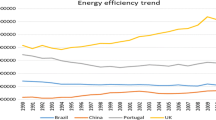
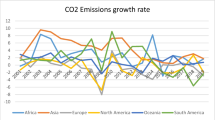
Abstract
Based on the premise of sustainable development of the environment, how to achieve the balance of energy utilization, economic development, and sustainable management of the environment is becoming increasingly important in the process of stable economic development. This paper analyzes the concept of environmental Kuznets curve, taking 35 European countries as the research objects, first discusses the trend of energy utilization efficiency from 1990 to 2013, and then analyzes the relationship between energy efficiency and economic development. Empirical results show that labor has a significant negative impact on energy efficiency and the increase in labor input will reduce energy efficiency. If the added value of national manufacturing accounts for a higher percentage in GDP, it will have a negative impact on the effectiveness of energy utilization. In addition, when the national price level is high, price fluctuation will increase the price of energy utilization, or the cost of energy input in economic activities, which will further reduce the country’s energy efficiency performance. Lastly, the empirical study also found that energy efficiency and economic development showed a quadratic U-shaped relationship, indicating that the long-term energy efficiency of the country will first decline and then rise during economic activities.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adom OK, Kwakwa PA, Amankwaa A (2018) The long-run effects of economic, demographic, and political indices on actual and potential CO2 emissions. J Environ Manag 218:516–526
Akella AK, Saini RP, Sharma MP (2009) Social, economical and environmental impacts of renewable energy systems. Renew Energy 34:390–396
Azapagic A (2004) Developing a framework for sustainable development indicators for the mining and minerals industry. J Clean Prod 12:639–662
Borghesi S (1999) The environmental Kuznets curve: a survey of the literature, FEEM Working Paper No 85–99
Chen TY (2001) The impact of mitigating CO2 emissions on Taiwan’s economy. Energy Econ 23:141–151
Cropper M, Griffiths C (1994) The interaction of population growth and environmental quality. Am Econ Rev 84:250–254
Dasgupta P (2001) Human well-being and the natural environment. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Dijkaraaf E, Vollebergh HRJ (2005) A test for parameter homogeneity in CO2 panel EKC estimations. Environ Resour Econ 32:229–239
Dinda S (2004) Environmental Kuznets curve hypothesis a survey. Ecol Econ 49:431–455
Fang H (2000) The significance and approach of public participation in environmental management. Law and Governance 12:003
Färe R, Grosskopf S, Heranadez-Sancho F (2004) Environmental performance: an index number approach. Resour Energy Econ 26:343–352
Fridel B, Getzner M (2003) Determinants of CO2 emissions in a small open economy. Ecol Econ 45:133–148
Grossman GM, Krueger AB (1995) Economic growth and the environment. Q J Econ 110:353–377
Heerink N, Mulatu A, Bulte E (2001) Income inequality and the environment: aggregation bias in environmental Kuznets curves. Ecol Econ 38:359–367
Heil MT, Selden TM (2001) Carbon emissions and economic development future trajectories based on historical experience. Environ Dev Econ 6:63–83
Kathuria V (2007) Informal regulation of pollution in a developing country: evidence from India. Ecol Econ 63(2–3):403–417
Lindmark M (2002) An EKC-pattern in historical perspective: carbon dioxide emissions, technology, fuel pieces and growth in Sweden. Ecol Econ 42:333–347
Mielnik O, Goldemberg J (1999) The evolution of the “carbonization index” in developing countries. Energy Policy 27:307–308
Nerlove M (1963) Chapter 7. Returns to Scale in Electricity Supply. In: Christ, C., et al., Eds, Measurement in Economics, Stanford University Press, Palo Alto, 167–198
Panayotou T (1997) Demystifying the environmental Kuznets curve turning black box into a policy tool. Environ Dev Econ 2:465–484
Pargal S, Mani M (2000) Citizen activism, environmental regulation, and the location of industrial plants: evidence from India. Econ Dev Cult Chang 48(4):829–846
Pargal S, Wheeler D (1996) Informal regulation of industrial pollution in developing countries: evidence from Indonesia. J Polit Econ 104(6):1314–1327
Ravallion M, Heil M, Jalan J (2000) Carbon emissions and income inequality. Oxford Economic Paper 52:651–669
Ren J, Andreasen KP, Sovacool BK (2014) Viability of hydrogen pathways that enhance energy security: a comparison of China and Denmark. Int J Hydrog Energy 39(28):15320–15329
Ren J, Gao S, Tan S, Dong L (2015) Hydrogen economy in China: strengths- weaknesses- opportunities- threats analysis and strategies prioritization. Renew Sust Energ Rev 41(1):1230–1243
Rezek JP, Rogers K (2008) Decomposing the CO2-income tradeoff: an output distance function approach. Environ Dev Econ 13:457–473
Richmond AK, Kaufmann RK (2006) Energy prices and turning points the relationship between income and energy use carbon emissions. Energy J 27:157–180
Schmalensee R, Stoker T, Judson RA (1998) World carbon dioxide emissions: 1950-2050. Rev Econ Stat 80:15–27
Scruggs LA (1998) Political and economic inequality and the environment. Ecol Econ 26:259–275
Selden TM, Song D (1994) Environmental quality and development: I there a Kuznets curve for air pollution emissions? J Environ Econ Manag 27:147–162
Stroup RL, Goodman SL (1992) Property rights, environmental resources, and the future. Harv JL Pub Pol’y 15:427
Suri V, Chapman D (1998) Economic growth, trade and energy: implications for the environmental Kuznets curve. Ecol Econ 25:195–208
Unruh GC, Moomaw WR (1998) An alternative analysis of apparent EKC-type transitions. Ecol Econ 25:221–229
Vaninsky A (2008) Environmental efficiency of electric power industry of the United States: a data envelopment analysis approach. Proceeding of World Academy of Science, Engineering and Technology 30:584–590
Wang B, Mi Z, Nistor I, Yuan XC (2018) How does hydrogen-based renewable energy change with economic development? Empirical evidence from 32 countries. Int J Hydrog Energy 43(25):11629–11638
Xepapadeas A, de Zeeuw A (1999) Environmental policy and competitiveness: the porter hypothesis and the composition of capital. J Environ Econ Manag 37(2):165–182
Zaim O, Taskin F (2000) A Kuznets curve in environmental efficiency: an application on OECD countries. Environ Resour Econ 17:21–36
Zeng Q, Hu J (2015) Research on the influencing factors of China’s public environmental participation -- based on the empirical analysis of China’s provincial panel data. China Popul Resour Environ 25(12):62–69
Zhou P, Ang BW, Zhou DQ (2012) Measuring economy-wide energy efficiency performance: a parametric frontier approach. Appl Energy 90:196–200
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Nicholas Apergis
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pan, XX., Chen, ML., Ying, LM. et al. An empirical study on energy utilization efficiency, economic development, and sustainable management. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27, 12874–12881 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-04787-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-04787-x