ZnCl2and physical activation with CO2. Carbon N Y 110:138–147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2016.08.092
Rodiguez MH, Yperman J, Carleer R et al (2018) Adsorption of Ni(II) on spent coffee and coffee husk based activated carbon. J Environ Chem Eng 6:1161–1170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2017.12.045
Rodríguez-Reinoso F, Molina-Sabio M (1992) Activated carbons from lignocellulosic materials by chemical and/or physical activation: an overview. Carbon N Y 30:1111–1118. https://doi.org/10.1016/0008-6223(92)90143-K
Schettino Junior MA, Freitas JCC, Cunha AG et al (2007) PREPARAÇÃO E CARACTERIZAÇÃO DE CARVÃO ATIVADO QUIMICAMENTE A PARTIR DA CASCA DE ARROZ. Quim Nova 30:1663–1668. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2006.08.001
Silverstein RM, Webster FX, David KJ (2013) Identificação espectrométrica de compostos orgânicos, 7rd edn. LTC, Rio de Janeiro, pp 71–122
Singh YD, Mahanta P, Bora U (2017) Comprehensive characterization of lignocellulosic biomass through proximate, ultimate and compositional analysis for bioenergy production. Renew Energy 103:490–500. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2016.11.039
Sodré FF, Montagner CC, Locatelli MAF, Jardim WF (2007) Ocorrência de Interferentes Endócrinos e Produtos Farmacêuticos em Águas Superficiais da Região de Campinas (SP, Brasil). J Brazilian Soc Ecotoxicol 2:187–196
Suhas CPJM, Carrott MMLR et al (2017) An innovative approach to develop microporous activated carbons in oxidising atmosphere. J Clean Prod 156:549–555. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.04.078
Tehrani NF, Aznar JS, Kiros Y (2015) Coffee extract residue for production of ethanol and activated carbons. J Clean Prod 91:64–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2014.12.031
Thommes M, Kaneko K, Neimark AV, Olivier JP, Rodriguez-Reinoso F, Rouquerol J, Sing KSW (2015) Physisorption of gases , with special reference to the evaluation of surface area and pore size distribution (IUPAC technical report). Pure Appl Chem 87:1051–1069. https://doi.org/10.1515/pac-2014-1117
WHO, FAO (2010) Toxicological and health aspects of bisphenol a report of joint FAO / WHO expert meeting. Ottawa
Wirasnita R, Hadibarata T, Yusoff ARM, Yusop Z (2014) Removal of bisphenol a from aqueous solution by activated carbon derived from oil palm empty fruit bunch. Water Air Soil Pollut 225:2148. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-014-2148-x
Xia J, Ge Y, Di J et al (2016) Ionic liquid-assisted strategy for bismuth-rich bismuth oxybromides nanosheets with superior visible light-driven photocatalytic removal of bisphenol-A. J Colloid Interface Sci 473:112–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2016.03.046
Yang H, Yan R, Hanping C et al (2007) Characteristics of hemicellulose, cellulose and lignin pyrolysis. Fuel 86:1781–1788. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2006.12.013
Yoon Y, Westerhoff P, Snyder SA, Esparza M (2003) HPLC-fluorescence detection and adsorption of bisphenol a, 17β-estradiol, and 17α-ethynyl estradiol on powdered activated carbon. Water Res 37:3530–3537. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1354(03)00239-2
Zbair M, Ainassaari K, Drif A, Ojala S, Bottlinger M, Pirilä M, Keiski RL, Bensitel M, Brahmi R (2017) Toward new benchmark adsorbents: preparation and characterization of activated carbon from argan nut shell for bisphenol a removal. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:1869–1882. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0634-6
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the support of the Federal University of Goiás (UFG), the Federal Institute of Goiás (IFG) and the Foundation for Research (FAPEG) for the master’s scholarship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Tito Roberto Cadaval Jr
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alves, A.C.F., Antero, R.V.P., de Oliveira, S.B. et al. Activated carbon produced from waste coffee grounds for an effective removal of bisphenol-A in aqueous medium. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26, 24850–24862 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05717-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05717-7