Abstract
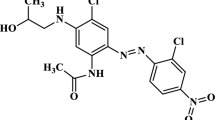
The aim of this study was to evaluate the performance of high purity magnesium and the magnesium-aluminum-zinc alloy AZ31 as sacrificial anodes in an electrocoagulation process with polarity change for the treatment of synthetic indigo carmine solution. It was studied the effect of the main parameters such as temperature, anodic material, current density, initial dye concentration, and agitation speed on the diminishing of indigo carmine concentration and non-purgeable organic carbon. Also, image analysis was used in conjunction with zeta potential measurements to understand the mechanism of flocs formation. The best results were 80% and 96% removal for non-purgeable organic carbon and dye content respectively at room temperature, by using turbulent regime, initial dye concentration of 100 mg L−1 and 50 A m−2 as current density with AZ31 alloy as electrodes. Particularly, high purity magnesium reached 75% in non-purgeable organic carbon removal and 86% in dye removal at the conditions described above. Finally, an additional improvement of 43% in the diminishing of the organic carbon content was observed when polarity change was used, a phenomenon that was attributed to the distribution of the oxidation reaction between electrodes, avoiding the saturation of the surface with oxide and hydroxide layers. Major areas and major fractal dimension were obtained by using a polarity change.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aguilar MI, Sáez LM, Soler A, Ortuño JF (2003) Microscopic observation of particle reduction in slaughterhouse wastewater by coagulation-flocculation using ferric sulphate as coagulant and different coagulant aids. Water Res 37(9):2233–2241. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1354(02)00525-0
Barrios-Ziolo LF, Gaviria-Restrepo LF, Agudelo EA, Cardona Gallo SA (2015) Tecnologías para la remoción de colorantes y pigmentos presentes en aguas residuales. Dyna 82(191):118–126. https://doi.org/10.15446/dyna.v82n191.42924
Bayar S, Yildiz YS, Yilmaz AE, Irdemez S (2011) The effect of stirring speed and current density on removal efficiency of poultry slaughterhouse wastewater by electrocoagulation method. Desalination 280(1–3):103–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2011.06.061
Brillas E, Sirés I, Cabot PL (2010) Use of both anode and cathode reactions in wastewater treatment. In: Comninellis C, Chen G (eds) Electrochemistry for the environment. Springer, New York, pp 515–552. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-0-387-68318-8_19
Chakraborti RK, Gardner KH, Atkinson JF, Van Benschoten JE (2003) Changes in fractal dimension during aggregation. Water Res 37(4):873–883. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1354(02)00379-2
Donneys-Victoria D, Ospina-Toro CC, Zapata-Villegas MV, Marriaga-Cabrales N, Machuca-Martínez F, Peralta-Hérnandez JM, Martínez-Huitle CA (2018) Electrocoagulación de soluciones de índigo carmín empleando ánodos de magnesio y de aleación AZ31. DYNA 85(206):258–267. https://doi.org/10.15446/dyna.v85n206.71067
Elnenay AEMH, Nassef E, Malash GF, Magid MHA (2017) Treatment of drilling fluids wastewater by electrocoagulation. Egypt J Pet 26(1):203–208. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejpe.2016.03.005
Fekry AM, Tammam RH (2011) Corrosion and impedance studies on magnesium alloy in oxalate solution. Mater Sci Eng B 176(10):792–798. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mseb.2011.03.014
García-Morales MA, Roa-Morales G, Barrera-Díaz C, Miranda VM, Hernández PB, Silva TBP (2013) Integrated advanced oxidation process (ozonation) and electrocoagulation treatments for dye removal in denim effluents. Int J Electrochem Sci 8(6):8752–8763
Garcia-Segura S, Eiband MMSG, de Melo JV, Martínez-Huitle CA (2017) Electrocoagulation and advanced electrocoagulation processes: a general review about the fundamentals, emerging applications and its association with other technologies. J Electroanal Chem 801(July):267–299. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2017.07.047
He W, Nan J, Li H, Li S (2012) Characteristic analysis on temporal evolution of floc size and structure in low-shear flow. Water Res 46(2):509–520. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2011.11.040
Hu Y, Chen X, Liu Z, Wang G, Liao S (2016) Activated carbon doped with biogenic manganese oxides for the removal of indigo carmine. J Environ Manag 166:512–518. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2015.10.043
Kandelbauer A, Maute O, Kessler RW, Erlacher A, Gubitz GM (2004) Study of dye decolorization in an immobilized laccase enzyme-reactor using online spectroscopy. Biotechnol Bioeng 87(4):552–563. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.20162
Kant R (2012) Textile dyeing industry an environmental hazard. Nat Sci 4(1):22–26. https://doi.org/10.4236/ns.2012.41004
Khaled B, Wided B, Béchir H, Elimame E, Mouna L, Zied T (2015) Investigation of electrocoagulation reactor design parameters effect on the removal of cadmium from synthetic and phosphate industrial wastewater. Arab J Chem:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2014.12.012
Lee SY, Gagnon GA (2016a) Comparing the growth and structure of flocs from electrocoagulation and chemical coagulation. J Water Process Eng 10:20–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2016.01.012
Lee SY, Gagnon GA (2016b) Growth and structure of flocs following electrocoagulation. Sep Purif Technol 163:162–168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2016.02.049
Liang S, Zhang B, Shi J, Wang T, Zhang L, Wang Z, Chen C (2018) Bioelectrochemistry improved decolorization of dye wastewater in an electrochemical system powered by microbial fuel cells and intensified by micro-electrolysis. Bioelectrochemistry 124:112–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bioelechem.2018.07.008.
Manu B (2007) Physico-chemical treatment of indigo dye wastewater. Color Technol 123(3):197–202. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1478-4408.2007.00080.x
Oliveira C, Rodrigues RT, Rubio J (2010) A new technique for characterizing aerated flocs in a flocculation- microbubble flotation system. Int J Miner Process 96(1–4):36–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.minpro.2010.07.001
Palma-goyes RE, Silva-agredo J, González I, Torres-palma RA (2014) Electrochimica Acta comparative degradation of indigo carmine by electrochemical oxidation and advanced oxidation processes. Electrochim Acta 140:427–433. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2014.06.096
Pardo A, Merino MC, Coy AE, Arrabal R, Viejo F, Matykina E (2008) Corrosion behaviour of magnesium/aluminium alloys in 3.5 wt.% NaCl. Corros Sci 50(3):823–834. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.corsci.2007.11.005
Pi K-W, Xiao Q, Zhang H-Q, Xia M, Gerson AR (2014) Decolorization of synthetic methyl orange wastewater by electrocoagulation with periodic reversal of electrodes and optimization by RSM. Process Saf Environ Prot 92(6):796–806. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2014.02.008
Qu R, Xu B, Meng L, Wang L, Wang Z (2014) Ozonation of indigo enhanced by carboxylated carbon nanotubes: performance optimization, degradation products, reaction mechanism and toxicity evaluation. Water Res 68:316–327. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2014.10.017
Rajic L, Fallahpour N, Yuan S, Alshawabkeh A (2013) Electrochemical transformation of trichloroethylene in aqueous solution by electrode polarity reversal. Magn Reson Imaging 31(3):477–479. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2010.12.017.Two-stage
Ramesh TN, Sreenivasa VP (2015) Removal of indigo carmine dye from aqueous solution using magnesium hydroxide as an adsorbent. J Mater 2015(1):10–10. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/753057
Ramesh TN, Kirana DV, Ashwini A, Manasa TR (2014) Calcium hydroxide as low cost adsorbent for the effective removal of indigo carmine dye in water. J Saudi Chem Soc 21:165–171. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jscs.2015.03.001
Ren P, Nan J, Zhang X, Zheng K (2017) Analysis of floc morphology in a continuous-flow flocculation and sedimentation reactor. J Environ Sci (China) 52:268–275. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2016.04.007
Secula MS, Cretescu I, Petrescu S (2011) An experimental study of indigo carmine removal from aqueous solution by electrocoagulation. Desalination 277(1–3):227–235. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2011.04.031
Secula MS, Cagnon B, de Oliveira TF, Chedeville O, Fauduet H (2012) Removal of acid dye from aqueous solutions by electrocoagulation/GAC adsorption coupling: kinetics and electrical operating costs. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 43(5):767–775. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2012.03.003
Semerjian L, Ayoub G (2003) High pH magnesium coagulation flocculation in wastewater treatment. Adv Environ Res 7:389–403
Shammas NK, Pouet M-F, Grasmick A (2010) Wastewater treatment by electrocoagulation–flotation. In: Wang L, Shammas N, Selke W, Aulenbach D (eds) Flotation technology, handbook of environmental engineering, vol 12. Humana Press, Totowa, pp 199–220. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-60327-133-2_6
Shi J, Zhang B, Liang S, Li J, Wang Z (2018) Simultaneous decolorization and desalination of dye wastewater through electrochemical process. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:8455–8464. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-1159-8
Singh IB, Singh M, Das S (2015) A comparative corrosion behavior of Mg, AZ31 and AZ91 alloys in 3.5% NaCl solution. J Magnesium Alloys 3(2):142–148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jma.2015.02.004
Superintendencia de sociedades (2017) Desempeño del sector textil - confección. Retrieved from https://incp.org.co/Site/publicaciones/info/archivos/Textiles.pdf. Accessed 26 May 2018
Tan J, Wang J, Wang L, Xu J, Sun D (2011) In situ formed Mg(OH)2 nanoparticles as pH-switchable stabilizers for emulsions. J Colloid Interface Sci 359(1):155–162. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2010.10.038
Thomas S, Medhekar NVV, Frankel GSS, Birbilis N (2015) Corrosion mechanism and hydrogen evolution on mg. Curr Opinion Solid State Mater Sci 19(2):85–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cossms.2014.09.005
Vong YM, Garey DG (2014) Wastewater treatment by electrocoagulation. In: Kreysa G, Ota K, Savinell RF (eds) Encyclopedia of applied electrochemistry. Springer, New York, pp 2117–2122. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4419-6996-5
Wei L, Zhao J, Xu C, Liu M (2014) Experimental analysis of magnesium hydroxide-reactive orange floc formation time and rate in coagulation process. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 45(5):2605–2609. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2014.06.016
Zaghouane-Boudiaf H, Boutahala M, Arab L (2012) Removal of methyl orange from aqueous solution by uncalcined and calcined MgNiAl layered double hydroxides (LDHs). Chem Eng J 187:142–149. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2012.01.112
Zhao J, Su R, Guo X, Li W, Feng N (2014) Role of mixing conditions on coagulation performance and flocs breakage formed by magnesium hydroxide. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 45(4):1685–1690. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2013.12.014
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge Universidad del Valle (Cali, Colombia) for supporting the study under Grant No. 2863: Electrocoagulation of textile industrial effluents using magnesium. Case study of indigo carmine solutions and Departamento Administrativo de Ciencia, Tecnología e Innovación-Colciencias (Colombia) for the National Doctorate Scholarship of one of the authors. Additionally, the contribution of Augusto Gómez and Maria Patricia Trujillo from Systems Engineering and Computational Sciences Department from Universidad del Valle for image analysis software and the contribution of the research group Procesos Avanzados para Tratamientos Biológicos y Químicos (GAOX) from same university is recognized.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Bingcai Pan
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Donneys-Victoria, D., Bermúdez-Rubio, D., Torralba-Ramírez, B. et al. Removal of indigo carmine dye by electrocoagulation using magnesium anodes with polarity change. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26, 7164–7176 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-04160-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-04160-y