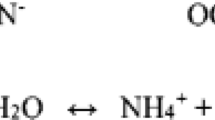Abstract
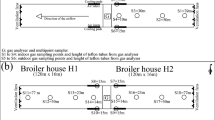
The husbandry of chicken for meat generates high levels of gases, being a serious problem for the health of birds and workers as well as for the environment. The aim of the present study was to assess the effect of clinoptilolite as litter additive on the concentrations and emissions of ammonia (NH3), nitrous oxide (N2O), carbon dioxide (CO2), and methane (CH4) from a breeding hen house under Mediterranean climate conditions. Two similar breeding hen houses were selected, and one house was assigned as control whereas the other house was treated with clinoptilolite as a litter additive. Data were collected during the winter season, in two occasions, first between 26 November and 18 December 2017 and second from 1 to 20 February 2018. Results showed that the application of clinoptilolite on the litter of a breeding hen house reduces the NH3 and N2O losses in 28 and 34%, respectively, but appears to have no effect on CO2 losses. In addition, the in-house CH4 concentrations were below the detection limits.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amon M, Dobeic M, Sneath RW, Phillips VR, Misselbrook TH, Pain BF (1997) A farm-scale study on the use of clinoptilolite zeolite and De-Odorases for reducing odour and ammonia emissions from broiler houses. Bioresour Technol 61:229–237
Berto DA, Garcia EA, Pelícia K, Vercese F, Molino A d B, da Silveira AF, Vieira Filho JA, Murakami ESF (2013) Effects of dietary clinoptilolite and calcium levels on the performance and egg quality of commercial layers. Braz J Poultry Sci 15:263–268
Guiziou F, Béline F (2005) In situ measurement of ammonia and greenhouse gas emissions from broiler houses in France. Bioresour Technol 96:203–207
Latifah O, Ahmed OH, Majid NMA (2017) Enhancing nitrogen availability from urea using clinoptilolite zeolite. Geoderma 306:152–159
Naseem S, King AJ (2018) Ammonia production in poultry houses can affect health of humans, birds, and the environment-techniques for its reduction during poultry production. Environ Sci Pollut R 25:15269–15293
Nikolakakis I, Dotas V, Kargopoulos A, Hatzizisis L, Dotas D, Ampas Z (2013) Effect of natural zeolite (clinoptilolite) on the performance and litter quality of broiler chickens. Turk J Vet Anim Sci 37:682–686
Nuernberg GB, Moreira MA, Ernani PR, Almeida JA, Maciel TM (2016) Efficiency of basalt zeolite and Cuban zeolite to adsorb ammonia released from poultry litter. J Environ Manag 183:667–672
Pereira JLS (2017) Assessment of ammonia and greenhouse gas emissions from broiler houses in Portugal. Atmos Pollut Res 8:949–955
Pereira JLS, Ferreira S, Garcia CSP, Conde A, Ferreira P, Pinheiro V, Trindade H (2017) Assessment of ammonia and carbon dioxide concentrations in a breeding hen building under Portuguese winter. Int J Food Biosyst Eng 5:1–6
Pereira JLS, Ferreira S, Pinheiro V, Trindade H (2018) Ammonia, nitrous oxide, carbon dioxide and methane emissions from commercial broiler houses in Mediterranean Portugal. Water Air Soil Pollut 229:377
Prasai TP, Walsh KB, Midmore DJ, Bhattarai SP (2017) Effect of biochar, zeolite and bentonite feed supplements on egg yield and excreta attributes. Anim Prod Sci 58:1632–1641
Wlazło Ł, Nowakowicz-Dębek B, Kapica J, Kwiecień M, Pawlak H (2016) Removal of ammonia from poultry manure by aluminosilicates. J Environ Manag 183:722–725
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge Pedro Ferreira and André Conde (LUSIAVES) for the facilities and technical data.
Funding
This work was supported by the European Investment Funds by FEDER/COMPETE/POCI—Operational Competitiveness and Internationalisation Programme, under project POCI-01-0145-FEDER-006958, project Ovislab ICT-2013-05-004-5314 ID-64757, and project POCI-01-0247-FEDER-003430 AMONIAVE and the National Funds by FCT—Portuguese Foundation for Science and Technology, under the projects UID/AGR/04033/2019 and Portugal2020.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pereira, J.L.S., Ferreira, S., Pinheiro, V. et al. Ammonia and greenhouse gas emissions following the application of clinoptilolite on the litter of a breeding hen house. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26, 8352–8357 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-04429-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-04429-2