Abstract
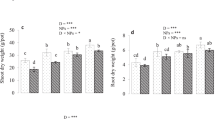
Cadmium (Cd) is among the non-essential elements for the growth of crops while silicon (Si) is a beneficial element for plant growth. There is little evidence regarding the use of silicon nanoparticles (Si NPs) on the reduction of Cd accumulation in crops especially wheat. The present study determined the impact of seed priming with Si NPs on Cd-induced responses in wheat in terms of growth, yield, photosynthesis, oxidative stress, and Si and Cd accumulation in wheat. Seed priming was done by different levels of Si NPs (0, 300, 600, 900, 1200 mg/L) for 24 h by providing continuous aeration. Afterwards, seeds were sown in soil contaminated with Cd. The results depicted that Si NPs positively affected the wheat growth and chlorophyll contents over the control. The Si NPs diminished the oxidative stress and positively affected the antioxidant enzyme activity. The Si NPs decreased the Cd concentrations in wheat, especially in grains, and increased the Si concentrations in plants. The Si NPs reduced the Cd contents by 10–52% in shoot, by 11–60% in roots, and by 12–75% in grains as compared with respective controls. The study suggested that the use of Si NPs may be a tool for reducing the Cd toxicity in wheat and declining its concentration in grains. Thus, Si NPs application by seed priming method might be helpful in increasing plants biomass and yield while reducing the oxidative stress and Cd uptake in wheat grains.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbas T, Rizwan M, Ali S, Rehman MZ, Qayyum MF, Abbas F, Hannan F, Rinklebe J, Ok YS (2017) Effect of biochar on cadmium bioavailability and uptake in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) grown in a soil with aged contamination. Ecotoxicol Environ Safe 140:37–47
Abou-Zeid HM, Ismail GSM (2018) The role of priming with biosynthesized silver nanoparticles in the response of Triticum aestivum L. to Salt Stress. Egypt J Bot 58:73–85
Adrees M, Ali S, Rizwan M, Rehman MZ, Ibrahim M, Abbas F, Farid M, Qayyum MF, Irshad MK (2015) Mechanisms of silicon-mediated alleviation of heavy metal toxicity in plants: a review. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 119:186–197
Aebi H (1984) Catalase in vitro. Methods Enzymol 105:121–126
Ali B, Huang CR, Qi ZY, Ali S, Daud MK, Geng XX, Liu HB, Zhou WJ (2013a) 5-aminolevulinic acid ameliorates cadmium-induced morphological, biochemical, and ultrastructural changes in seedlings of oilseed rape. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20:7256–7267
Ali B, Wang B, Ali S, Ghani MA, Hayat MT, Yang C, Xu L, Zhou WJ (2013b) 5-aminolevulinic acid ameliorates the growth, photosynthetic gas exchange capacity, and ultrastructural changes under cadmium stress in Brassica napus L. J Plant Growth Regul 32:604–614
Ali B, Gill RA, Yang S, Gill MB, Farooq MA, Liu D, Daud MK, Ali S, Zhou W (2015) Regulation of cadmium-induced proteomic and metabolic changes by 5-aminolevulinic acid in leaves of Brassica napus L. PLoS One. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0123328
Ali S, Rizwan M, Ullah N, Bharwana SA, Waseem M, Farooq MA, Abbasi GH, Farid M (2016) Physiological and biochemical mechanisms of silicon-induced copper stress tolerance in cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.). Acta Physiol Plant 38:1–11
Alzahrani Y, Kuşvuran A, Alharby HF, Kuşvuran S, Rady MM (2018) The defensive role of silicon in wheat against stress conditions induced by drought, salinity or cadmium. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 154:187–196
Anjum M, Miandad R, Waqas M, Gehany F, Barakat MA (2016) Remediation of wastewater using various nano-materials. Arab J Chem. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2016.10.004
Asgari F, Majd A, Jonoubi P, Najafi F (2018) Effects of silicon nanoparticles on molecular, chemical, structural and ultrastructural characteristics of oat (Avena sativa L.). Plant Physiol Biochem 127:152–160
Bouyoucos GJ (1962) Hydrometer method improved for making particle size analyses of soils 1. Agron J 54:464–465
Chen R, Zhang C, Zhao Y, Huang Y, Liu Z (2018) Foliar application with nano-silicon reduced cadmium accumulation in grains by inhibiting cadmium translocation in rice plants. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:2361–2368
Choppala G, Saifullah BN, Bibi S, Iqbal M, Rengel Z, Kunhikrishnan A, Ashwath N, Ok YS (2014) Cellular mechanisms in higher plants governing tolerance to cadmium toxicity. Crit Rev Plant Sci 33:374–391
Clemens S, Aarts MG, Thomine S, Verbruggen N (2013) Plant science: the key to preventing slow cadmium poisoning. Trends Plant Sci 18:92–99
Cui J, Liu T, Li F, Yi J, Liu C, Yu H (2017) Silica nanoparticles alleviate cadmium toxicity in rice cells: mechanisms and size effects. Environ Pollut 228:363–369
Curtis T, Halford NG (2014) Food security: the challenge of increasing wheat yield and the importance of not compromising food safety. Ann Appl Biol 164:354–372
Dionisio-Sese ML, Tobita S (1998) Antioxidant responses of rice seedlings to salinity stress. Plant Sci 135:1–9
Faizan M, Faraz A, Yusuf M, Khan ST, Hayat S (2018) Zinc oxide nanoparticle-mediated changes in photosynthetic efficiency and antioxidant system of tomato plants. Photosyn 56:678–686
Farid M, Ali S, Rizwan M, Ali Q, Abbas F, Bukhari SA, Saeed R, Wu L (2017) Citric acid assisted phytoextraction of chromium by sunflower; morpho-physiological and biochemical alterations in plants. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 145:90–102
Farooq MA, Detterbeck A, Clemens S, Dietz KJ (2016) Silicon-induced reversibility of cadmium toxicity in rice. J Exp Bot 67:3573–3585
Gao M, Zhou J, Liu H, Zhang W, Hu Y, Liang J, Zhou J (2018) Foliar spraying with silicon and selenium reduces cadmium uptake and mitigates cadmium toxicity in rice. Sci Total Environ 631:1100–1108
Geng A, Wang X, Wu L, Wang F, Wu Z, Yang H, Chen Y, Wen D, Liu X (2018) Silicon improves growth and alleviates oxidative stress in rice seedlings (Oryza sativa L.) by strengthening antioxidant defense and enhancing protein metabolism under arsanilic acid exposure. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 158:266–273
Guntzer F, Keller C, Meunier JD (2010) Determination of the silicon concentration in plant material using tiron extraction. New Phytol 188:902–906
Harris NS, Taylor GJ (2013) Cadmium uptake and partitioning in durum wheat during grain filling. BMC Plant Biol 13:1–16
Heath RL, Packer L (1968) Photoperoxidation in isolated chloroplasts: I Kinetics and stoichiometry of fatty acid peroxidation. Arch Biochem Biophys 125:189–198
Hussain A, Ali S, Rizwan M, ur Rehman MZ, Hameed A, Hafeez F, Alamri SA, Alyemeni MN, Wijaya L (2018a, 2018) Role of zinc–lysine on growth and chromium uptake in rice plants under Cr stress. J Plant Growth Regul:1–10
Hussain A, Ali S, Rizwan M, ur Rehman MZ, Javed MR, Imran M, Chatha SA, Nazir R (2018b) Zinc oxide nanoparticles alter the wheat physiological response and reduce the cadmium uptake by plants. Environ Pollut 242:1518–1526
Ibrahim EA (2016) Seed priming to alleviate salinity stress in germinating seeds. J Plant Physiol 192:38–46
Jan S, Alyemeni MN, Wijaya L, Alam P, Siddique KH, Ahmad P (2018) Interactive effect of 24-epibrassinolide and silicon alleviates cadmium stress via the modulation of antioxidant defense and glyoxalase systems and macronutrient content in Pisum sativum L. seedlings. BMC Plant Biol 18:146. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-018-1359-5
Janmohammadi M, Sabaghnia N (2015) Effect of pre-sowing seed treatments with silicon nanoparticles on germinability of sunflower (Helianthus annuus). Bot Lith 21:13–21
Jisha KC, Vijayakumari K, Puthur JT (2013) Seed priming for abiotic stress tolerance: an overview. Acta Physiol Plant 35:1381–1396
Kabir AH, Hossain MM, Khatun MA, Mandal A, Haider SA (2016) Role of silicon counteracting cadmium toxicity in alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.). Front Plant Sci 7:1117. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2016.01117
Keller C, Rizwan M, Davidian JC, Pokrovsky OS, Bovet N, Chaurand P, Meunier JD (2015) Effect of silicon on wheat seedlings (Triticum turgidum L.) grown in hydroponics and exposed to 0 to 30 μM Cu. Planta 241:847–860
Latef AA, Alhmad MF, Abdelfattah KE (2017) The possible roles of priming with zno nanoparticles in mitigation of salinity stress in lupine (Lupinus termis) plants. J Plant Growth Regul 36:60–70
Lichtenthaler HK (1987) Chlorophylls and carotenoids: pigments of photosynthetic biomembranes. Methods Enzymol 148:350–382
Liu R, Lal R (2015) Potentials of engineered nanoparticles as fertilizers for increasing agronomic productions. Sci Total Environ 514:131–139
Lu MM, De Silva DM, Peralta EK, Fajardo AN, Peralta MM (2015) Effects of nanosilica powder from rice hull ash on seed germination of tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum). Appl Res Develop 5:11–22
Mahakham W, Theerakulpisut P, Maensiri S, Phumying S, Sarmah AK (2016) Environmentally benign synthesis of phytochemicals-capped gold nanoparticles as nanopriming agent for promoting maize seed germination. Sci Total Environ 573:1089–1102
Mahakham W, Sarmah AK, Maensiri S, Theerakulpisut P (2017) Nanopriming technology for enhancing germination and starch metabolism of aged rice seeds using phytosynthesized silver nanoparticles. Sci Rep 7:8263. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-08669-5
Merwad AR, Desoky ES, Rady MM (2018) Response of water deficit-stressed Vigna unguiculata performances to silicon, proline or methionine foliar application. Sci Hortic 228:132–144
Mohamed AKSH, Qayyum MF, Abdel-Hadi AM, Rehman RA, Ali S, Rizwan M (2017) Interactive effect of salinity and silver nanoparticles on photosynthetic and biochemical parameters of wheat. Arch Agron Soil Sci 63:1736–1747
Mousavi SM, Motesharezadeh B, Hosseini HM, Alikhani H, Zolfaghari AA (2018) Geochemical fractions and phytoavailability of zinc in a contaminated calcareous soil affected by biotic and abiotic amendments. Environ Geochem Health 40:1221–1235
Munir T, Rizwan M, Kashif M, Shahzad A, Ali S, Amin N, Zahid R, Alam MF, Imran M (2018) Effect of zinc oxide nanoparticles on the growth and Zn uptake in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) by seed priming method. Digest J Nanomater Biostruc 13:315–323
Naeem A, Saifullah RMZ, Akhtar T, Ok YS, Rengel Z (2016) Genetic variation in cadmium accumulation and tolerance among wheat cultivars at the seedling stage. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 47:554–562
Nazaralian S, Majd A, Irian S, Najafi F, Ghahremaninejad F, Landberg T, Greger M (2017) Comparison of silicon nanoparticles and silicate treatments in fenugreek. Plant Physiol Biochem 115:25–33
Page AL, Miller RH, Keeny DR (1982) Methods of soil analysis (part 2). Chem Microbiol Proper Agron 9 SSSA, Madison
Paparella S, Araújo SS, Rossi G, Wijayasinghe M, Carbonera D, Balestrazzi A (2015) Seed priming: state of the art and new perspectives. Plant Cell Rep 34:1281–1293
Pereira AS, Dorneles AOS, Bernardy K, Sasso VM, Bernardy D, Possebom G, Rossato LV, Dressler VL, Tabaldi LA (2018) Selenium and silicon reduce cadmium uptake and mitigate cadmium toxicity in Pfaffia glomerata (Spreng.) Pedersen plants by activation antioxidant enzyme system. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:18548–18558
Pullagurala VL, Adisa IO, Rawat S, Kalagara S, Hernandez-Viezcas JA, Peralta-Videa JR, Gardea-Torresdey JL (2018) ZnO nanoparticles increase photosynthetic pigments and decrease lipid peroxidation in soil grown cilantro (Coriandrum sativum). Plant Physiol Biochem 132:120–127
Qayyum MF, ur Rehman MZ, Ali S, Rizwan M, Naeem A, Maqsood MA, Khalid H, Rinklebe J, Ok YS (2017) Residual effects of monoammonium phosphate, gypsum and elemental sulfur on cadmium phytoavailability and translocation from soil to wheat in an effluent irrigated field. Chemosphere 174:515–523
Rameshaiah GN, Pallavi J, Shabnam S (2015) Nano fertilizers and nano sensors–an attempt for developing smart agriculture. Int J Eng Res Gen Sci 3:314–320
Rehman MZ, Rizwan M, Ghafoor A, Naeem A, Ali S, Sabir M, Qayyum MF (2015) Effect of inorganic amendments for in situ stabilization of cadmium in contaminated soils and its phyto-availability to wheat and rice under rotation. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:16897–16906
Rehman MZ, Khalid H, Akmal F, Ali S, Rizwan M, Qayyum MF, Iqbal M, Khalid MU, Azhar M (2017) Effect of limestone, lignite and biochar applied alone and combined on cadmium uptake in wheat and rice under rotation in an effluent irrigated field. Environ Pollut 227:560–568
Rehman MZ, Rizwan M, Hussain A, Saqib M, Ali S, Sohail MI, Shafiq M, Hafeez F (2018) Alleviation of cadmium (Cd) toxicity and minimizing its uptake in wheat (Triticum aestivum) by using organic carbon sources in Cd-spiked soil. Environ Pollut 241:557–565
Rizwan M, Meunier JD, Miche H, Keller C (2012) Effect of silicon on reducing cadmium toxicity in durum wheat (Triticum turgidum L. cv. Claudio W.) grown in a soil with aged contamination. J Hazard Mater 209:326–34
Rizwan M, Ali S, Adrees M, Rizvi H, Zia-ur-Rehman M, Hannan F, Qayyum MF, Hafeez F, Ok YS (2016a) Cadmium stress in rice: toxic effects, tolerance mechanisms, and management: a critical review. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:17859–17879
Rizwan M, Ali S, Abbas T, Zia-ur-Rehman M, Hannan F, Keller C, Al-Wabel MI, Ok YS (2016b) Cadmium minimization in wheat: a critical review. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 130:43–53
Rizwan M, Meunier JD, Davidian JC, Pokrovsky OS, Bovet N, Keller C (2016c) Silicon alleviates Cd stress of wheat seedlings (Triticum turgidum L. cv. Claudio) grown in hydroponics. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:1414–1427
Rizwan M, Ali S, Adrees M, Ibrahim M, Tsang DC, Zia-ur-Rehman M, Zahir ZA, Rinklebe J, Tack FM, Ok YS (2017a) A critical review on effects, tolerance mechanisms and management of cadmium in vegetables. Chemosphere 182:90–105
Rizwan M, Ali S, Hussain A, Ali Q, Shakoor MB, Rehman MZ, Farid M, Asma M (2017b) Effect of zinc-lysine on growth, yield and cadmium uptake in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) and health risk assessment. Chemosphere 187:35–42
Rizwan M, Ali S, Rehman MZ, Rinklebe J, Tsang DC, Bashir A, Maqbool A, Tack FM, Ok YS (2018) Cadmium phytoremediation potential of Brassica crop species: a review. Sci Total Environ 631:1175–1191
Rizwan M, Ali S, Ali B, Adrees M, Arshad M, Hussain A, Rehman MZ, Waris AA (2019) Zinc and iron oxide nanoparticles improved the plant growth and reduced the oxidative stress and cadmium concentration in wheat. Chemosphere 214:269–277
Sebastian A, Nangia A, Prasad MN (2018) A green synthetic route to phenolics fabricated magnetite nanoparticles from coconut husk extract: implications to treat metal contaminated water and heavy metal stress in Oryza sativa L. J Clean Prod 174:355–366
Shi Z, Yang S, Han D, Zhou Z, Li X, Liu Y, Zhang B (2018) Silicon alleviates cadmium toxicity in wheat seedlings (Triticum aestivum L.) by reducing cadmium ion uptake and enhancing antioxidative capacity. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:7638–7646
Shoeva OY, Khlestkina EK (2018) Anthocyanins participate in the protection of wheat seedlings against cadmium stress. Cereal Res Commun 46:242–252
Silva AJ, Nascimento CWA, Gouveia-Neto AS (2017) Assessment of cadmium toxicities in potted garlic plants. Acta Physiol Plant 38:211
Singh K, Gupta N, Dhingra M (2018) Effect of temperature regimes, seed priming and priming duration on germination and seedling growth on American cotton. J Environ Biol 39:83–91
Soltanpour PN (1985) Use of ammonium bicarbonate DTPA soil test to evaluate elemental availability and toxicity. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 16:323–338
Sundaria N, Singh M, Upreti P, Chauhan RP, Jaiswal JP, Kumar A (2018) Seed priming with Iron oxide nanoparticles triggers Iron acquisition and biofortification in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) grains. J Plant Growth Regul 2018:1–10
Tripathi DK, Singh VP, Prasad SM, Chauhan DK, Dubey NK (2015) Silicon nanoparticles (SiNp) alleviate chromium (VI) phytotoxicity in Pisum sativum (L.) seedlings. Plant Physiol Biochem 96:189–198
Tripathi DK, Singh S, Singh VP, Prasad SM, Chauhan DK, Dubey NK (2016) Silicon nanoparticles more efficiently alleviate arsenate toxicity than silicon in maize cultiver and hybrid differing in arsenate tolerance. Front Environ Sci 4:1–14
Ullah H, Luc PD, Gautam A, Datta A (2018) Growth, yield and silicon uptake of rice (Oryza sativa) as influenced by dose and timing of silicon application under water-deficit stress. Arch Agron Soil Sci 64:318–330
US Salinity Laboratory Staff (1954) Diagnosis and improvement of saline and alkali soils. Agriculture handbook 60. United States Salinity Laboratory, USDA, Washington DC, p. 160
Walkley A, Black IA (1934) An examination of the Degtjareff method for determining soil organic matter, and a proposed modification of the chromic acid titration method. Soil Sci 37:29–38
Wang S, Wang F, Gao S, Wang X (2016) Heavy metal accumulation in different rice cultivars as influenced by foliar application of nano-silicon. Water Air Soil Pollut 227:228. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-016-2928-6
Wojtyla Ł, Lechowska K, Kubala S, Garnczarska M (2016) Molecular processes induced in primed seeds—increasing the potential to stabilize crop yields under drought conditions. J Plant Physiol 203:116–126
Yadav RK, Saini PK, Pratap M, Tripathi SK (2018) Techniques of seed priming in field crops. IJCS 6:1588–1594
Yao Y (2016) Pollution: spend more on soil clean-up in China. Nature 533:469. https://doi.org/10.1038/533469a
Yousaf B, Liu G, Wang R, Zia-ur-Rehman M, Rizwan MS, Imtiaz M, Murtaza G, Shakoor A (2016) Investigating the potential influence of biochar and traditional organic amendments on the bioavailability and transfer of Cd in the soil–plant system. Environ Earth Sci 75:374. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-016-5285-2
Yuvakkumar R, Elango V, Rajendran V, Kannan NS, Prabu P (2011) Influence of nanosilica powder on the growth of maize crop (Zea mays L.). Int J Green Nanotechnol 3:180–190
Zhang XZ (1992) The measurement and mechanism of lipid peroxidation and SOD, POD and CAT activities in biological system. Res Methodol Crop Physiol. Agriculture Press, Beijing 208–211
Zhang W, Yu X, Li M, Lang D, Zhang X, Xie Z (2018) Silicon promotes growth and root yield of Glycyrrhiza uralensis under salt and drought stresses through enhancing osmotic adjustment and regulating antioxidant metabolism. Crop Prot 107:1–11
Zhao FJ, Ma Y, Zhu YG, Tang Z, McGrath SP (2014) Soil contamination in China: current status and mitigation strategies. Environ Sci Technol 49:750–759
Zhu Y, Gong H (2014) Beneficial effects of silicon on salt and drought tolerance in plants. Agron Sustain Dev 34:455–472
Zulfiqar U, Subhani T, Husain SW (2016) Synthesis of silica nanoparticles from sodium silicate under alkaline conditions. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 77:753–758
Funding
The financial support is from the Government College University, Faisalabad and Higher Education Commission (HEC) of Pakistan under NRPU Project No. 20-3653/NRPU/R&D/HEC/14/437 and NRPU Project No. 5634/Punjab/NRPU/R&D/HEC/2016.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Gangrong Shi
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hussain, A., Rizwan, M., Ali, Q. et al. Seed priming with silicon nanoparticles improved the biomass and yield while reduced the oxidative stress and cadmium concentration in wheat grains. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26, 7579–7588 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-04210-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-04210-5