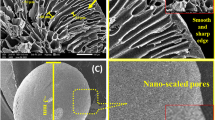
Abstract
The disodium salt of Rose Bengal [4, 5, 6, 7-tetrachloro-2′, 4′, 5′, 7′-tetraiodofluorescein] commonly finds application in medical procedures and its removal from aqueous solution is difficult owing to its high molecular weight of 1017.67 g/mol. Activated carbon was prepared from Prosopis juliflora and immobilized into sodium alginate beads and doped with aniline for enhanced adsorption of Rose Bengal. The effect of initial dye concentration, beads’ dosage, contact time, and the temperature over the adsorption of Rose Bengal dye were studied. The optimum conditions derived for maximum dye uptake capacity were 4 mg/L of initial dye concentration, contact time of 60 min with the adsorbent dosage of 0.2 g, and temperature of 303 K at neutral pH. The equilibrium data were found to be best fitted for Langmuir −1 model, whereas the kinetics were interpreted through Ho-Mckay’s pseudo-second-order equation. The adsorbents were subjected to thermo-gravimetric studies to determine the activation energy under a heating rate of 20 °C/min. The activation energy was computed using Broido’s plot and was found to be 35.21 ± 0.84 kJ/mol for the activated carbon, and 16.77 ± 2.19 kJ/mol for the dye-adsorbed beads. The heat capacity was determined through differential scanning calorimetry and was calculated to be 19.41 J/g °C for activated carbon and 39.43 J/g °C for beads post-adsorption of Rose Bengal dye.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agrawal A, Chakraborty S (2013) A kinetic study of pyrolysis and combustion of microalgae Chlorella vulgaris using thermo-gravimetric analysis. Bioresour Technol 128:72–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2012.10.043
Aljeboree AM, Alshirifi AN, Alkaim AF (2017) Kinetics and equilibrium study for the adsorption of textile dyes on coconut shell activated carbon. Arab J Chem 10:S3381–S3393. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2014.01.020
Ameen S, Seo HK, Shaheer Akhtar M, Shin HS (2012) Novel graphene/polyaniline nanocomposites and its photocatalytic activity toward the degradation of rose Bengal dye. Chem Eng J 210:220–228. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2012.08.035
Ameen S, Shaheer Akhtar M, Ansari SG, Yang OB, Shin HS (2009) Electrophoretically deposited polyaniline/ZnO nanoparticles for p-n heterostructure diodes. Superlattice Microst 46:872–880. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.spmi.2009.09.007
Anoop K (2010) Progress of Prosopis juliflora eradication work in Keoladeo National Park
Ashour SS (2010) Kinetic and equilibrium adsorption of methylene blue and remazol dyes onto steam-activated carbons developed from date pits. J Saudi Chem Soc 14:47–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jscs.2009.12.008
Bi F, Mahmood SJ, Arman M, Taj N, Iqbal S (2007) Physicochemical characterization and ionic studies of sodium alginate from Sargassum terrarium (brown algae). Phys Chem Liq 45:453–461. https://doi.org/10.1080/00319100600745198
Broido A (1969) A simple, sensitive graphical method of treating thermogravimetric analysis data. J Polym Sci Part A-2 Polym Phys 7:1761–1773. https://doi.org/10.1002/pol.1969.160071012
Ceylan S, Kazan D (2015) Pyrolysis kinetics and thermal characteristics of microalgae Nannochloropsis oculata and Tetraselmis sp. Bioresour Technol 187:1–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2015.03.081
Cumming JW (1984) Reactivity assessment of coals via a weighted mean activation energy. Fuel 63:1436–1440. https://doi.org/10.1016/0016-2361(84)90353-3
Demirbaş Ö, Alkan M (2015) Adsorption kinetics of a cationic dye from wastewater. Desalin Water Treat 53:3623–3631. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2013.874705
Demirbaş Ö, Turhan Y, Alkan M (2015) Thermodynamics and kinetics of adsorption of a cationic dye onto sepiolite. Desalin Water Treat 54:707–714. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2014.886299
Doherty W, Reynolds A, Kennedy D (2009) The effect of air preheating in a biomass CFB gasifier using ASPEN plus simulation. Biomass Bioenergy 33:1158–1167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biombioe.2009.05.004
Dutta AK, Maji SK, Adhikary B (2014) ??-Fe2O3 nanoparticles: an easily recoverable effective photo-catalyst for the degradation of rose bengal and methylene blue dyes in the waste-water treatment plant. Mater Res Bull 49:28–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2013.08.024
Erol M, Haykiri-Acma H, Küçükbayrak S (2010) Calorific value estimation of biomass from their proximate analyses data. Renew Energy 35:170–173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2009.05.008
Freundlich HMF (1906) Over the adsorption in solution. J Phys Chem 57:385–471
Garcia R, Pizarro C, Lavin AG, Bueno JL (2013) Biomass proximate analysis using thermogravimetry. Bioresour Technol 139:1–4. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2013.03.197
Geetha A, Palanisamy N (2016) Equilibrium and kinetic studies for the adsorption of Basic Red 29 from aqueous solutions using activated carbon and conducting polymer composite. Desalin Water Treat 57:8406–8419. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2015.1020510
Gopal N, Asaithambi M (2015) Adsorption of acid blue- 40 (A textile dye) using prosopis juliflora activated carbon embedded in polyaniline matrix. Rasayan J Chem 8:279–286
Gopal N, Asaithambi M, Sivakumar P, Sivakumar V (2014) Adsorption studies of a direct dye using polyaniline coated activated carbon prepared from Prosopis juliflora. J Water Process Eng 2:87–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2014.05.008
Gopal N, Asaithambi M, Sivakumar P, Sivakumar V (2016) Continuous fixed bed adsorption studies of Rhodamine-B dye using polymer bound adsorbent. Indian J Chem Technol 23:53–58
Gottifredi JC, Gonzo EE, Quiroga OD (1981) Isothermal effectiveness factor—II: Analytical expression for single reaction with arbitrary kinetics, geometry and activity distribution. Chem Eng Sci 36:721–730. https://doi.org/10.1016/0009-2509(81)85087-7
Gupta VK, Mittal A, Jhare D, Mittal J (2012) Batch and bulk removal of hazardous colouring agent rose Bengal by adsorption techniques using bottom ash as adsorbent. RSC Adv 2:8381. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2ra21351f
Gupta VK, Mohan D, Sharma S, Sharma M (2000) Removal of basic dyes (rhodamine B and methylene blue) from aqueous solutions using bagasse fly ash. Sep Sci Technol 35:2097–2113. https://doi.org/10.1081/SS-100102091
Haug A, Larsen B, Smidsrød O (1966) A study on the constitution of alginic acid by partial hydrolysis. 183–190
Haug A, Larsen B, Smidsrød O, Painter T, Borch G, Craig JC (1969) Development of compositional heterogeneity in alginate degraded in homogeneous solution. Acta Chem Scand 23:2955–2962
Hiremath AJ, Sundaram B (2013) Plant invasions in protected areas. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-007-7750-7
Ho YS (2006) Review of second-order models for adsorption systems. J Hazard Mater 136:681–689. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2005.12.043
Ho YS, McKay G (1998) A comparison of chemisorption kinetic models applied to pollutant removal on various sorbents. Process Saf Environ Prot 76:332–340. https://doi.org/10.1205/095758298529696
Jayaram K, Prasad MNV (2009) Removal of Pb(II) from aqueous solution by seed powder of Prosopis juliflora DC. J Hazard Mater 169:991–997. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.04.048
Juang R-S, Swei S-L (1996) Effect of Dye Nature on Its Adsorption from Aqueous Solutions onto Activated Carbon. Sep Sci Technol 31:37–41. https://doi.org/10.1080/01496399608001036
Juang R-S, Tseng R-L, Wu F-C, Lee S-H (1997) Adsorption behavior of reactive dyes from aqueous solutions on chitosan. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 70:391–399. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1097-4660(199712)70:4<391::AID-JCTB792>3.0.CO;2-V
Kaur J, Singhal S (2014) Heterogeneous photocatalytic degradation of rose bengal: effect of operational parameters. Phys B Condens Matter 450:49–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2014.05.069
Khare P, Baruah BP (2014) Thermogravimetric analysis of perhydrous Indian coals. Energy Sources, Part A Recover Util Environ Eff 36:774–782. https://doi.org/10.1080/15567036.2010.547919
Kragovic M, Dakovic A, Markovic M, Petkovic A (2016) Kinetic of thermal degradation of alginate-zeolite composites. Zast Mater 57:559–564. https://doi.org/10.5937/ZasMat1604559K
Kumar M, Tamilarasan R (2013a) Modeling studies: adsorption of aniline blue by using Prosopis Juliflora carbon/Ca/alginate polymer composite beads. Carbohydr Polym 92:2171–2180. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2012.11.076
Kumar M, Tamilarasan R (2013b) Modeling of experimental data for the adsorption of methyl orange from aqueous solution using a low cost activated carbon prepared from Prosopis
Kumar M, Tamilarasan R (2013c) Kinetics and equilibrium studies on the removal of Victoria blue using Prosopis juliflora -modified carbon/Zn/alginate polymer composite beads. J Chem Eng Data 58:517–527
Kumar M, Tamilarasan R (2014) Removal of Victoria blue using Prosopis juliflora bark carbon: kinetics and thermodynamic modeling studies. J Mater Environ Sci 5:510–519
Kumar M, Tamilarasan R (2017) Kinetics, equilibrium data and modeling studies for the sorption of chromium by Prosopis juliflora bark carbon. Arab J Chem 10:S1567–S1577. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2013.05.025
Kumar M, Tamilarasan R, Sivakumar V (2013) Adsorption of Victoria blue by carbon/Ba/alginate beads: kinetics, thermodynamics and isotherm studies. Carbohydr Polym 98:505–513. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2013.05.078
Lagergren S (1898) About the theory of so called adsorption of soluble substances. K Sven Vetenskapsakademiens Handl 1–39
Li D, Chen L, Yi X, Zhang X, Ye N (2010) Pyrolytic characteristics and kinetics of two brown algae and sodium alginate. Bioresour Technol 101:7131–7136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2010.03.145
Mahmoud MS, Mohamed SA (2015) Calcium alginate as an eco-friendly supporting material for Baker’s yeast strain in chromium bioremediation. HBRC J 13:245–254. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hbrcj.2015.06.003
Mittal N, Shah A, Punjabi PB, Sharma VK (2009) Photodegradation of rose bengal using MnO 2 (Manganese dioxide). Rasayan J Coin 2:516–520
Mondal MK, Singh RS, Kumar A, Prasad BM (2011) Removal of acid red-94 from aqueous solution using sugar cane dust: an agro-industry waste. Korean J Chem Eng 28:1386–1392. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-010-0523-x
Muller GC, Junnila A, Traore MM, Traore SF, Doumbia S, Sissoko F, Dembele SM, Schlein Y, Arheart KL, Revay EE, Kravchenko VD, Witt A, Beier JC (2017) The invasive shrub Prosopis juliflora enhances the malaria parasite transmission capacity of Anopheles mosquitoes: a habitat manipulation experiment. Malar J 16:237. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12936-017-1878-9
Nevase SS, Gangde CN, Gangil S, Dubey AK (2013) Studies on characterisation of biomass fuel. 6:547–551
Nińã I, Iorgulescu M, Spiroiu MF (2007) The adsorption of heavy metal ions on porous calcium alginate microparticles. Anal Chem I:4–12
ÖzyuǧUran A, Yaman S (2017) Prediction of calorific value of biomass from proximate analysis. Energy Procedia 107:130–136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egypro.2016.12.149
Pandey A, Bera D, Shukla A, Ray L (2007) Studies on Cr(VI), Pb(II) and Cu(II) adsorption-desorption using calcium alginate as biopolymer. Chem Speciat Bioavailab 19:17–24. https://doi.org/10.3184/095422907X198031
Park YH, Kim J, Kim SS, Park YK (2009) Pyrolysis characteristics and kinetics of oak trees using thermogravimetric analyzer and micro-tubing reactor. Bioresour Technol 100:400–405. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2008.06.040
Pasiecznik NM (2001) The Prosopis juliflora - Prosopis pallida complex : the Prosopis juliflora - Prosopis pallida complex
Peretz S, Florea-Spiroiu M, Anghel D-F et al (2013) Preparation of porous calcium alginate beads and their use for adsorption of O-Nitrophenol from aqueous solutions. Microfluid Nanoeng 22:123–136
Raghunathan K, Yang RYK (1987) New method for estimation of activation energies associated with coal gasification reactions. ACS Div Fuel Chem Prepr 32:478–485
Raheem A, Sivasangar S, Wan Azlina WAKG, Taufiq Yap YH, Danquah MK, Harun R (2015) Thermogravimetric study of Chlorella vulgaris for syngas production. Algal Res 12:52–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.algal.2015.08.003
Rajendran A, Basu SK (2009) Alginate-chitosan particulate system for sustained release of nimodipine. Trop J Pharm Res 8:433–440. https://doi.org/10.4314/tjpr.v8i5.48087
Rauf MA, Marzouki N, Körbahti BK (2008) Photolytic decolorization of Rose Bengal by UV/H2O2 and data optimization using response surface method. J Hazard Mater 159:602–609. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.02.098
Robbins P (2001) Tracking invasive land covers in India, or why our landscapes have never been modern. Ann Assoc Am Geogr 91:637–659. https://doi.org/10.1111/0004-5608.00263
Saravanakumar SS, Kumaravel A, Nagarajan T, Moorthy IG (2014) Effect of chemical treatments on physicochemical properties of Prosopis juliflora fibers. Int J Polym Anal Charact 19:383–390. https://doi.org/10.1080/1023666X.2014.903585
Saravanakumar SS, Kumaravel A, Nagarajan T, Sudhakar P, Baskaran R (2013) Characterization of a novel natural cellulosic fiber from Prosopis juliflora bark. Carbohydr Polym 92:1928–1933. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2012.11.064
Selvakumar KV, Badarinarayanan NS, Umesh A et al (2016) Acid dye degradation using electrochemical batch recirculation flow reactor. J Chem Pharm Sci 9:308–312
Shackleton RT, Le Maitre DC, Pasiecznik NM, Richardson DM (2014) Prosopis: a global assessment of the biogeography, benefits, impacts and management of one of the world’s worst woody invasive plant taxa. AoB Plants 6:1–18. https://doi.org/10.1093/aobpla/plu027
Sharma R, Dakshini KMM (1996) Ecological implications of seed characteristics of the native Prosopis cineraria and the alien P. juliflora. Vegetatio 124:101–105. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00045148
Smidsrod O, Skjak-Braek G (2000) Alginate as immobilization matrix for cells. Min Biotecnol 12:223–233. https://doi.org/10.1016/0167-7799(90)90139-O
Soares JP, Santos JE, Chierice GO, Cavalheiro ETG (2004) Thermal behavior of alginic acid and its sodium salt. Ecletica Quim 29:57–63. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0100-46702004000200009
Taylor P, Anuradha K, Bangal P, Madhavendra SS (2015) Desalination and water treatment structural characterization and water turbidity removing efficacy of Portulaca mucilage – alginate ( PMA ) beads. 37–41. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2014.994108
Thilagavathi M, Arivoli S, Vijayakumaran V (2015) Adsorption of malachite green from waste water using prosopis juliflora bark carbon. 42:120–133
Thirumavalavan M, Lai Y-L, Lee J-F (2011) Fourier transform infrared spectroscopic analysis of fruit peels before and after the adsorption of heavy metal ions from aqueous solution. J Chem Eng Data 56:2249–2255. https://doi.org/10.1021/je101262w
Tiwari JWK (1999) Exotic weed Prosopis juliflora in Gujarat and Rajasthan, India: boon or bane? Tigerpaper (FAO) 26:21–25
Van’t Hoff JH (1901) Osmotic pressure and chemical equilibrium. Nobel Lect 5–10
Venugopal T, Kannan K (2014) Effect of particle size of Prosopis juliflora seeds activated carbon and raw material in the removal of methylene blue in waste water. EnviroGeoChemica Acta 1:32–45
Wang Z-Y, Zhang Q-Z, Konno M, Saito S (1994) Sol–gel transition of alginate solution by the addition of various divalent cations: a rheological study. Biopolymers 34:737–746. https://doi.org/10.1002/bip.360340606
Weber W, Chakravorti RK (1974) Pore and solid diffusion models for fixed bed adsorbers. Am Inst Chem Eng J 20:229–238
Wong YC, Szeto YS, Cheung WH, McKay G (2004) Pseudo-first-order kinetic studies of the sorption of acid dyes onto chitosan. J Appl Polym Sci 92:1633–1645. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.13714
Xiao C, Liu H, Lu Y, Zhang L (2007) Blend films from sodium alginate and blend films from sodium alginate. J Macromol Sci A Pure Appl Chem 37–41. https://doi.org/10.1081/MA-100103352
Zhen H, Xiaoxu Y, Xi P, et al (2010) Thermal degradation study of sodium alginate-zeolite 4A composites. Proc 17th IAPRI World Conf Packag, p 406–409
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 1281 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sriram, A., Swaminathan, G. Utilization of dye-loaded activated carbon as a potential alternative fuel source: a feasibility study through calorific and thermo-gravimetric analysis. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25, 33140–33152 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-3279-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-3279-1