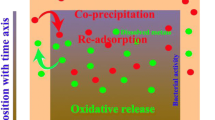
Abstract
Development of mineral resources and the increasing mining waste emissions have created a series of environmental and health-related issues. Nowadays, the ecological restoration of mining tailings has become one of the urgent tasks for mine workers and environmental engineers all over the world. Aim of the present paper is to highlight the previous restoration techniques and the challenges encountered during the restoration of mine tailings. As it is a common practice that, before restoring of tailings, the site should be evaluated carefully. Studies showed that the mine tailings’ adverse properties, including excessive heavy metal concentration, acidification, improper pH value, salinization and alkalization, poor physical structure and inadequate nutrition, etc., are the major challenges of their restoration. Generally, four restoration technologies, including physical, chemical, phytoremediation, and bioremediation, are used to restore the mining tailings. The working mechanism, advantages, and disadvantages of these techniques are described in detail. In addition, selection of the suitable restoration techniques can largely be carried out by considering both the economic factors and time required. Furthermore, the ecosystem restoration is perceived to be a more promising technology for mine tailings. Therefore, this extensive review can act as a valuable reference for the researchers involved in mine tailing restoration.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abumaizar RJ, Smith EH (1999) Heavy metal contaminants removal by soil washing. J Hazard Mater 70:71–86
Acar YB, Alshawabkeh AN (1993) Principles of electrokinetic remediation. Environ Sci Technol 27:2638–2647
Adiansyah JS, Rosano M, Vink S, Keir G (2015) A framework for a sustainable approach to mine tailings management: disposal strategies. J Clean Prod 108:1050–1062
Akcil A, Koldas S (2006) Acid mine drainage (AMD): causes, treatment and case studies. J Clean Prod 14:1139–1145
Alcantara HJP, Doronila AI, Nicolas M, Ebbs SD, Kolev SD (2015) Growth of selected plant species in biosolids-amended mine tailings. Miner Eng 80:25–32
Álvarez E, Fernández-Sanjurjo M, Otero XL, Macías F (2010) Aluminium geochemistry in the bulk and rhizospheric soil of the species colonising an abandoned copper mine in Galicia (NW Spain). J Soils Sediments 10:1236–1245
Antonovics J, Bradshaw AD, Turner RG (1971) Heavy metal tolerance in plants. Adv Ecol Res 7:1–85
Asensio V, Vega FA, Singh BR, Covelo EF (2013a) Effects of tree vegetation and waste amendments on the fractionation of Cr, Cu, Ni, Pb and Zn in polluted mine soils. Sci Total Environ 443:446–453
Asensio V, Covelo EF, Kandeler E (2013b) Soil management of copper mine tailing soils—sludge amendment and tree vegetation could improve biological soil quality. Sci Total Environ 456-457:82–90
Babel S, Kurniawan TA (2003) Low-cost adsorbents for heavy metals uptake from contaminated water: a review. J Hazard Mater 97:219–243
Banerjee R, Goswami P, Pathak K, Mukherjee A (2016) Vetiver grass: an environment clean-up tool for heavy metal contaminated iron ore mine-soil. Ecol Eng 90:25–34
Barona A, Aranguiz I, Elías A (2001) Metal associations in soils before and after EDTA extractive decontamination: implications for the effectiveness of further clean-up procedures. Environ Pollut 113:79–85
Beesley L, Morenojiménez E, Gomezeyles JL (2010) Effects of biochar and greenwaste compost amendments on mobility, bioavailability and toxicity of inorganic and organic contaminants in a multi-element polluted soil. Environ Pollut 158:2282–2287
Bell LC (2001) Establishment of native ecosystems after mining—Australian experience across diverse biogeographic zones. Ecol Eng 17:179–186
Benschoten JEV, Matsumoto MR, Young WH (1997) Evaluation and analysis of soil washing for seven lead-contaminated soils. J Environ Eng 123:217–224
Bhattacharya A, Routh J, Jacks G, Bhattacharya P, Mörth M (2006) Environmental assessment of abandoned mine tailings in Adak, Västerbotten district (northern Sweden). Appl Geochem 21:1760–1780
Blaylock MJ, Salt DE, Dushenkov S, Zakharova O, Gussman C, Kapulnik Y, Ensley BD, Raskin I (1997) Enhanced accumulation of Pb in Indian mustard by soil-applied chelating agents. Environ Sci Technol 31:860–865
Boonstra J, Lier RV, Janssen G, Dijkman H, Buisman CJN (1999) Biological treatment of acid mine drainage. Process Metall 9:559–567
Bradshaw A (1997) Restoration of mined lands—using natural processes. Ecol Eng 8:255–269
Bradshaw AD, Hüttl RF (2001) Future minesite restoration involves a broader approach. Ecol Eng 17:87–90
Brooks RR (1998) Plants that hyperaccumulate heavy metals: their role in phytoremediation, microbiology, archaeology, mineral exploration and phytomining. J Environ Qual 28:1045
Cao XD, Wang XR, Zhao GW (2000) Assessment of the bioavailability of rare earth elements in soils by chemical fractionation and multiple regression analysis. Chemosphere 40:23–28
Cao X, Chen Y, Wang X, Deng X (2001) Effects of redox potential and pH value on the release of rare earth elements from soil. Chemosphere 44:655–661
Cao X, Ma LQ, Chen M, Singh SP, Harris WG (2002) Impacts of phosphate amendments on lead biogeochemistry at a contaminated site. Environ Sci Technol 36:5296–5304
Cao RX, Ma LQ, Chen M, Singh SP, Harris WG (2003) Phosphate-induced metal immobilization in a contaminated site. Environ Pollut 122:19–28
Cao X, Ma LQ, Rhue DR, Appel CS (2004): Mechanisms of lead, copper, and zinc retention by phosphate rock, 435–444 pp
Chen HM, Zheng CR, Tu C, Shen ZG (2000) Chemical methods and phytoremediation of soil contaminated with heavy metals. Chemosphere 41:229–234
Chen F, Wang S, Mou S, Azimuddin I, Zhang D, Pan X, Al-Misned FA, Mortuza MG (2015) Physiological responses and accumulation of heavy metals and arsenic of Medicago sativa L. growing on acidic copper mine tailings in arid lands. J Geochem Explor 157:27–35
Cheng Y, Huang F, Li W, Liu R, Li G, Wei J (2016) Test research on the effects of mechanochemically activated iron tailings on the compressive strength of concrete. Constr Build Mater 118:164–170
Ciarkowska K, Hanus-Fajerska E, Gambus F, Muszynska E, Czech T (2017) Phytostabilization of Zn-Pb ore flotation tailings with Dianthus carthusianorum and Biscutella laevigata after amending with mineral fertilizers or sewage sludge. J Environ Manag 189:75–83
Courtney R, Kirwan L (2012) Gypsum amendment of alkaline bauxite residue—plant available aluminium and implications for grassland restoration. Ecol Eng 42:279–282
Courtney RG, Timpson JP (2005) Nutrient status of vegetation grown in alkaline bauxite processing residue amended with gypsum and thermally dried sewage sludge—a two year field study. Plant Soil 266:187–194
Craze B (1977) Investigations into the revegetation problems of captains flat mining area. J Soil Conserv Serv N S W 16:204–204
Deram A, Denayer FO, Dubourgier HC, Douay F, Petit D, Van Haluwyn C (2007) Zinc and cadmium accumulation among and within populations of the pseudometalophytic species Arrhenatherum elatius: implications for phytoextraction. Sci Total Environ 372:372–381
Dermont G, Bergeron M, Mercier G, Richer-Lafleche M (2008) Soil washing for metal removal: a review of physical/chemical technologies and field applications. J Hazard Mater 152:1–31
Derome J (2000) Detoxification and amelioration of heavy-metal contaminated forest soils by means of liming and fertilisation. Environ Pollut 107:79–88
Development S (2002): Mining for the future appendix A: large volume waste working paper
Dunker RE, Hooks CL, Vance SL, Darmody RG (1995) Deep tillage effects on compacted surface-mined land. Soilence Soc Am J 59:192–199
Edraki M, Baumgartl T, Manlapig E, Bradshaw D, Franks DM, Moran CJ (2014) Designing mine tailings for better environmental, social and economic outcomes: a review of alternative approaches. J Clean Prod 84:411–420
Egiebor NO, Ben O (2010) Acid rock drainage formation and treatment: a review. Asia Pac J Chem Eng 2:47–62
Enright NJ, Lamont BB (1992) Survival, growth and water relations of Banksia seedlings on a sand mine rehabilitation site and adjacent scrub-heath sites. J Appl Ecol 29:663–671
Farrell M, Jones DL (2010) Use of composts in the remediation of heavy metal contaminated soil. J Hazard Mater 175:575–582
Fawzy EM (2008) Soil remediation using in situ immobilisation techniques. Chem Ecol 24:147–156
Fellet G, Marchiol L, Perosa D, Zerbi G (2007) The application of phytoremediation technology in a soil contaminated by pyrite cinders. Ecol Eng 31:207–214
Foy CD, And RLC, White MC (2003) The physiology of metal toxicity in plants. Annu Rev Plant Physiol 29:511–566
Gilbert M (2000) Minesite rehabilitation. Tropical Grasslands 34:147–153
Gil-Loaiza J, White SA, Root RA, Solis-Dominguez FA, Hammond CM, Chorover J, Maier RM (2016) Phytostabilization of mine tailings using compost-assisted direct planting: translating greenhouse results to the field. Sci Total Environ 565:451–461
Glaser B, Birk JJ (2012) State of the scientific knowledge on properties and genesis of Anthropogenic Dark Earths in Central Amazonia (terra preta de Índio). Geochim Cosmochim Acta 82:39–51
Gray CW, Dunham SJ, Dennis PG, Zhao FJ, Zhao FJ, Mcgrath SP (2006) Field evaluation of in situ remediation of a heavy metal contaminated soil using lime and red-mud. Environ Pollut 142:530–539
Grimalt JO, Ferrer M, Macpherson E (1999) The mine tailing accident in Aznalcollar. Sci Total Environ 242:3–11
Guo G, Zhou Q, Ma LQ (2006) Availability and assessment of fixing additives for the in situ remediation of heavy metal contaminated soils: a review. Environ Monit Assess 116:513–528
Haidouti C (1997) Inactivation of mercury in contaminated soils using natural zeolites. Sci Total Environ 208:105–109
Halim M, Conte P, Piccolo A (2003) Potential availability of heavy metals to phytoextraction from contaminated soils induced by exogenous humic substances. Chemosphere 52:265–275
Hansen HK, Rojo A (2007) Testing pulsed electric fields in electroremediation of copper mine tailings. Electrochim Acta 52:3399–3405
Hansen HK, Rojo A, Ottosen LM (2005) Electrodialytic remediation of copper mine tailings. J Hazard Mater 117:179–183
Hewitt EJ (1952): Sand and water culture methods used in the study of plant nutrition. Commonwealth Agricultural Bureaux, x + 241 ; 202–32 . pp
Holmes PM (2001) Shrubland restoration following woody alien invasion and mining: effects of topsoil depth, seed source, and fertilizer addition. Restor Ecol 9:71–84
Holmes PM, Richardson DM (1999) Protocols for restoration based on recruitment dynamics, community structure, and ecosystem function: perspectives from South African fynbos. Restor Ecol 7:215–230
Hutchinson SL, Banks MK, Schwab AP (2001) Phytoremediation of aged petroleum sludge: effect of inorganic fertilizer. J Environ Qual 30:395
Jang A, Kim IS (2000) Solidification and stabilization of Pb, Zn, Cd and Cu in tailing wastes using cement and fly ash. Miner Eng 13:1659–1662
Johnson MS, McNeilly T, Putwain PD (1977) Revegetation of metalliferous mine spoil contaminated by lead and zinc. Environ Pollut 12:261–277
Jones H, Boger DV (2012) Sustainability and waste management in the resource industries. Indonesia 51:10057–10065
Jurjovec J, Ptacek CJ, Blowes DW (2002) Acid neutralization mechanisms and metal release in mine tailings: a laboratory column experiment. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 66:1511–1523
Kabata PA, Pendias H (1992): Trace elements in soils and plants. 2nd ed.
Kaur G, Singh HP, Batish DR, Kohli RK (2014) Pb-inhibited mitotic activity in onion roots involves DNA damage and disruption of oxidative metabolism. Ecotoxicology 23:1292–1304
Keeley JE, Bond WJ (1997) Convergent seed germination in South African fynbos and Californian chaparral. Plant Ecol 133:153–167
Khan MJ, Jones DL (2009) Effect of composts, lime and diammonium phosphate on the phytoavailability of heavy metals in a copper mine tailing soil. PEDOSPHERE(土壤圈(英文版)) 19:631–641
Koptsik GN (2014) Problems and prospects concerning the phytoremediation of heavy metal polluted soils: a review. Eurasian Soil Sci 47:923–939
Kossoff D, Dubbin WE, Alfredsson M, Edwards SJ, Macklin MG, Hudson-Edwards KA (2014) Mine tailings dams: characteristics, failure, environmental impacts, and remediation. Appl Geochem 51:229–245
Kumpiene J, Ore S, Lagerkvist A, Maurice C (2007) Stabilization of Pb- and Cu-contaminated soil using coal fly ash and peat. Environ Pollut 145:365–373
Kumpiene J, Lagerkvist A, Maurice C (2008) Stabilization of As, Cr, Cu, Pb and Zn in soil using amendments—a review. Waste Manag 28:215–225
Kusin FM, Azani NNM, Hasan SNMS, Sulong NA (2018) Distribution of heavy metals and metalloid in surface sediments of heavily-mined area for bauxite ore in Pengerang, Malaysia and associated risk assessment. CATENA 165:454–464
Lageman R (1993) Electroreclamation. Applications in the Netherlands. Environ Sci Technol 27:2648–2650
Lan CY, Shu WS, Wong MH (1998) Reclamation of Pb/Zn mine tailings at Shaoguan, Guangdong Province, People’s Republic of China: the role of river sediment and domestic refuse. Bioresour Technol 65:117–124
Lazerte BD (1984) Forms of aqueous aluminum in acidified catchments of Central Ontario. J Can Sci Halieutiques Aquat 41:766–776
Ledin M, Pedersen K (1996) The environmental impact of mine wastes—roles of microorganisms and their significance in treatment of mine wastes. Earth Sci Rev 41:67–108
Lee SH, Lee JS, Choi YJ, Kim JG (2009) In situ stabilization of cadmium-, lead-, and zinc-contaminated soil using various amendments. Chemosphere 77:1069–1075
Lee SH, Ji W, Lee WS, Koo N, Koh IH, Kim MS, Park JS (2014) Influence of amendments and aided phytostabilization on metal availability and mobility in Pb/Zn mine tailings. J Environ Manag 139:15–21
Li MS (2006) Ecological restoration of mineland with particular reference to the metalliferous mine wasteland in China: a review of research and practice. Sci Total Environ 357:38–53
Li W, Zhang M, Shu H (2005) Distribution and fractionation of copper in soils of apple orchards. Environ Sci Pollut Res 12:168–172
Li Y, Sun Q, Zhan J, Yang Y, Wang D (2016) Vegetation successfully prevents oxidization of sulfide minerals in mine tailings. J Environ Manag 177:153–160
Liu Y, Huang L (2017) Magnetite recovery from copper tailings increases arsenic distribution in solution phase and uptake in native grass. J Environ Manag 186:175–182
Liu Y, Lin C, Wu Y (2007) Characterization of red mud derived from a combined Bayer process and bauxite calcination method. J Hazard Mater 146:255–261
Liu M, Hu F, Chen X, Huang Q, Jiao J, Zhang B, Li H (2009) Organic amendments with reduced chemical fertilizer promote soil microbial development and nutrient availability in a subtropical paddy field: the influence of quantity, type and application time of organic amendments. Appl Soil Ecol 42:166–175
Liu Y, Du F, Yuan L, Zeng H, Kong S (2010) Production of lightweight ceramisite from iron ore tailings and its performance investigation in a biological aerated filter (BAF) reactor. J Hazard Mater 178:999–1006
Liu X, Zhang A, Ji C, Joseph S, Bian R, Li L, Pan G, Paz-Ferreiro J (2013) Biochar’s effect on crop productivity and the dependence on experimental conditions—a meta-analysis of literature data. Plant Soil 373:583–594
Lottermoser BG, Ashley PM (2011) Trace element uptake by Eleocharis equisetina (spike rush) in an abandoned acid mine tailings pond, northeastern Australia: implications for land and water reclamation in tropical regions. Environ Pollut 159:3028–3035
Lu J, Chen T, Wu J, Chris Wilson P, Hao X, Qian J (2011) Acid tolerance of an acid mine drainage bioremediation system based on biological sulfate reduction. Bioresour Technol 102:10401–10406
Luptakova A, Kusnierova M (2005) Bioremediation of acid mine drainage contaminated by SRB. Hydrometallurgy 77:97–102
Maiz I, Arambarri I, Garcia R, Millán E (2000) Evaluation of heavy metal availability in polluted soils by two sequential extraction procedures using factor analysis. Environ Pollut 110:3–9
Marijan S, Horvat D, Josip Š (2006) Soil compaction in timber skidding in winter conditions. Croatian Journal of Forest Engineering 27:3–15
Marques APGC, Rangel AOSS, Castro PML (2009) Remediation of heavy metal contaminated soils: phytoremediation as a potentially promising clean-up technology. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 39:622–654
Marques AP, Moreira H, Franco AR, Rangel AO, Castro PM (2013) Inoculating Helianthus annuus (sunflower) grown in zinc and cadmium contaminated soils with plant growth promoting bacteria—effects on phytoremediation strategies. Chemosphere 92:74–83
Martı́Nez CE, Motto HL (2000) Solubility of lead, zinc and copper added to mineral soils. Environ Pollut 107:153–158
Martins M, Santos ES, Pires C, Barros RJ, Costa MC (2010) Production of irrigation water from bioremediation of acid mine drainage: comparing the performance of two representative systems. J Clean Prod 18:248–253
Martins M, Santos ES, Faleiro ML, Chaves S, Tenreiro R, Barros RJ, Barreiros A, Costa MC (2011) Performance and bacterial community shifts during bioremediation of acid mine drainage from two Portuguese mines. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 65:972–981
Matsumoto H (2000) Cell biology of aluminum toxicity and tolerance in higher plants. Int Rev Cytol 200:1–46
Mcgowen SL, Basta NT, Brown GO (2001) Use of diammonium phosphate to reduce heavy metal solubility and transport in smelter-contaminated soil. J Environ Qual 30:493
McGrath SP, Zhao FJ (2003) Phytoextraction of metals and metalloids from contaminated soils. Curr Opin Biotechnol 14:277–282
McIntyre T (2003) Phytoremediation of heavy metals from soils. Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol 78:97–123
Moreno L, Neretnieks I (2006) Long-term environmental impact of tailings deposits. Hydrometallurgy 83:176–183
Mouazen AM, Alhwaimel SA, Kuang B, Waine T (2014) Multiple on-line soil sensors and data fusion approach for delineation of water holding capacity zones for site specific irrigation. Soil Tillage Res 143:95–105
Nissen LR, Lepp NW, Edwards R (2000) Synthetic zeolites as amendments for sewage sludge-based compost. Chemosphere 41:265–269
Ober JA (2017): Mineral commodity summaries 2017
Odom JM, Jr RS (1993): The sulfate-reducing bacteria: contemporary perspectives. Springer New York
Orendorff BDE (2009): An experimental study of embankment dam breaching. University of Ottawa
Ottosen LM, Hansen HK, Bech-Nielsen G, Villumsen A (2000) Electrodialytic remediation of an arsenic and copper polluted soil—continuous addition of ammonia during the process. Environ Technol 21:1421–1428
PARAMGURU RK, RATH PC, MISRA VN (2005) Trends in red mud utilization—a review. Miner Process Extr Metall Rev 26:1–29
Peng JF, Song YH, Peng Y, Cui XY, Qiu GL (2009) The remediation of heavy metals contaminated sediment. J Hazard Mater 161:633–640
Penner TJ, Foght JM (2010) Mature fine tailings from oil sands processing harbour diverse methanogenic communities. Can J Microbiol 56:459–470
Pogrzeba M, Galimskastypa R, Krzyżak J, Sasnowosielska A (2015) Sewage sludge and fly ash mixture as an alternative for decontaminating lead and zinc ore regions. Environ Monit Assess 187:4120
Probstein RF, Hicks RE (1993) Removal of contaminants from soils by electric fields. Science 260:498–503
Putwain PD, Gillham DA (1990) The significance of the dormant viable seed bank in the restoration of heathlands. Biol Conserv 52:1–16
Rah S, Bradshaw AD (1979) The use of metal tolerant plant populations for the reclamation of metalliferous wastes. J Appl Ecol 16:595–612
Redente EF, Mclendon T, Agnew W (1997) Influence of topsoil depth on plant community dynamics of a seeded site in northwest Colorado. Arid Soil Res Rehabil 11:139–149
Renault S, Lait C, Zwiazek JJ, Mackinnon M (1998) Effect of high salinity tailings waters produced from gypsum treatment of oil sands tailings on plants of the boreal forest. Environ Pollut 102:177–184
Rodriguez L, Ruiz E, Alonso-Azcarate J, Rincon J (2009) Heavy metal distribution and chemical speciation in tailings and soils around a Pb-Zn mine in Spain. J Environ Manag 90:1106–1116
Rojo A, Hansen HK, Ottosen LM (2006) Electrodialytic remediation of copper mine tailings: comparing different operational conditions. Miner Eng 19:500–504
Rotkittikhun P, Chaiyarat R, Kruatrachue M, Pokethitiyook P, Baker AJ (2007) Growth and lead accumulation by the grasses Vetiveria zizanioides and Thysanolaena maxima in lead-contaminated soil amended with pig manure and fertilizer: a glasshouse study. Chemosphere 66:45–53
Sakai H, Nordfjell T, Suadicani K, Talbot B (2008) Soil compaction on forest soils from different kinds of tires and tracks and possibility of accurate estimate. Croat J For Eng 29:15–27
Salazar-Villalpando MD, Neelameggham NR, Guillen DP, Pati S, Krumdick GK (2012) Global primary aluminium industry 2010 life cycle inventory. Wiley, pp 85–92
Schaaf W (2001) What can element budgets of false-time series tell us about ecosystem development on post-lignite mining sites? Ecol Eng 17:241–252
Schoenberger E (2016) Environmentally sustainable mining: the case of tailings storage facilities. Res Policy 49:119–128
Seregin IV, Ivanov VB (2001) Physiological aspects of cadmium and lead toxic effects on higher plants. Russ J Plant Physiol 48:523–544
Shahid M, Pinelli E, Dumat C (2012) Review of Pb availability and toxicity to plants in relation with metal speciation; role of synthetic and natural organic ligands. J Hazard Mater 219-220:1–12
Shetron SG, Spindler JJ (1983) Alfalfa, Medicago sativa L., establishment in mine mill tailings: II. Root patterns of alfalfa in iron tailings and natural soils. Plant Soil 73:239–246
Shim D, Kim S, Choi Y-I, Song W-Y, Park J, Youk ES, Jeong S-C, Martinoia E, Noh E-W, Lee Y (2013) Transgenic poplar trees expressing yeast cadmium factor 1 exhibit the characteristics necessary for the phytoremediation of mine tailing soil. Chemosphere 90:1478–1486
Shu WS, Ye ZH, Lan CY, Zhang ZQ, Wong MH (2001) Acidification of lead/zinc mine tailings and its effect on heavy metal mobility. Environ Int 26:389–394
Tang W, Huang J, Heng LI, Wenxing XU, Huang W (2017) Research on soil heavy metal form of a manganese ore zone in Guangxi. Environ Sci Technol
Tessier A, Campbell PGC, Bisson M (1979) Sequential extraction procedure for the speciation of particulate trace metals. Anal Chem 51:844–851
Thavamani P, Samkumar RA, Satheesh V, Subashchandrabose SR, Ramadass K, Naidu R, Venkateswarlu K, Megharaj M (2017) Microbes from mined sites: harnessing their potential for reclamation of derelict mine sites. Environ Pollut 230:495–505
Tokoro C, Yatsugi Y, Koga H, Owada S (2010) Sorption mechanisms of arsenate during coprecipitation with ferrihydrite in aqueous solution. Environ Sci Technol 44:638–643
Usman A, Kuzyakov Y, Stahr K (2005) Effect of clay minerals on immobilization of heavy metals and microbial activity in a sewage sludge-contaminated soil (8 pp). J Soils Sediments 5:245–252
Valls M, Lorenzo VD (2002) Exploiting the genetic and biochemical capacities of bacteria for the remediation of heavy metal pollution. FEMS Microbiol Rev 26:327–338
Wang YM, Chen TC, Yeh KJ, Shue MF (2001) Stabilization of an elevated heavy metal contaminated site. J Hazard Mater 88:63–74
Wang AS, Angle JS, Chaney RL, Delorme TA, Reeves RD (2006) Soil pH effects on uptake of cd and Zn by Thlaspi caerulescens. Plant Soil 281:325–337
Wang X, Liu Y, Zeng G, Chai L, Xiao X, Song X, Min Z (2008) Pedological characteristics of Mn mine tailings and metal accumulation by native plants. Chemosphere 72:1260–1266
Wilson SC, Jones KC (1993) Bioremediation of soil contaminated with polynuclear aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs): a review. Environ Pollut 81:229–249
Xia W, Gao H, Wang X, Zhou C, Liu Y, Fan T, Wang X (2009) Application of EDTA decontamination on soils affected by mining activities and impact of treatment on the geochemical partition of metal contaminants. J Hazard Mater 164:936–940
Xue S, Zhu F, Kong X, Wu C, Huang L, Huang N, Hartley W (2016) A review of the characterization and revegetation of bauxite residues (Red mud). Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 23:1120–1132
Yang JS, Lee JY, Baek K, Kwon TS, Choi J (2009) Extraction behavior of As, Pb, and Zn from mine tailings with acid and base solutions. J Hazard Mater 171:443–451
Ye ZH, Wong JWC, Wong MH (2000) Vegetation response to lime and manure compost amendments on acid lead/zinc mine tailings: a greenhouse study. Restor Ecol 8:289–295
Yin G, Li G, Wei Z, Wan L, Shui G, Jing X (2011) Stability analysis of a copper tailings dam via laboratory model tests: a Chinese case study. Miner Eng 24:122–130
Young TP (2000) Restoration ecology and conservation biology. Biol Conserv 92:73–83
Zhang X, Zhu Y, Zhang Y, Liu Y, Liu S, Guo J, Li R, Wu S, Chen B (2014) Growth and metal uptake of energy sugarcane (Saccharum spp.) in different metal mine tailings with soil amendments. J Environ Sci 26:1080–1089
Zhang X, Yang H, Cui Z (2018) Evaluation and analysis of soil migration and distribution characteristics of heavy metals in iron tailings. J Clean Prod:172
Zhou YF, Haynes RJ (2010) Sorption of heavy metals by inorganic and organic components of solid wastes: significance to use of wastes as low-cost adsorbents and immobilizing agents. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 40:909–977
Zhou H, Zhou X, Zeng M, Liao BH, Liu L, Yang WT, Wu YM, Qiu QY, Wang YJ (2014) Effects of combined amendments on heavy metal accumulation in rice (Oryza sativa L.) planted on contaminated paddy soil. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 101:226–232
Zufiaurre R, Olivar A, Chamorro P, Callizo A, Zufiaurre R (1998) Speciation of metals in sewage sludge for agricultural uses. Analyst 123:255–259
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51704329, 51634009); by the National 111 Project (No. B14034) and Collaborative Innovation Center for Clean and Efficient utilization of Strategic Metal Mineral Resources.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, W., Ji, B., Khoso, S.A. et al. An extensive review on restoration technologies for mining tailings. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25, 33911–33925 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-3423-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-3423-y