Abstract
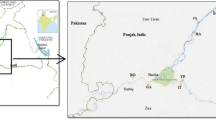
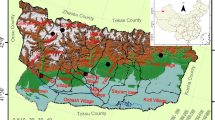
The farmland irrigation with the sewage is a common and better pathway to save the resource of groundwater in Northern China. The investigation was conducted in the farmland along the Fuhe River to explore characteristics of heavy metals in soils and grains of wheat and maize from a long-term sewage-irrigated area of Baoding region. The results showed that the topsoil with long-term sewage irrigation accumulated more Cd, Pb, and Hg compared with that of soil irrigated with groundwater and their corresponding natural background values. Cd concentrations in 48% of sewage-irrigated soil samples exceeded the Chinese safety limitation at 0.6 mg/kg, but less Cd accumulated in crop grains and did not pose the potential health risk. On the contrary, Pb levels in soils irrigated with sewage were lower than the safety limitation but Pb concentrations in 24% of wheat grain samples exceeded the Chinese national safety limit. Long-term sewage irrigation did not increase As, Cr, and Ni concentrations in soils or crop grains. The target hazard quotient (THQ) of heavy metals in edible grains of crops was selected to assess their risk to human health. Total THQ values were higher than 1.0 for the wheat samples from sewage-irrigated area and both sewage-irrigated and smelter-impacted areas, and As is the main contributor to the total THQ and posed the potential risk to human health. Therefore, the accumulation of Cd, Pb, Hg, and As in soils and crops in sewage-irrigated area should be monitored continuously to ensure food safety and security.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amin NU, Hussain A, Alamzeb S, Begum S (2013) Accumulation of heavy metals in edible parts of vegetables irrigated with waste water and their daily intake to adults and children, district Mardan, Pakistan. Food Chem 136:1515–1523
Cao C, Chen XP, Ma ZB, Jia HH, Wang JJ (2016) Greenhouse cultivation mitigates metal-ingestion-associated health risks from vegetables in wastewater-irrigated agroecosystems. Sci Total Environ 560-561:204–211
CEPA and CGSEM (1990) Soil chemical element background values of China. Chinese Environmental Protection Agency, Chinese General Station of Environmental Monitoring. Chinese Environmental Science, Beijing (in Chinese)
Chen ZF, Zhao Y, Zhu Y, Yang X, Qiao J, Tian Q, Zhang Q (2010) Health risks of heavy metals in sewage-irrigated soils and edible seeds in Langfang of Hebei Province, China. J Sci Food Agric 90:314–320
Chen W, Lu S, Peng C, Jiao W, Wang M (2013) Accumulation of Cd in agricultural soil under long-term reclaimed water irrigation. Environ Pollut 178:294–299
Clemens S, Ma JF (2016) Toxic heavy metal and metalloid accumulation in crop plants and foods. Annu Rev Plant Biol 67:489–512
Du P, Xie YF, Wang SJ, Zhao HH, Zhang Z, Wu B, Li FS (2015) Potential sources of and ecological risks from heavy metals in agricultural soils, Daye City, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:3498–3507
Gray C, McLaren R, Roberts A (2003) Atmospheric accessions of heavy metals to some New Zealand pastoral soils. Sci Total Environ 305:105–115
Hu GC, Xu ZC, Dai JY, Mai BX, Cao H, Wang JS, Shi ZM, Xu MQ (2010) Distribution of polybrominated diphenylethers and decabromodiphenylethane in surface sediments from Fuhe River and Baiyangdian Lake, North China. J Environ Sci 22(12):1833–1839
Huang SS, Liao QL, Hua M, Wu XM, Bi KS, Yan CY, Chen B, Zhang XY (2007) Survey of heavy metal pollution and assessment of agricultural soil in Yangzhong District, Jiangsu Province, China. Chemosphere 67:2148–2155
Huang M, Zhou S, Sun B, Zhao Q (2008) Heavy metals in wheat grain: assessment of potential health risk for inhabitants in Kunshan, China. Sci Total Environ 405:54–61
Khan S, Cao Q, Zheng YM, Huang YZ, Zhu YG (2008) Health risks of heavy metals in contaminated soils and food crops irrigated with wastewater in Beijing, China. Environ Pollut 152:686–692
Khan MU, Malik RN, Muhammad S (2013) Human health risk from heavy metal via food crops consumption with wastewater irrigation practices in Pakistan. Chemosphere 93:2230–2238
Li P, Wang X, Allinson G, Li X, Xiong X (2009) Risk assessment of heavy metals in soil previously irrigated with industrial wastewater in Shenyang, China. J Hazard Mater 161:516–521
Liang J, Feng CT, Zeng GM, Gao X, Zhong MZ, Li XD, Li X, He XY, Fang YL (2017) Spatial distribution and source identification of heavy metals in surface soils in a typical coal mine city, Lianyuan, China. Environ Pollut 225:681–690
Liu WH, Zhao JZ, Ouyang ZY, Soderlund L, Liu GH (2005) Impacts of sewage irrigation on heavy metal distribution and contamination in Beijing, China. Environ Int 31:805–812
Liu B, Ma X, Ai S, Zhu S, Zhang W, Zhang Y (2016) Spatial distribution and source identification of heavy metals in soils under different land uses in a sewage irrigation region, Northwest China. J Soils Sediments 16:1547–1556
Lottermoser BG (2012) Effect of long-term irrigation with sewage effluent on the metal content of soils, Berlin, Germany. Environ Geochem Health 34:67–76
MEE and SAMR (2018) Chinese soil environmental quality, risk control standard for soil contamination of agricultural land. Ministry of Ecological and Environment of People’s Republic of China, State Administration for Market Regulation. GB15618-2018 (in Chinese)
Meng W, Wang Z, Hu B, Wang Z, Li H, Goodman RC (2016) Heavy metals in soil and plants after long-term sewage irrigation at Tianjin China: a case study assessment. Agric Water Manag 171:153–161
Muchuweti M, Birkett JW, Chinyanga E, Zvauya R, Scrimshaw MD, Lester JN (2006) Heavy metal content of vegetables irrigated with mixtures of wastewater and sewage sludge in Zimbabwe: implications for human health. Agric Ecosyst Environ 112:41–48
NHFPC and SFDA (2017) National food safety standard. National Health and Family Planning Commission, State Food and Drug Administration. GB2762-2017 (in Chinese)
Pereira BFF, He ZL, Stoff PJ, Montes CR, Melfi AJ, Baligar VC (2012) Nutrients and nonessential elements in soil after 11 years of wastewater irrigation. J Environ Qual 41:920–927
Qi Y, Wang Z, Pei Y (2012) Evaluation of water quality and nitrogen removal bacteria community in Fuhe River, the 18th biennial conference of International Society for Ecological Modelling. Procedia Environ Sci 13:1809–1819
Rattan RK, Datta SP, P k C, Suribabu K, Singh AK (2005) Long-term impact of irrigation with sewage effluents on heavy metal content in soils, crops and groundwater—a case study. Agric Ecosyst Environ 109:310–322
Rothenberg SE, Du X, Zhu YG, Jay JA (2007) The impact of sewage irrigation on the uptake of mercury in corn plants (Zea mays) from suburban Beijing. Environ Pollut 149:246–251
Sabin LD, Lim JH, Stolzenbach KD, Schiff KC (2006) Atmospheric dry deposition of trace metals in the coastal region of Los Angeles, California, USA. Environ Toxicol Chem 25:2334–2341
Saha S, Hazra GC, Saha B, Mandal B (2015) Assessment of heavy metals contamination in different crops grown in long-term sewage-irrigated areas of Kolkata, West Bengal, India. Environ Monit Assess 187:4087
Singh PK, Deshbhratar PB, Ramteke DS (2012) Effects of sewage wastewater irrigation on soil properties, crop yield and environment. Agric Water Manag 103:100–104
Sun CY, Liu JS, Wang Y, Sun LQ, Yu HW (2013) Multivariate and geostatistical analyses of the spatial distribution and sources of heavy metals in agricultural soil in Dehui, Northeast China. Chemosphere 92:517–523
Sun HX, Yang Y, Wang QQ, Guan PB, Xue PY, Liu WJ (2015a) An investigation of the situation of sewage irrigation and local farmers concern the relationship between sewage irrigation and human health along the Fu Rive. Chin Agric Sci Bull 2:197–200 (in Chinese)
Sun YF, Wang ZW, Meng WQ, Hu BB, Hu YY, Wang ZL, Zhang H (2015b) Contents and health risk assessment of heavy metals in wheat and rice grown in Tianjin sewage irrigation area, China. J Agro-Environ Sci 4:769–685 (in Chinese)
Tang J, Bai X, Zhang W (2011) Cadmium pollution and its transfer in agricultural systems in the suburbs of Tianjin, China. Soil Sediment Contam 20:722–732
Teng Y, Wu J, Lu S, Wang Y, Jiao X, Song L (2014) Soil and soil environmental quality monitoring in China: a review. Environ Int 69:177–199
UNEP (2008) Draft final review of scientific information on cadmium. http://www.unep.org/hazardoussubstances/Portals/9/Lead_Cadmium/docs/Interim_reviews/Final_UNEP_Cadmium_review_Nov_2008.pdf. Accessed Nov 2008
USEPA (2000) Risk-based concentration table. United States Environmental Protection Agency,Washington DC, Philadelphia
USEPA IRIS (2015) United States, Environmental Protection Agency, Integrated Risk Information System. http://www.epa.gov/iris. Accessed 05 July 2017
Wang Y, Qiao M, Liu Y, Zhu Y (2012) Health risk assessment of heavy metals in soils and vegetables from wastewater irrigated area, Beijing-Tianjin City cluster, China. J Environ Sci 24:690–698
Xu J, Wu LS, Chang AC, Zhang Y (2010) Impact of long-term reclaimed wastewater irrigation on agricultural soils: a preliminary assessment. J Hazard Mater 183:780–786
Xue ZJ, Liu SQ, Liu YL, Yan YL (2012) Health risk assessment of heavy metals for edible parts of vegetables grown in sewage-irrigated soils in suburbs of Baoding City, China. Environ Monit Assess 184:3503–3513
Yang P, Mao R, Shao H, Gao Y (2009) An investigation on the distribution of eight hazardous heavy metals in the suburban farmland of China. J Hazard Mater 167:1246–1251
Yi LL, Jiao WT, Chen XN, Chen WP (2011) An overview of reclaimed water reuse in China. J Environ Sci 23:1585–1593
Zhang XM, Tang YJ, Zhang S (1997) Study on the content and distribution of contamination in soil-plant system in Baiyangdian region. Prog Geogr 1(2):62–69 (in Chinese)
Zhao FJ, Ma Y, Zhu YG, Tang Z, McGrath SP (2015) Soil contamination in China: current status and mitigation strategies. Environ Sci Technol 49:750–759
Zhu YE, Zhao Y, Sun K, Chen ZF, Qiao JJ, Ji YQ (2011) Heavy metals in wheat grain and soil: assessment of the potential health risk for inhabitants. Fresenius Environ Bull 20:1109–1116
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China (grant number 41471398); the National Science Foundation for Young Scientists of Hebei Province, China (grant number D2015204109); the Foundation for Young Talents in Higher Education of Hebei Province, China (grant number BJ2014033); and the Global Research Project of International Environmental Research Institute (IERI).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Zhihong Xu
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 42.9 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xue, P., Zhao, Q., Sun, H. et al. Characteristics of heavy metals in soils and grains of wheat and maize from farmland irrigated with sewage. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26, 5554–5563 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-3997-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-3997-4