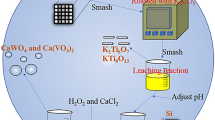
Abstract
In this work, an environmental friendly industrial regeneration approach has been proposed to remove the surface poisoning and recover the catalytic activity of waste V2O5-WO3/TiO2 catalyst. Alkaline treatment and acid wash are combined for the waste catalyst regeneration process, which is applied for the arsenic and alkali metal removal, respectively. The crystal structure was well maintained as anatase phase and the surface area was increased during the regeneration, which is favorable for the following active component addition step and regenerated process. The XPS results illustrated that the surface contaminants (arsenic and sodium) were removed and V(IV) was loaded on the regenerated catalyst. Based on the deNOx evaluations, the catalytic activity of the regenerated sample is increased to the level of commercial fresh catalyst. The present industrial regeneration process provides a promising method for the comprehensive recovery of waste catalyst and further understanding in the field of secondary resource recycle.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen JX, Pan KL, Yu SJ, Yen SY, Chang MB (2017) Combined fast selective reduction using Mn-based catalysts and nonthermal plasma for NOx removal. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:21496–21508
Choi I-H, Kim H-R, Moon G, Jyothi RK, Lee J-Y (2018) Spent V2O5-WO3/TiO2 catalyst processing for valuable metals by soda roasting-water leaching. Hydrometallurgy 175:292–299
Du X, Yang G, Chen Y, Ran J, Zhang L (2017) The different poisoning behaviors of various alkali metal containing compounds on SCR catalyst. Appl Surf Sci 392:162–168
Erust C, Akcil A, Bedelova Z, Anarbekov K, Baikonurova A, Tuncuk A (2016) Recovery of vanadium from spent catalysts of sulfuric acid plant by using inorganic and organic acids: laboratory and semi-pilot tests. Waste Manag 49:455–461
Hu W, Gao X, Deng Y, Qu R, Zheng C, Zhu X, Cen K (2016) Deactivation mechanism of arsenic and resistance effect of SO4 2− on commercial catalysts for selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3. Chem Eng J 293:118–128
Ilie AG, Scarisoareanu M, Morjan I, Dutu E, Badiceanu M, Mihailescu I (2017) Principal component analysis of Raman spectra for TiO2 nanoparticle characterization. Appl Surf Sci 417:93–103
Jeon J-K, Kim H, Park Y-K, Peden CHF, Kim DH (2011) Regeneration of field-spent activated carbon catalysts for low-temperature selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3. Chem Eng J 174:242–248
Kong M, Liu Q, Wang X, Ren S, Yang J, Zhao D, Xi W, Yao L (2015) Performance impact and poisoning mechanism of arsenic over commercial V2O5–WO3/TiO2 SCR catalyst. Catal Commun 72:121–126
Lei J, Peng B, Liang Y-J, Min X-B, Chai L-Y, Ke Y, You Y (2018) Effects of anions on calcium arsenate crystalline structure and arsenic stability. Hydrometallurgy 177:123–131
Li X, Li J, Peng Y, Si W, He X, Hao J (2015) Regeneration of commercial SCR catalysts: probing the existing forms of arsenic oxide. Environ Sci Technol 49:9971–9978
Li X, Li J, Peng Y, Chang H, Zhang T, Zhao S, Si W, Hao J (2016) Mechanism of arsenic poisoning on SCR catalyst of CeW/Ti and its novel efficient regeneration method with hydrogen. Appl Catal B-environ 184:246–257
Li M-Y, Guo R-T, Hu C-X, Sun P, Pan W-G, Liu S-M, Sun X, Liu S-W, Liu J (2018) The enhanced resistance to K deactivation of Ce/TiO2 catalyst for NH3-SCR reaction by the modification with P. Appl Surf Sci 436:814–822
Liu Z, Zhang S, Li J, Zhu J, Ma L (2014) Novel V2O5–CeO2/TiO2 catalyst with low vanadium loading for the selective catalytic reduction of NOx by NH3. Appl Catal B-environ 158-159:11–19
Liu Y, Liu Z, Mnichowicz B, Harinath AV, Li H, Bahrami B (2016) Chemical deactivation of commercial vanadium SCR catalysts in diesel emission control application. Chem Eng J 287:680–690
Marberger A, Elsener M, Ferri D, Kröcher O (2015) VOx surface coverage optimization of V2O5/WO3-TiO2 SCR catalysts by variation of the V loading and by aging. Catalysts 5:1704–1720
Nazari AM, Radzinski R, Ghahreman A (2017) Review of arsenic metallurgy: treatment of arsenical minerals and the immobilization of arsenic. Hydrometallurgy 174:258–281
Peng Y, Li J, Si W, Luo J, Dai Q, Luo X, Liu X, Hao J (2014) Insight into deactivation of commercial SCR catalyst by arsenic: an experiment and DFT study. Environ Sci Technol 48:13895–13900
Peng Y, Li J, Si W, Luo J, Wang Y, Fu J, Li X, Crittenden J, Hao J (2015) Deactivation and regeneration of a commercial SCR catalyst: comparison with alkali metals and arsenic. Appl Catal B-Environ 168-169:195–202
Qiu Y, Liu B, Du J, Tang Q, Liu Z, Liu R, Tao C (2016) The monolithic cordierite supported V2O5–MoO3/TiO2 catalyst for NH3-SCR. Chem Eng J 294:264–272
Shang X, Hu G, He C, Zhao J, Zhang F, Xu Y, Zhang Y, Li J, Chen J (2012) Regeneration of full-scale commercial honeycomb monolith catalyst (V2O5–WO3/TiO2) used in coal-fired power plant. J Ind Eng Chem 18:513–519
Wang JX, Miao JF, Yu WJ, Chen YT, Chen J (2017a) Study on the local difference of monolithic honeycomb V2O5-WO3/TiO2 denitration catalyst. Mater Chem Phys 198:193–199
Wang R, Zhao Z, Qiu L, Liu J (2017b) Experimental investigation of synergistic behaviors of lignite and wasted activated sludge during their co-combustion. Fuel Process Technol 156:271–279
Wang D, Peng Y, Xiong S-C, Li B, Gan L-N, Lu C-M, Chen J-J, Ma Y-L, Li J-H (2018) De-reducibility mechanism of titanium on maghemite catalysts for the SCR reaction: an in situ DRIFTS and quantitative kinetics study. Appl Catal B-environ 221:556–564
Xiao H, Chen Y, Qi C, Ru Y (2018) Effect of Na poisoning catalyst (V2O5–WO3/TiO2) on denitration process and SO3 formation. Appl Surf Sci 433:341–348
Yan Z, Qu Y, Liu L, Ge X, Yang J, Wei L, Yang T, Wang X (2017) Promotional effect of rare earth-doped manganese oxides supported on activated semi-coke for selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:24473–24484
Ye C-P, Yang Z-J, Li W-Y, Rong H-L, Feng J (2017) Effect of adjusting coal properties on HulunBuir lignite pyrolysis. Fuel Process Technol 156:415–420
Zhang Q, Wu Y, Zuo T (2018) Green recovery of titanium and effective regeneration of TiO2 photocatalysts from spent selective catalytic reduction catalysts. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 6:3091–3101
Zhao Z, Guo M, Zhang M (2015) Extraction of molybdenum and vanadium from the spent diesel exhaust catalyst by ammonia leaching method. J Hazard Mater 286:402–409
Zheng Y, Jensen AD, Johnsson JE (2005) Deactivation of V2O5-WO3-TiO2 SCR catalyst at a biomass-fired combined heat and power plant. Appl Catal B-environ 60:253–264
Funding
The financial support of the UCAS (UCAS[2015]37) Joint PhD Training Program is greatly acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Responsible editor: Suresh Pillai
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xue, Y., Wang, Y. Effective industrial regeneration of arsenic poisoning waste selective catalytic reduction catalyst: contaminants removal and activity recovery. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25, 34114–34122 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-3369-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-3369-0