Abstract
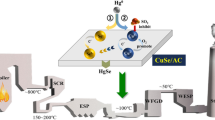
Adsorption is a typical method for air pollutant removal from flue gas. A CuS-modified active coke (CuS/AC) sorbent was developed to improve the elemental mercury removal efficiency from municipal solid waste incineration (MSWI) flue gas. The influences of the loading amount of CuS, reaction temperature, and flue gas components including O2, SO2, H2O, and HCl on Hg0 removal efficiency were investigated, respectively. The results showed that the mercury adsorption capacity of CuS/AC(20%) sorbent was about 7.17 mg/g with 50% breakthrough threshold, which is much higher than that of virgin active coke. The analysis of XPS indicated that HgS was the main species of mercury on spent CuS/AC, which implied that adsorption and oxidation were both included in Hg0 removal. S22− played a vital role in the oxidation of physically adsorbed Hg0. Meanwhile, the common components of MSWI flue gas exhibited no significant inhibition effect on Hg0 removal by CuS/AC sorbent. CuS/AC sorbent is a promising sorbent for the mercury removal from MSWI flue gas.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pacyna EG, Pacyna JM, Sundseth K, Munthe J, Kindbom K, Wilson S, Steenhuisen F, Maxson P (2010) Global emission of mercury to the atmosphere from anthropogenic sources in 2005 and projections to 2020. Atmos Environ 44:2487–2499
UNEP (2018): global mercury assessment 2018
Zhang L, Wang S, Wang L, Wu Y, Duan L, Wu Q, Wang F, Yang M, Yang H, Hao J, Liu X (2015) Updated emission inventories for speciated atmospheric mercury from anthropogenic sources in China. Environ Sci Technol 49:3185–3194
Hong J, Chen Y, Wang M, Ye L, Qi C, Yuan H, Zheng T, Li X (2017) Intensification of municipal solid waste disposal in China. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 69:168–176
Cheng H, Hu Y (2010) China needs to control mercury emissions from municipal solid waste (MSW) incineration. Environ Sci Technol 44:7994–7995
Li G, Wu Q, Wang S, Li Z, Liang H, Tang Y, Zhao M, Chen L, Liu K, Wang F (2017) The influence of flue gas components and activated carbon injection on mercury capture of municipal solid waste incineration in China. Chem Eng J 326:561–569
Cheng H, Hu Y (2012) Mercury in municipal solid waste in China and its control: a review. Environ Sci Technol 46:593–605
Zhang H, He PJ, Shao LM (2008) Fate of heavy metals during municipal solid waste incineration in Shanghai. J Hazard Mater 156:365–373
Li G, Wu Q, Wang S, Duan Z, Su H, Zhang L, Li Z, Tang Y, Zhao M, Chen L (2018a) Improving flue gas mercury removal in waste incinerators by optimization of carbon injection rate. Environ Sci Technol 52
Tan Z, Sun L, Xiang J, Zeng H, Liu Z, Hu S, Qiu J (2012) Gas-phase elemental mercury removal by novel carbon-based sorbents. Carbon 50:362–371
Liu Y (2008) Impact of sulfur oxides on mercury capture by activated carbon. Environ Sci Technol 42:6579–6584
Du X, Li C, Zhao L, Zhang J, Gao L, Sheng J, Yi Y, Chen J, Zeng G (2018) Promotional removal of HCHO from simulated flue gas over Mn-Fe oxides modified activated coke. Appl Catal B Environ 232:37–48
Li LT, Xie W, Liang DM, Sun ZC, Xu ZG (2010) Mechanism of removal of SO2 and NO on activated coke. Environ Sci Technol 33:79–83
Yuan J, Jiang X, Zou MJ, Yao L, Zhang CJ, Jiang WJ (2018) Copper ore-modified activated coke: highly efficient and regenerable catalysts for the removal of SO2. Ind Eng Chem Res 57:15731–15739
Zhang K, He Y, Wang ZH, Huang TH, Li Q, Kumar S, Cen KF (2017) Multi-stage semi-coke activation for the removal of SO2 and NO. Fuel 210:738–747
Chen Y, Guo X, Wu F, Huang Y, Yin Z (2018) Experimental and theoretical studies for the mechanism of mercury oxidation over chlorine and cupric impregnated activated carbon. Appl Surf Sci 458:790–799
Liu W, Vidic RD, Brown TD (2000) Impact of flue gas conditions on mercury uptake by sulfur-impregnated activated carbon. Environ Sci Technol 34:154–159
Xie Y, Li C, Zhao L, Zhang J, Zeng G, Zhang X, Zhang W, Tao S (2015) Experimental study on Hg0 removal from flue gas over columnar MnOx-CeO2/activated coke. Appl Surf Sci 333:59–67
Zeng H, Jin F, Guo J (2004) Removal of elemental mercury from coal combustion flue gas by chloride-impregnated activated carbon. Fuel 83:143–146
Li H, Zhu L, Wang J, Li L, Shih K (2016) Development of nano-sulfide sorbent for efficient removal of elemental mercury from coal combustion fuel gas. Environ Sci Technol 50:9551–9557
Li H, Zhu W, Yang J, Zhang M, Zhao J, Qu W (2018b) Sulfur abundant S/FeS 2 for efficient removal of mercury from coal-fired power plants. Fuel 232:476–484
Yang Z, Li H, Feng S, Li P, Liao C, Liu X, Zhao J, Yang J, Lee PH, Shih K (2018) Multiform sulfur adsorption centers and copper-terminated active sites of Nano-CuS for efficient elemental mercury capture from coal combustion flue gas. Langmuir 34:8739–8749
Liu H, You Z, Yang S, Liu C, Xie X, Xiang K, Wang X, Yan X (2019) High-efficient adsorption and removal of elemental mercury from smelting flue gas by cobalt sulfide. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int
Hua XY, Zhou JS, Li Q, Luo ZY, K-f C (2010) Gas-phase elemental mercury removal by CeO2 impregnated activated coke. Energy Fuel 24:5426–5431
Serrano-Ruiz JC, Ramos-Fernández EV, Silvestre-Albero J, Sepúlveda-Escribano A, Rodríguez-Reinoso F (2008) Preparation and characterization of CeO2 highly dispersed on activated carbon. Mater Res Bull 43:1850–1857
Shen B, Li G, Wang F, Wang Y, He C, Zhang M, Singh S (2015) Elemental mercury removal by the modified bio-char from medicinal residues. Chem Eng J 272:28–37
Xiao Y, Pudasainee D, Gupta R, Xu Z, Diao Y (2017) Bromination of petroleum coke for elemental mercury capture. J Hazard Mater 336:232–239
Suresh Kumar Reddy K, Al Shoaibi A, Srinivasakannan C (2013) elemental mercury adsorption on sulfur-impregnated porous carbon – a review. Environ Technol 35:18–26
Li H, Wu CY, Li Y, Zhang J (2011) CeO2-TiO2 catalysts for catalytic oxidation of elemental mercury in low-rank coal combustion flue gas. Environ Sci Technol 45:7394–7400
Yan Z, Liu L, Zhang Y, Liang J, Wang J, Zhang Z, Wang X (2013) Activated semi-coke in SO2 removal from flue gas: selection of activation methodology and desulfurization mechanism study. Energy Fuel 27:3080–3089
Liao Y, Chen D, Zou S, Xiong S, Xiao X, Dang H, Chen T, Yang S (2016) Recyclable naturally derived magnetic pyrrhotite for elemental mercury recovery from flue gas. Environ Sci Technol 50:10562–10569
Xu H, Yuan Y, Liao Y, Xie J, Qu Z, Shangguan W, Yan N (2017): [MoS4) Cluster bridges in Co-Fe layered double hydroxides for mercury uptake from S-Hg mixed flue gas. Environ Sci Technol 51(2):10109–10116
Wu S, Uddin MA, Nagano S, Ozaki M, Sasaoka E (2011) Fundamental study on decomposition characteristics of mercury compounds over solid powder by temperature-programmed decomposition desorption mass spectrometry. Energy Fuel 25:144–153
Rumayor M, Fernandez-Miranda N, Lopez-Anton MA, Diaz-Somoano M, Martinez-Tarazona MR (2015) Application of mercury temperature programmed desorption (HgTPD) to ascertain mercury/char interactions. Fuel Process Technol 132:9–14
Funding
This study was financially supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (No. 2017YFC0806300) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21677096).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 56 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, W., Zhou, Y., Hua, Y. et al. A sulfur-resistant CuS-modified active coke for mercury removal from municipal solid waste incineration flue gas. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26, 24831–24839 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05645-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05645-6