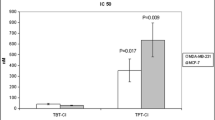
Abstract
Selective estrogen receptor modulators such as tamoxifen (TAM) significantly reduce the risks of developing estrogen receptor–positive (ER+) breast cancer. Low concentrations (nanomolar range) of bisphenol A (BPA) shows estrogenic effects and further promotes the proliferation of hormone-dependent breast cancer cells. However, whether or not BPA can influence TAM-treatment resistance in breast cancer has not drawn much attention. In the current study, low concentrations of BPA reduced TAM-induced cytotoxicity of MCF-7 cells, which was proved by the suppression of cell apoptosis, transition of cell cycle from G1 to S phase, and upregulation of cyclin D1 and ERα. Simultaneously, the mRNA levels of estrogen-related receptor γ (ERRγ) and its coactivators, peroxisome proliferation–activated receptor γ coactivator-1α (PGC-1α), and PGC-1β, were increased. However, the similar effects were not observed in MDA-MB-231 cells. Our results indicated that low concentrations of BPA decreased the sensitivity of TAM in MCF-7 cells rather than in MDA-MB-231 cells. These different actions likely involved the interaction of relative receptors and coactivators. This study provided a possible support that the exposure of BPA in environmental media may potentially induce TAM resistance to breast cancer treatment.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abad MC, Askari H, O’Neill J, Klinger AL, Milligan C, Lewandowski F, Springer B, Spurlino J, Rentzeperis D (2008) Structural determination of estrogen-related receptor γ in the presence of phenol derivative compounds. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 108(1–2):44–54
Andersen HR, Andersson AM, Arnold SF, Autrup H, Barfoed M, Beresford NA, Bjerregaard P, Christiansen LB, Gissel B, Hummel R, Jørgensen EB, Korsgaard B, Guevel RL, Leffers H, McLachlan J, Møller A, Nielsen JB, Olea N, Oles-Karasko A, Pakdel F, Pedersen KL, Perez P, Skakkebœk NE, Sonnenschein C, Soto AM, Sumpter JP, Thorpe SM, Grandjean P (1999) Comparison of short-term estrogenicity tests for identification of hormone-disrupting chemicals. Environ Health Persp 107(Suppl 1):89–108
Chen ZJ, Yang XL, Liu H, Wei W, Zhang KS, Huang HB, Giesy JP, Liu HL, Du J, Wang HS (2015) Bisphenol A modulates colorectal cancer protein profile and promotes the metastasis via induction of epithelial to mesenchymal transitions. Arch Toxicol 89(8):1371–1381
Coates AS, Keshaviah A, Thürlimann B, Mouridsen H, Mauriac L, Forbes JF, Paridaens R, Castiglione-Gertsch M, Gelber RD, Colleoni M, Láng I, Mastro LD, Smith I, Chirgwin J, Nogaret JM, Pienkowski T, Wardley A, Jakobsen EH, Price KN, Goldhirsch A (2007) Five years of letrozole compared with tamoxifen as initial adjuvant therapy for postmenopausal women with endocrine-responsive early breast cancer: update of study BIG 1-98. J Clin Oncol 25(5):486–492
Cover CM, Hsieh SJ, Cram EJ, Hong C, Riby JE, Bjeldanes LF, Firestone GL (1999) Indole-3-carbinol and tamoxifen cooperate to arrest the cell cycle of MCF-7 human breast cancer cells. Cancer Res 59(6):1244–1251
Dairkee SH, Luciani-torres MG, Moore DH (2013) Bisphenol-A-induced inactivation of the p53 axis underlying deregulation of proliferation kinetics, and cell death in non-malignant human breast epithelial cells. Carcinogenesis 34:703–712
Delgado M, Ribeiro-Varandas E (2015) Bisphenol a at the reference level counteracts doxorubicin transcriptional effects on cancer related genes in HT29 cells. Toxicol in Vitro 29(8):2009–2014
Diel P, Olff S, Schmidt S, Michna H (2002) Effects of the environmental estrogens bisphenol A, o, p′-DDT, p-tert-octylphenol and coumestrol on apoptosis induction, cell proliferation and the expression of estrogen sensitive molecular parameters in the human breast cancer cell line MCF-7. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 80(1):61–70
Evan GI, Vousden KH (2001) Proliferation, cell cycle and apoptosis in cancer. Nature 411(6835):342–348
Geens T, Aerts D, Berthot C, Bourguignon JP, Goeyens L, Lecomte P, Maghuin-Rogister G, Pironnet AM, Pussemier L, Scippo ML, Loco JV, Covaci A (2012) A review of dietary and non-dietary exposure to bisphenol-A. Food Chem Toxicol 50(10):3725–3740
Giguère V (2008) Transcriptional control of energy homeostasis by the estrogen-related receptors. Endocr Rev 29(6):677–696
Girard BJ, Anderson TMR, Welch SL, Nicely J, Seewaldt VL, Ostrander JH (2015) Cytoplasmic PELP1 and ERRgamma protect human mammary epithelial cells from tam-induced cell death. PLoS One 10(3):e0121206
Goodson WH III, Luciani MG, Sayeed SA, Jaffee IM, Moore IIDH, Dairkee SH (2011) Activation of the mTOR pathway by low levels of xenoestrogens in breast epithelial cells from high-risk women. Carcinogenesis 32(11):1724–1733
Gould JC, Leonard LS, Maness SC, Wagner BL, Conner K, Zacharewski T, Safe S, McDonnell DP, Gaido KW (1998) Bisphenol A interacts with the estrogen receptor α in a distinct manner from estradiol. Mol Cell Endocrinol 142(1):203–214
Hoekstra EJ, Simoneau C (2013) Release of bisphenol A from polycarbonate—a review. Crit Rev Food Sci 53(4):386–402
Hong H, Yang L, Stallcup MR (1999) Hormone-independent transcriptional activation and coactivator binding by novel orphan noclear receptor ERR3. J Biol Chem 274(32):22618–22626
Im J, Loffler FE (2016) Fate of bisphenol A in terrestrial and aquatic environments. Environ Sci Technol 50(16):8403–8416
Jacobson MD, Weil M, Raff MC (1997) Programmed cell death in animal development. Cell 88(3):347–354
Katchy A, Pinto C, Jonsson P, Nguyen-Vu T, Pandelova M, Riu A, Schramm KW, Samarov D, Gustafsson JÅ, Bondesson M, Williams C (2013) Coexposure to phytoestrogens and bisphenol A mimics estrogenic effects in an additive manner. Toxicol Sci 138(1):21–35
Kelly PN, Strasser A (2011) The role of Bcl-2 and its pro-survival relatives in tumourigenesis and cancer therapy. Cell Death Differ 18(9):1414–1424
Kim HS, Ishizaka M, Kazusaka A, Fujita S (2007) Di-(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate suppresses tamoxifen-induced apoptosis in GH3 pituitary cells. Arch Toxicol 81(1):27–33
Kuiper GGJM, Lemmen JG, Carlsson BO, Corton JC, Safe SH, Saag PTVD, Burg BVD, Gustafsson JÅ (1998) Interaction of estrogenic chemicals and phytoestrogens with estrogen receptor β. Endocrinology 139(10):4252–4263
LaPensee EW, Tuttle TR, Fox S, Ben-Jonathanet N (2009) Bisphenol A at low nanomolar doses confers chemoresistance in estrogen receptor-α–positive and–negative breast cancer cells. Environ Health Persp 117(2):175–180
LaPensee EW, LaPensee CR, Fox S, Schwemberger S, Afton S, Ben-Jonathanet N (2010) Bisphenol A and estradiol are equipotent in antagonizing cisplatin-induced cytotoxicity in breast cancer cells. Cancer Lett 290(2010):167–173
La Rosa P, Pellegrini M, Totta P, Acconcia F, Marino M (2014) Xenoestrogens alter estrogen receptor (ER) α intracellular levels. PLoS One 9(2):e88961
Lee SY, Ahn BT, Baik SH, Baik SH, Lee BL (1998) Tamoxifen inhibits GH3 cell growth in culture via enhancement of apoptosis. Neurosurgery 43(1):116–123
Lee HR, Hwang KA, Park MA (2012) Treatment with bisphenol A and methoxychlor results in the growth of human breast cancer cells and alteration of the expression of cell cycle-related genes, cyclin D1 and p21, via an estrogen receptor-dependent signaling pathway. Int J Mol Med 29(5):883–890
Li Y, Birnbaumer L, Teng CT (2010) Regulation of ERRα gene expression by estrogen receptor agonists and antagonists in SKBR3 breast cancer cells: differential molecular mechanisms mediated by G protein-coupled receptor GPR30/GPER-1. Mol Endocrinol 24(5):969–980
Lillo MA, Nichols C, Seagroves TN, Miranda-Carboni GA, Krum SA (2017) Bisphenol A induces Sox2 in ER+ breast cancer stem-like cells. Horm Cancer-US 8(2):90–99
Liu H, Chen F, Zhang L, Zhou Q, Gui S, Wang Y (2016) A novel all-trans retinoic acid derivative 4-amino-2-trifluoromethyl-phenyl retinate inhibits the proliferation of human hepatocellular carcinoma HepG2 cells by inducing G0/G1 cell cycle arrest and apoptosis via upregulation of p53 and ASPP1 and downregulation of iASPP. Oncol Rep 36(1):333–341
Loi S, Haibe-Kains B, Desmedt C, Wirapati P, Lallemand F, Tutt AM, Gillet C, Ellis P, Ryder K, Reid JF, Daidone MG, Pierotti MA, Berns EM, Jansen MPHM, Foekens JA, Delorenzi M, Bontempi G, Piccart MJ, Sotiriou C (2008) Predicting prognosis using molecular profiling in estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer treated with tamoxifen. BMC Genomics 9(1):239
Luciani-Torres MG, Moore DH, Goodson IIIWH, Dairkee SH (2014) Exposure to the polyester PET precursor—terephthalic acid induces and perpetuates DNA damage-harboring non-malignant human breast cells. Carcinogenesis 36(1):168–176
Madhavan S, Gusev Y, Singh S, Riggins RB (2015) ERRγ target genes are poor prognostic factors in tamoxifen-treated breast cancer. J Exp Clin Canc Res 34(1):45
Mandlekar S, Yu R, Tan TH, Kong ANT (2000) Activation of caspase-3 and c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase-1 signaling pathways in tamoxifen-induced apoptosis of human breast cancer cells. Cancer Res 60(21):5995–6000
Matsushima A, Kakuta Y, Teramoto T, Koshiba T, Liu X, Okada H, Tokunaga T, Kawabata S, Kimura M, Shimohigashi Y (2007) Structural evidence for endocrine disruptor bisphenol A binding to human nuclear receptor ERRγ. J Biochem 142(4):517–524
Mesner PW, Budihardjo II (1997) Kaufmann SH. Chemotherapy-induced apoptosis. Adv Pharmacol 41: 461–499
Michałowicz J (2014) Bisphenol A–sources, toxicity and biotransformation. Environ Toxicol Phar 37(2):738–758
Nigam M, Ranjan V, Srivastava S, Sharma R, Balapure AK (2008) Centchroman induces G0/G1 arrest and caspase-dependent apoptosis involving mitochondrial membrane depolarization in MCF-7 and MDA MB-231 human breast cancer cells. Life Sci 82(11):577–590
Okada H, Tokunaga T, Liu XH, Takayanagi S, Matsushima A, Shimohigashi Y (2008) Direct evidence revealing structural elements essential for the high binding ability of bisphenol A to human estrogen-related receptor-γ. Environ Health Persp 116(1):32–38
Osborne CK, Schiff R (2011) Mechanisms of endocrine resistance in breast cancer. Annu Rev Med 62:233–247
Peyrade F, Frenay M, Etienne MC, Ruch F, Guillemare C, Francois E, Namer M, Ferrece JM, Milano G (1996) Age-related difference in tamoxifen disposition. Clin Pharmacol Ther 59(4):401–410
Pfeifer D, Chung YM, Hu MCT (2015) Effects of low-dose bisphenol A on DNA damage and proliferation of breast cells: the role of c-Myc. Environ Health Persp 123(12):1271–1279
Riggins RB, Lan JPJ, Klimach U, Zwart A, Cavalli LR, Haddad BR, Chen L, Gong T, Xuan J, Ethier SP, Clarke R (2008) ERRγ mediates tamoxifen resistance in novel models of invasive lobular breast cancer. Cancer Res 68(21):8908–8917
Schwartz GK, Shah MA (2015) Targeting the cell cycle: a new approach to cancer therapy. J Clin Oncol 23(36):9408–9421
Song H, Zhang T, Yang P, Li MH, Yang YH, Wang YY, Du J, Pan KJ, Zhang K (2015) Low doses of bisphenol A stimulate the proliferation of breast cancer cells via ERK1/2/ERRγ signals. Toxicol in Vitro 30(1):521–528
Suzuki T, Miki Y, Moriya T, Shimada N, Ishida T, Hirakawa H, Ohuchi N, Sasano H (2004) Estrogen-related receptor α in human breast carcinoma as a potent prognostic factor. Cancer Res 64(13):4670–4676
Thiantanawat A, Long BJ, Brodie AM (2003) Signaling pathways of apoptosis activated by aromatase inhibitors and antiestrogens. Cancer Res 63(22):8037–8050
Vandenberg LN, Maffini MV, Sonnenschein C, Rubin S, Soto AM (2009) Bisphenol-A and the great divide: a review of controversies in the field of endocrine disruption. Endocr Rev 30(1):75–95
Vandenberg LN, Chahoud I, Heindel JJ, Padmanabhan V, Paumgartten FJR, Schoenfelder G (2010) Urinary, circulating, and tissue biomonitoring studies indicate widespread exposure to bisphenol A. Environ Health Persp 118(8):1055–1070
Vandenberg LN, Colborn T, Hayes TB, Heindel JJ, Jacobs DR, Lee DH, Shioda T, Soto AM, Saal FS, Welshons WV, Zoeller RT, Myers JP (2012) Hormones and endocrine-disrupting chemicals: low-dose effects and nonmonotonic dose responses. Endocr Rev 33(3):378–455
Wang Z, Liu HY, Liu SJ (2017) Low-dose bisphenol A exposure: a seemingly instigating carcinogenic effect on breast cancer. Adv Sci 4(2):1600248
Wetherill YB, Akingbemi BT, Kanno J, McLachlan JA, Nadal A, Sonnenschein C, Watson CS, Zoeller RT, Belcher SM (2007) In vitro molecular mechanisms of bisphenol A action. Reprod Toxicol 24(2):178–198
Wu J, Jiang Y, Cao W, Li X, Xie C, Geng S (2018) mir-19 targeting of pten mediates butyl benzyl phthalate-induced proliferation in both ER(+) and ER(-) breast cancer cells. Toxicol Lett 295:124–133
Xu ZX, Liu J, Gu LP, Ma XD, Huang B, Pan XJ (2016) Research progress on the reproductive and non-reproductive endocrine tumors by estrogen-related receptors. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 158:22–30
Xu ZX, Liu J, Gu LP, Huang B, Pan XJ (2017a) Biological effects of xenoestrogens and the functional mechanisms via genomic and nongenomic pathways. Environ Rev 25(3):306–322
Xu ZX, Liu J, Wu XH, Huang B, Pan XJ (2017b) Nonmonotonic responses to low doses of xenoestrogens: a review. Environ Res 155:199–207
Xu ZX, Huang B, Liu J, Wu XH, Luo N, Wang XX, Zheng ZY, Pan XJ (2018) Combinatorial anti-proliferative effects of tamoxifen and naringenin: the role of four estrogen receptor subtypes. Toxicology 410:231–246
Yeh WL, Lin HY, Wu HM, Chen DR (2014) Combination treatment of tamoxifen with risperidone in breast cancer. PLoS One 9(6):e98805
Zuccarello P, Oliveri CG, Cavallaro F, Copat C, Cristaldi A, Fiore M, Ferrante M (2018) Implication of dietary phthalates in breast cancer: a systematic review. Food Chem Toxicol 118:667–674
Funding
This project was sponsored by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant no. 21567014) and the Yunnan Province Scholarship Award (Grant no. 1319880239).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 68 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, B., Luo, N., Wu, X. et al. The modulatory role of low concentrations of bisphenol A on tamoxifen-induced proliferation and apoptosis in breast cancer cells. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26, 2353–2362 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-3780-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-3780-6