Abstract
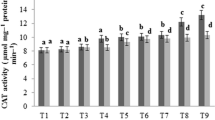
Production of large quantities of organic waste all over the world poses major environmental and disposal problems. The present study was conducted to explore the deleterious effects of Parthenium hysterophorus and milk processing industry sludge on the health of earthworm, Eisenia fetida. Earthworms were allowed to grow in the mixture of cow dung:Parthenium hysterophorus (75:25) and cow dung:milk processing industry sludge (60:40) for 60 days. The biochemical markers viz. superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT), glutathione peroxidase (GPx), and malondialdehyde (MDA) levels and histological changes in earthworm’s intestine were assessed after 15, 30, 45, and 60 days of exposure. The results revealed increased MDA level, while SOD, CAT, and GPx activities showed variation in both treatments. Furthermore, histopathological changes revealed damage in the intestinal tissue in both treatments during all intervals. More severe effects were registered in P. hysterophorus treatment. Obtained results may contribute to the understanding of P. hysterophorus and milk processing industry sludge induced toxic effects on earthworms and to identify defense mechanism of Eisenia fetida.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aebi HE (1983) Catalase. In: Methods of enzymatic analysis. Bergmeyr.H.U.(ed.).Verlag Chemie. Weinheim, vol 3, pp 273–286
Annapurna C, Singh JS (2003) Variation of Parthenium hysterophorus in response to soil quality: implications for invasiveness. Weed Res 43:190–198
Asad S, Rukhsana B (2006) Distribution of parthenium weed (Parthenium hysterophorus, L.), an alien invasive weed species threatening the biodiversity of Islamabad. Weed Biol Manag 6:89–95
Bakthavathsalam R, Geetha T (2004) Reproductive influence of the earthworm, Lampito mauritii cultured in different media of paddy chaff and weed plants materials. Environ Ecol 22(3):574–578
Britz TJ, van Schdkwyk C, Hung YT (2006) Treatment of dairy processing waste water. In: Yapijakis C, Hung YT, Lo HH, Wang LK (eds) Waste treatment in the food processing industry. CRC Press, New York, pp 1–28
Cancio I, ap Gwynn I, Ireland M, Cajaraville M (1995) The effect of sublethal lead exposure on the ultrastructure and on the distribution of acid phosphatase activity in chloragocytes of earthworms (Annelida, Oligochaeta). Histochem J 27:965–973
Cnubben NHP, Rietjens IMCM, Wortelboer H, van Zanden J, van Bladeren PJ (2001) The interplay of glutathione-related processes in antioxidant defense. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 10:141–152
Company R, Serafim A, Bebianno MJ, Cosson R, Shillito B, Fiala-Medioni A (2004) Effect of cadmium, copper and mercury on antioxidant enzyme activities and lipid peroxidation in the gills of the hydrothermal vent mussel Bathymodiolus azoricus. Mar Environ Res 58:377–381
Das K, Samanta L, Chainy GBN (2000) A modified spectrophotometric assay for superoxide dismutase using nitrite formation by superoxide radicals. Indian J Biochem Biophys 37:201–204
Dhande AD, Ingle ST, Attarde SB, Wagh ND (2005) Eco friendly approach of urban solid waste management - a case study of Jalgaon city Maharastra. J Environ Biol 26(4):747–752
Di Giulio RT, Washburn PC, Wenning RJ, Winston GW, Jewell CS (1989) Biochemical responses in aquatic animals: a review of determinants of oxidative stress. Environ Toxicol Chem 8:1103–1123
Dipankar CR, Munan S (2013) Toxicology, phytochemistry, bioactive compounds and pharmacology of Parthenium hysterophorus. J Med Plants Stud 1(3):126–141
Drury RA, Wallington EA (1980) Carleton’s histological techniques, 5th edn. Oxford University Press, New York, p 195
Edwards CA, Bater JE (1992) The use of earthworm in environmental management. Soil Biol Biochem 24:1683–1689
Edwards CA, Dominguez J, Neuhauser EF (1998) Growth and reproduction of Perionyx excavatus (Perr.) (Megascolecidae) as factors in organic waste management. Biol Fertil Soils 27:155–161
Eida MF, Matter IA, Zaher FHA (2016) Isolation and characterization of cellulose and hemicellulolytic fungi from salt affected soils and compost. J Innov Pharm Biol Sci 3(4):164–170
Elumalai M, Antunes C, Guillhermino L (2007) Enzymatic biomarkers in the crab Carcinus maenas from Minho River estuary (NW Portugal) exposed to zinc and mercury. Chemosphere 66(7):1249–1255
Elvira C, Dominguez J, Sampedro L, Mato S (1995) Vermicomposting for the paper-pulp industry. Biocycle 36(6):62–63
Escobar JA, Rubio MA, Lissi EA (1996) SOD and catalase inactivation by singlet oxygen and peroxyl radicals. Free Radic Biol Med 20:285–290
Fatima M, Mandiki SNM, Douxfils J, Silvestre F, Coppe P, Kestemont P (2007) Combined effects of herbicides on biomarkers reflecting immune-endocrine interactions in goldfish immune and antioxidant effects. Aquat Toxicol 81:159–167
Ferreira-Cravo M, Ventura-Lima J, Sandrini JZ, Amado LL, Geracitano LA, Rebelo M, Bianchini A, Monserrat JM (2009) Antioxidant responses in different body regions of the polychaeta Laeonereis acuta (Nereididae) exposed to copper. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 72:388–393
Gastaldi L, Ranzato E, Caprì F, Hankard P, Pé- res G, Canesi L, Viarengo A, Pons G (2007) Application of a biomarker battery for the evaluation of the sublethal effects of pollutants in the earthworm Eisenia andrei. Comp Biochem Physiol C 146:398–405
Giovanetti A, Fesenko S, Cozzella ML, Asencio LD, Sansone U (2010) Bioaccumulation and biological effects in the earthworm Eisenia fetida exposed to natural and depleted uranium. J Environ Radioact 101:509–516
Gómez-Brandón M, Lazcano C, Lores M, Domínguez J (2011) Short-term stabilization of grape marc through earthworms. J Hazard Mater 187:291–295
Gu¨nzler WA, Flohe L (1985) Glutathione peroxidase. In: Greenwald RA (ed) Handbook of methods for oxygen research. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 285–290
Hodgson EK, Fridovich I (1975) The interaction of bovine erythrocyte superoxide dismutase with hydrogen peroxide: inactivation of the enzyme. Biochemistry 14:5294–5299
ISO (1993) Soil quality—effects of pollutants on earthworms (Eisenia fetida). 11268–1 determination of acute toxicity using artificial soil substrate. International Organization for Standardization, Geneva
ISO (1998) Soil quality—effects of pollutants on earthworms (Eisenia fetida). 11268–2 determination of effects on reproduction. International Organization for Standardization, Geneva
Krauss M, Wilcke W, Zech W (2000) Availability of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) and polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) to earthworms in urban soils. Environ Sci Technol 34:4335–4340
Lam P, Gray J (2003) The use of biomarkers in environmental monitoring programmes. Mar Pollut Bull 46(2):182–186
Langdon CJ, Piearce TG, Black S, Semple KT (1999) Resistance to arsenic toxicity in a population of the earthworm Lumbricus rubellus. Soil Biol Biochem 31:1963–1967
Langdon CJ, Piearce TG, Meharg AA, Semple KT (2001a) Resistance to copper toxicity in populations of the earthworms Lumbricus rubellus and Dendrodrilus rubidus from contaminated mine wastes. Environ Toxicol Chem 20:2336–2341
Langdon CJ, Piearce TG, Meharg AA, Semple KT (2001b) Survival and behavior of the earthworms Lumbricus rubellus and Dendrodrilus rubidus from arsenate contaminated and non-contaminated sites. Soil Biol Biochem 33:1239–1244
Łaszczyca P, Augustyniak M, Babczynska A, Bednarska K, Kafel A, Migula P, Wilczek G, Witas I (2004) Profiles of enzymatic activity in earthworms from zinc lead and cadmium polluted areas near Olkusz (Poland). Environ Int 30: 901–910
Lemaire C, Damhaut P, Plenevoux A, Cpmar D (1994) Enantioselective synthesis of 6-[fluorine-18]-fluoro-L-dopa from no-carrier-added fluorine-18-fluoride. J Nucl Med Technol 35:1996–2002
Lin D, Zhou Q, Xie X, Liu Y (2010) Potential biochemical and genetic toxicity of triclosan as an emerging pollutant on earthworms (Eisenia fetida). Chemosphere 18:1328–1333
Liu S, Zhou QX, Wang YY (2011) Ecotoxicological responses of the earthworm Eisenia fetida exposed to soil contaminated with HHCB. Chemosphere 83:1080–1086
Livingstone DR (1993) Review biotechnology and pollution monitoring: use of molecular biomarkers in the aquatic environment. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 57:195–211
Livingstone DR, Archbald S, Chipman JK, Marsh JW (1992) Antioxidant enzymes in liver of dab Limanda limanda from North Sea. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 91:97–104
Lourenco JI, Pereira RO, Silva AC, Morgado JM, Carvalho FP, Oliveira JM, Malta MP, Paiva AA, Mendo SA, Goncalves FJ (2011) Genotoxic endpoints in the earthworms/sub-lethal assay to evaluate natural soils contaminated by metals and radionuclides. J Hazard Mater 186:788–795
Maenpaa KA, Kukkonen JVK, Lydy MJ (2002) Remediation of heavy metal contaminated soils using phosphorus: evaluation of bioavailability using an earthworm bioassay. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 43:389–0398
Marino F, Morgan AJ (1999) The time-course of metal (Ca, Cd, Cu, Pb, Zn) accumulation from a contaminated soil by three populations of the earthworm Lumbricus rubellus. Appl Soil Ecol 12:169–177
Markad VL, Kodam KM, Ghole VS (2012) Effect of fly ash on biochemical responses and DNA damage in earthworm Dichogaster curgensis. J Hazard Mater 215–216:191–198
Masum SM, Hasanuzzaman M, Ali MH (2013) Threats of Parthenium hysterophorus on agroecosystems and its management: a review. Intl J Agri Crop Sci 6(11):684–697
Morgan AJ, Turner MP, Morgan JE (2002) Morphological plasticity in metal sequestering earthworm chloragocytes: morphometric electron microscopy provides a biomarker of exposure in field populations. Environ Toxicol Chem 21:610–618
Mosleh Y, Paris-Palacios S, Ahmed M, Mahmoud F, Osman F, Biagianti-Risbourg S (2007) Effects of chitosan on oxidative stress and metallothioneins in aquatic worm Tubifex tubifex (Oligochaeta, Tubificidae). Chemosphere 67:167–175
Muthukaruppan G, Janardhanan S, Vijayalakshmi G (2005) Sublethal toxicity of the herbicide butachlor on the earthworm Perionyx sansibaricus and its histological changes. J Soils Sediments 5:82–86
Nahmani J, Hodson ME, Black S (2007) A review of studies performed to assess metal uptake by earthworms. Environ Pollut 145:402–424
Narasimhan TR, Keshava MBS, Harindranath N (1984) Characterization of a toxin from Parthenium hysterophorus and its mode of excretion in animals. J Biosci 6(5):729–738
Nath R (1988) Parthenium hysterophorus L. A general account. Agric Rev 9(4):171–179
Neuhauser EF, Hartenstein R, Kaplan DL (1980) Growth of the earthworm Eisenia foetida in relation to population density and food rationing. OIKOS 35:93–98
OECD (1984) Guidelines for testing of chemicals—section 2. Effects on biotic systems. Earthworm, acute toxicity tests (filter paper test and artificial soil test). Organisation for Economic Cooperation and Development, Paris
OECD (2004) Guideline for testing of chemicals. Earthworm reproduction test (Eisenia fetida/Eisenia andrei). Organisation for Economic Cooperation and Development, Paris
Posthuma L, Van Straalen MM (1993) Heavy metal adaptation in terrestrial invertebrates: a review of occurrence, genetics, physiology and ecological consequences. Comp Biochem Physiol C 100:11–38
Rajiv P, Rajeshwari S, Venckatesh R (2014) Impact of Parthenium weeds on earthworms (Eudrilus eugeniae) during vermicomposting. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21:12364–12371
Reinecke SA, Reinecke AJ (2004) The Comet assay as biomarker of heavy metal genotoxicity in earthworms. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 46:208–215
Ribera D, Narbonne JF, Arnaud C, Saint-Denis M (2001) Biochemical responses of the earthworm Eisenia fetida andrei exposed to contaminated artificial soil, effects of carbaryl. Soil Biol Biochem 33:1123–1130
Rotruck JT, Pope AL, Ganther HE, Swanson AB, Hafeman DG, Hoekstra WG (1973) Selenium: biochemical role as a component of glutathione peroxidise. Science 179:588–590
Saint-Denis M, Labrot F, Narbonne JF, Ribera D (1998) Glutathione, glutathione related enzymes, and catalase in the earthworm Eisenia fetida Andrei. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 35:602–614
Saint-Denis M, Narbonne JF, Arnaud C, Ribera D (2001) Biochemical responses of the earthworm Eisenia fetida andrei exposed to contaminated artificial soil: effects of lead acetate. Soil Biol Biochem 33:395–404
Sandrini JZ, Lima JV, Regoli F, Fattorini D, Notti A, Marins LF, Monserrat JM, Kapoor RT (2008) Antioxidant responses in the nereidid Laeonereis acuta (Annelida, Polychaeta) after cadmium exposure. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 70:115–120
Singh D, Suthar S (2012) Vermicomposting of herbal pharmaceutical industry waste solids. Ecol Eng 39:1–6
Sinha RK, Bharambe G, Chaudhari U (2008) Sewage treatment by vermifiltration with synchronous treatment of sludge by earthworms: a low cost sustainable technology over conventional systems with potential for decentralization. Environmentalist 28:409–420
Slater RA, Frederickson J (2001) Composting municipal waste in the UK: some lessons from Europe. Resour Conserv Recycl 32:359–374
Stürzenbaum SR, Kille P, Morgan AJ (1998) The identification, cloning and characterization of earthworm metallothionein. FEBS Lett 431:437–442
Suthar S (2007) Nutrient changes and biodynamics of epigenic earthworm Perionyx excavatus (Perrier) during recycling of some agriculture wastes. Bioresour Technol 98:1608–1614
Suthar S (2008) Development of a novel epigeic-anecic based polyculture vermireactor for efficient treatment of municipal sewage water sludge. Int J Environ Waste Manag 2(1–2):84–101
Suthar S (2012) Vermistabilization of wastewater sludge from milk processing industry. Ecol Eng 47:115–119
Suthar S, Mutiyar PK, Singh S (2012) Vermicomposting of milk processing industry sludge spiked with plant wastes. Bioresour Technol 116:214–219
Talemos S, Abreham A, Fisseha M (2013) Distribution status and the impact of parthenium weed (Parthenium hysterophorus L.) at Gedeo Zone (Southern Ethiopia). Afr J Agric Res 8(4):386–397
Valavanidis A, Vlahogianni T, Dassenakis M, Scoullos M (2006) Molecular biomarkers of oxidative stress in aquatic organisms in relation to toxic environmental pollutants. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 64:178–189
Wilbur KM, Bernheim F, Shapiro OW (1949) The thiobarbituric acid reagent as a test for the oxidation of unsaturated fatty acid by various agents. Acta Biochem Biophy 24:305–313
Yang X, Yufang S, Ackland ML, Yang L, Xiufeng C (2012) Biochemical responses of earthworm Eisenia fetida exposed to cadmium-contaminated soil with long duration. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 89:1148–1153
Zhang W, Zhang M, An S, Xiong B, Li H, Cui CZ, Lin KF (2012) Ecotoxicological effects of decabromodiphenyl ether and cadmium contamination on soil microbes and enzymes. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 82:71–79
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the facilities provided by Department of Zoology and Environmental Sciences, Punjabi University, Patiala, to pursue the research work.
Funding
This work received financial aid extended by UGC in the form of Rajiv Gandhi National Fellowship for minority students.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kaur, H., Sharma, S. & Vijaya, P. Toxicological effect of Parthenium hysterophorus and milk processing industry sludge on earthworms, Eisenia fetida. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27, 33464–33473 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05222-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05222-x