Abstract
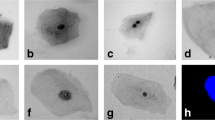
Since many different pesticides have been used occupationally, there have been inconsistent results regarding DNA damages among greenhouse workers. Thus, the aim of the study is to evaluate DNA damages, cell death, and chromosomal instability by using the buccal micronucleus cytome (BMcyt) assay in greenhouse workers and to compare those with a non-exposed group. The BMcyt assay was applied to the exfoliated buccal cell samples collected from 66 pesticide-exposed and 50 non-exposed individuals. We evaluated the frequency of micronucleus (MN), nuclear bud (NBUD), binucleated (BN) cells, and karyolitic (KL), pyknotic (PY), and karyorrhectic (KH) cells. The results showed that the MN, BN, PY, and KH frequencies of the pesticide-exposed group were significantly higher than those of the controls (P ˂ 0.05, P ˂ 0.05, P ˂ 0.01, and P ˂ 0.05, respectively). We observed that the MN, BN, PY, and KH frequencies in the autumn were statistically different compared with those in the control group (P = 0.037 for MN, P = 0.001 for BN, P = 0.016 for PY, and P = 0.033 for KH). The same comparison was done in the spring for the control, and there was a statistically significant difference for MN (P = 0.046) and PY (P = 0.014). We can conclude that pesticide exposure in greenhouse workers was one of the factors that altered DNA damages, cell death, and chromosomal instability in oral mucosa cells.

Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Andreotti G, Freeman LEB, Hou L, Coble J, Rusiecki J, Hoppin JA, Silverman DT, Alavanja MC (2009) Agricultural pesticide use and pancreatic cancer risk in the Agricultural Health Study Cohort. Int J Cancer 124:2495–2500
Ascherio A, Chen H, Weisskopf MG, O’Reilly E, McCullough ML, Calle EE, Schwarzschild MA, Thun MJ (2006) Pesticide exposure and risk for Parkinson’s disease. Ann Neurol: Official Journal of the American Neurological Association and the Child Neurology Society 60:197–203
Aslantürk ÖS, Çelik TA (2017) Genotoxic risk assessment in professionals working hairdressers area using buccal micronucleus assay, in Aydın City, Turkey. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:14700–14705
Band PR, Abanto Z, Bert J, Lang B, Fang R, Gallagher RP, Le ND (2011) Prostate cancer risk and exposure to pesticides in British Columbia farmers. Prostate 71:168–183
Benedetti D, Nunes E, Sarmento M, Porto C, dos Santos CEI, Dias JF, da Silva J (2013) Genetic damage in soybean workers exposed to pesticides: evaluation with the comet and buccal micronucleus cytome assays. Mutat Res Genet Toxicol Environ Mutagen 752:28–33
Bolognesi C (2003) Genotoxicity of pesticides: a review of human biomonitoring studies. Mutat Res Rev Mutat Res 543:251–272
Bolognesi C, Holland N (2016) The use of the lymphocyte cytokinesis-block micronucleus assay for monitoring pesticide-exposed populations. Mutat Res Rev Mutat Res 770:183–203
Bolognesi C, Creus A, Ostrosky-Wegman P, Marcos R (2011) Micronuclei and pesticide exposure. Mutagenesis 26:19–26
Bolognesi C, Knasmueller S, Nersesyan A, Thomas P, Fenech M (2013) The HUMN xl scoring criteria for different cell types and nuclear anomalies in the buccal micronucleus cytome assay–an update and expanded photogallery. Mutat Res Rev Mutat Res 753:100–113
Bolognesi C, Roggieri P, Ropolo M, Thomas P, Hor M, Fenech M, Nersesyan A, Knasmueller S (2015) Buccal micronucleus cytome assay: results of an intra-and inter-laboratory scoring comparison. Mutagenesis 30:545–555
Bonassi S, Coskun E, Ceppi M, Lando C, Bolognesi C, Burgaz S, Holland N, Kirsh-Volders M, Knasmueller S, Zeiger E (2011) The HUman MicroNucleus project on eXfoLiated buccal cells (HUMN XL): the role of life-style, host factors, occupational exposures, health status, and assay protocol. Mutat Res Rev Mutat Res 728:88–97
Carlin V, Fracalossi ACC, Miranda SR, Noguti J, Pereira da Silva VH, Oshima CT, Ribeiro DA (2013) Chromosome breakage and cellular death are induced in oral epithelial cells of hairdressers: a preliminary study. Toxicol Mech Methods 23:108–112
de Bortoli GM, de Azevedo MB, da Silva LB (2009) Cytogenetic biomonitoring of Brazilian workers exposed to pesticides: micronucleus analysis in buccal epithelial cells of soybean growers. Mutat Res Rev Mutat Res 675:1–4
Dutta S, Bahadur M (2016) Cytogenetic analysis of micronuclei and cell death parameters in epithelial cells of pesticide exposed tea garden workers. Toxicol Mech Methods 26:627–634
Fenech M (2007) Cytokinesis-block micronucleus cytome assay. Nat Protoc 2:1084
Gabriel HE, Crott JW, Ghandour H, Dallal GE, Choi S-W, Keyes MK, Jang H, Liu Z, Nadeau M, Johnston A (2006) Chronic cigarette smoking is associated with diminished folate status, altered folate form distribution, and increased genetic damage in the buccal mucosa of healthy adults. Am J Clin Nutr 83:835–841
Gorell JM, Johnson C, Rybicki B, Peterson E, Richardson R (1998) The risk of Parkinson’s disease with exposure to pesticides, farming, well water, and rural living. Neurology 50:1346–1350
Grover P, Danadevi K, Mahboob M, Rozati R, Banu BS, Rahman M (2003) Evaluation of genetic damage in workers employed in pesticide production utilizing the Comet assay. Mutagenesis 18:201–205
Haveric A, Haveric S, Ibrulj S (2010) Micronuclei frequencies in peripheral blood and buccal exfoliated cells of young smokers and non-smokers. Toxicol Mech Methods 20:260–266
Hayden KM, Norton MC, Darcey D, Østbye T, Zandi PP, Breitner J, Welsh-Bohmer K, Investigators CCS (2010) Occupational exposure to pesticides increases the risk of incident AD The Cache County Study. Neurology 74:1524–1530
Holland N, Bolognesi C, Kirsch-Volders M, Bonassi S, Zeiger E, Knasmueller S, Fenech M (2008) The micronucleus assay in human buccal cells as a tool for biomonitoring DNA damage: the HUMN project perspective on current status and knowledge gaps. Mutat Res Rev Mutat Res 659:93–108
Joshi M, Verma Y, Gautam A, Parmar G, Lakkad B, Kumar S (2011) Cytogenetic alterations in buccal mucosa cells of chewers of areca nut and tobacco. Arch Oral Biol 56:63–67
Karaagac SU (2012) Insecticide resistance. In: Farzana P (ed) Insecticides-advances in integrated pest management. InTech, London, pp 471-478
Kausar A, Giri S, Roy P, Giri A (2014) Changes in buccal micronucleus cytome parameters associated with smokeless tobacco and pesticide exposure among female tea garden workers of Assam, India. Int J Hyg Environ Health 217:169–175
Lee WJ, Sandler DP, Blair A, Samanic C, Cross AJ, Alavanja MC (2007) Pesticide use and colorectal cancer risk in the Agricultural Health Study. Int J Cancer 121:339–346
León-Mejía G, Quintana M, Debastiani R, Dias J, Espitia-Pérez L, Hartmann A, Henriques JAP, Da Silva J (2014) Genetic damage in coal miners evaluated by buccal micronucleus cytome assay. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 107:133–139
Lucero L, Pastor S, Suarez S, Durban R, Gómez C, Parron T, Creus A, Marcos R (2000) Cytogenetic biomonitoring of Spanish greenhouse workers exposed to pesticides: micronuclei analysis in peripheral blood lymphocytes and buccal epithelial cells. Mutat Res Genet Toxicol Environ Mutagen 464:255–262
Mark GL, Gleich LL, Fukasawa K, Chadwell J, Ann Miller M, Stambrook PJ, Gluckman JL (2000) Centrosome hyperamplification in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: a potential phenotypic marker of tumor aggressiveness. Laryngoscope 110:1798–1801
Meraldi P, Honda R, Nigg EA (2002) Aurora-A overexpression reveals tetraploidization as a major route to centrosome amplification in p53−/− cells. EMBO J 21:483–492
Moretti M, Marcarelli M, Villarini M, Fatigoni C, Scassellati-Sforzolini G, Pasquini R (2002) In vitro testing for genotoxicity of the herbicide terbutryn: cytogenetic and primary DNA damage. Toxicol in Vitro 16:81–88
Nersesyan A, Muradyan R, Kundi M, Knasmueller S (2010) Impact of smoking on the frequencies of micronuclei and other nuclear abnormalities in exfoliated oral cells: a comparative study with different cigarette types. Mutagenesis 26:295–301
Normand G, King RW (2010) Understanding cytokinesis failure. Adv Exp Med Biol 676:27-55
Pastor S, Gutiérrez S, Creus A, Cebulska-Wasilewska A, Marcos R (2001) Micronuclei in peripheral blood lymphocytes and buccal epithelial cells of Polish farmers exposed to pesticides. Mutat Res Genet Toxicol Environ Mutagen 495:147–156
Pastor S, Creus A, Xamena N, Siffel C, Marcos R (2002a) Occupational exposure to pesticides and cytogenetic damage: results of a Hungarian population study using the micronucleus assay in lymphocytes and buccal cells. Environ Mol Mutagen 40:101–109
Pastor S, Lucero L, Gutiérrez S, Durban R, Gomez C, Parron T, Creus A, Marcos R (2002b) A follow-up study on micronucleus frequency in Spanish agricultural workers exposed to pesticides. Mutagenesis 17:79–82
Piyathilake C, Macaluso M, Hine R, Vinter D, Richards E, Krumdieck C (1995) Cigarette smoking, intracellular vitamin deficiency, and occurrence of micronuclei in epithelial cells of the buccal mucosa. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 4:751–758
Popova L, Kishkilova D, Hadjidekova V, Hristova R, Atanasova P, Hadjidekova V, Ziya D, Hadjidekov V (2007) Micronucleus test in buccal epithelium cells from patients subjected to panoramic radiography. Dentomaxillofac Radiol 36:168–171
Preethi N, Chikkanarasaiah N, Bethur SS (2016) Genotoxic effects of X-rays in buccal mucosal cells in children subjected to dental radiographs. BDJ Open 2:16001
Ramirez A, Saldanha PH (2002) Micronucleus investigation of alcoholic patients with oral carcinomas. Genet Mol Res 1:246–260
Remor AP, Totti CC, Moreira DA, Dutra GP, Heuser VD, Boeira JM (2009) Occupational exposure of farm workers to pesticides: biochemical parameters and evaluation of genotoxicity. Environ Int 35:273–278
Sanchez-Siles M, Ros-Llor I, Camacho-Alonso F, Lopez-Jornet P (2011) A novel application of the buccal micronucleus cytome assay in oral lichen planus: a pilot study. Arch Oral Biol 56:1148–1153
Sato N, Mizumoto K, Nakamura M, Nakamura K, Kusumoto M, Niiyama H, Ogawa T, Tanaka M (1999) Centrosome abnormalities in pancreatic ductal carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 5:963–970
Thirthagiri E, Robinson CM, Huntley S, Davies M, Yap LF, Prime SS, Paterson IC (2007) Spindle assembly checkpoint and centrosome abnormalities in oral cancer. Cancer Lett 258:276–285
Thomas P, Harvey S, Gruner T, Fenech M (2008) The buccal cytome and micronucleus frequency is substantially altered in Down’s syndrome and normal ageing compared to young healthy controls. Mutat Res Fundam Mol Mech Mutagen 638:37–47
Thomas P, Holland N, Bolognesi C, Kirsch-Volders M, Bonassi S, Zeiger E, Knasmueller S, Fenech M (2009) Buccal micronucleus cytome assay. Nat Protoc 4:825
U.S. EPA (2018) Chemicals evaluated for carcinogenic potential annual cancer report 2018 http://npic.orst.edu/chemicals_evaluated.pdf Accessed 5 May 2019
Weber R, Bridger J, Benner A, Weisenberger D, Ehemann V, Reifenberger G, Lichter P (1998) Centrosome amplification as a possible mechanism for numerical chromosome aberrations in cerebral primitive neuroectodermal tumors with TP53 mutations. Cytogenet Cell Genet 83:266–269
WHO (2010) The WHO Recommended Classification of Pesticides by Hazard and Guidelines to Classification 2009. World Health Organization, Geneva
Funding
This study was supported by Canakkale Onsekiz Mart University (Grant number: 2010/128).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cobanoglu, H., Coskun, M., Coskun, M. et al. Results of buccal micronucleus cytome assay in pesticide-exposed and non-exposed group. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26, 19676–19683 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05249-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05249-0