Abstract
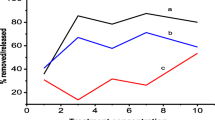
Pretreatment is a vital step to enhance the yield of total reducing sugars and biofuel production from lignocellulose biomass. An effective new lignin-degrading and polysaccharide-hydrolyzing bacteria, Ochrobactrum oryzae BMP03 and Bacillus sp. BMP01 strains, were isolated and identified from wood-feeding termite’s guts. Wheat straw was biodelignified by Ochrobactrum oryzae BMP03 bacteria strains to degrade lignin and to release the trapped cellulose and hemicellulose. The biodelignified wheat straw was hydrolyzed by Bacillus sp. BMP01 strains. Ochrobactrum oryzae BMP03-Bacillus sp. BMP01 consortia were also performed to analyze the effect of the simultaneous system. It was shown that the production of total reducing sugars in a separate hydrolysis system by Bacillus sp. BMP01 strain achieved 439 mg/g at 16 days of hydrolysis time, which is 9.45% higher than the simultaneous system. About 44.47% lignin was degraded by the Ochrobactrum oryzae BMP03 strain after 16 days of biotreatment. This also contributed for increment in cellulose content by 22.38% and hemicellulose content by 18.64%. The simultaneous system converted 368 mg of reducing sugars/g of wheat straw. Separate biodelignification and hydrolysis have an advantage over the simultaneous system in terms of hydrolysis efficiency and vice versa in terms of biotreatment time. Scanning electron microscope, mid-infrared analysis by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) and X-ray diffraction analysis confirmed the change in composition due to biotreatment. The biotreatment improved hydrolysis efficiency, which reduces the cost of biofuel production and increases the yield of biofuel. These results indicate the possibilities of biofuel production from wheat straw by employing Ochrobactrum oryzae BMP03 and Bacillus sp. BMP01 bacteria strains.





Similar content being viewed by others

References
Anjum SI, Shah AH, Aurongzeb M, Kori J, Azim MK, Ansari MJ, Bin L (2017) Characterization of gut bacterial flora of Apis mellifera from north-west Pakistan. Saudi J Biol Sci 25:388–392. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sjbs.2017.05.008
Anwar Z, Gulfraz M, Irshad M (2014) Agro-industrial lignocellulosic biomass a key to unlock the future bio-energy : a brief review. J Radiat Res Appl Sci 7:163–173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrras.2014.02.003
Azizi-shotorkhoft A, Mohammadabadi T, Motamedi H, Chaji M (2016) Isolation and identification of termite gut symbiotic bacteria with lignocellulose-degrading potential, and their effects on the nutritive value for ruminants of some by-products. Anim Feed Sci Technol 221:234–242. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anifeedsci.2016.04.016
Balat M, Balat H (2009) Recent trends in global production and utilization of bio-ethanol fuel. Appl Energy 86:2273–2282. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2009.03.015
Canam T, Town JR, Tsang A, Mcallister TA, Dumonceaux TJ (2011) Biological pretreatment with a cellobiose dehydrogenase-deficient strain of Trametes versicolor enhances the biofuel potential of canola straw. Bioresour Technol 102:10020–10027. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2011.08.045
Canam T, Dumonceaux TJ, Record E, Li Y (2013) White-rot fungi: the key to sustainable biofuel production? Biofuels 4:247–250
Chai L, Chen Y, Tang C (2014) Depolymerization and decolorization of kraft lignin by bacterium Comamonas sp. B-9. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98:1907–1912. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-013-5166-5
Chandra R, Raj A, Purohit HJ, Kapley A (2007) Characterisation and optimisation of three potential aerobic bacterial strains for kraft lignin degradation from pulp paper waste. Chemosphere 67(4):839–846
Chen Y, Huang J, Li Y (2015) Study of the rice straw biodegradation in mixed culture of Trichoderma viride and Aspergillus niger by GC-MS and FTIR. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:9807–9815. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-4149-8
Doyle JD, Wang Z, Hendricks CW, Bentjen SA, Bolton H, Fredrickson JK, Bleakley BH (1993) Effects of a lignin peroxidase-expressing recombinant, Streptomyces lividans TK23. 1, on biogeochemical cycling and the numbers and activities of microorganisms in soil. Appl Environ Microbiol 59:508–518
Guerra A, Mendonça R, Ferraz A (2003) Molecular weight distribution of wood components extracted from Pinus taeda biotreated by Ceriporiopsis subvermispora. Enzym Microb Technol 33:12–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0141-0229(03)00099-1
Hermosilla E, Schalchli H, Mutis A, Diez MC (2017) Combined effect of enzyme inducers and nitrate on selective lignin degradation in wheat straw by Ganoderma lobatum. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:21984–21996. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-9841-4
Hyun T, Seok J, Sunwoo C, Lee YY (2003) Pretreatment of corn stover by aqueous ammonia. Bioresour Technol 90:39–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0960-8524(03)00097-X
Ibrahim MM, Al-Turki A, Al-Sewedi D, Arif IA, El-Gaaly GA (2015) Molecular application for identification of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons degrading bacteria (PAHD) species isolated from oil polluted soil in Dammam, Saud Arabia. Saudi J Biol Sci 22:651–655. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sjbs.2015.04.018
Kim SM, Dien BS, Singh V (2016) Promise of combined hydrothermal/chemical and mechanical refining for pretreatment of woody and herbaceous biomass. Biotechnol Biofuels 2:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13068-016-0505-2
Kinya K, Shinya K, Masanori S (1998) Degradation of lignin compounds by bacteria from termite guts. Biotechnol Lett 20:459–462
Kuhad RC, Singh A, Eriksson KL (1997) Microorganisms and enzymes involved in the degradation of plant fiber cell walls. Biotechnol Pulp Pap Ind 57:45–125
Li M, Fan Y, Xu F, Sun R, Zhang X (2010) Cold sodium hydroxide/urea based pretreatment of bamboo for bioethanol production : characterization of the cellulose rich fraction. Ind Crop Prod 32:551–559. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2010.07.004
Liu Y, Deng Z, Tan H, Deng Q (2014) Characterization of cattle fecal Streptomyces strains converting cellulose and hemicelluloses into reducing sugars. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21:6069–6075. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-2564-x
Long Y, Xie L, Liu N, Yan X, Li M, Fan M, Wang Q (2010) Comparison of gut-associated and nest-associated microbial communities of a fungus-growing termite (Odontotermes yunnanensis ). Insect Sci 17:265–276. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1744-7917.2010.01327.x
Mansouri A, Rihani R, Nadia A, Özkan M (2016) Production of bioethanol from a mixture of agricultural feedstocks : biofuels characterization. Fuel 185:612–621. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2016.08.008
Marina G, Chacko D, Lo S, Mathew G, Yang J, Mahalingam J, Mahamadali T, Huang C (2013) Synergistic collaboration of gut symbionts in Odontotermes formosanus for lignocellulosic degradation and bio-hydrogen production. Bioresour Technol 145:337–344. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2012.12.055
Maroušek J (2013) Prospects in straw disintegration for biogas production. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20:7268–7274. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-013-1736-4
Masai E, Ichimura A, Sato Y, Miyauchi K, Katayama Y, Fukuda M (2003) Roles of the enantioselective glutathione S-transferases in cleavage of B-aryl ether. J Bacteriol 185:1768–1775. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.185.6.1768
Masarin F, Vicentim MP, Pavan PC (2008) Technological advances and mechanistic basis for fungal biopulping. Enzym Microb Technol 43:178–185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enzmictec.2007.10.002
Menon V, Rao M (2012) Trends in bioconversion of lignocellulose : biofuels, platform chemicals & biorefinery concept. Prog Energy Combust Sci 38:522–550. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pecs.2012.02.002
Miller GL (1959) Use of Dinitrosalicylic acid reagent for determination of reducing sugar. Anal Chem 31:426–428. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac60147a030
Mohanram S, Rajan K, Julie D, Nain L, Arora A (2015) Insights into biological delignification of rice straw by Trametes hirsuta and Myrothecium roridum and comparison of saccharification yields with dilute acid pretreatment. Biomass Bioenergy 76:54–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biombioe.2015.02.031
Mosier N, Wyman C, Dale B, Elander R, Lee YY, Holtzapple M, Ladisch M (2005) Features of promising technologies for pretreatment of lignocellulosic biomass. Bioresour Technol 96:673–686. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2004.06.025
Ni J, Tokuda G (2013) Lignocellulose-degrading enzymes from termites and their symbiotic microbiota. Biotechnol Adv 31:838–850. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2013.04.005
Pandey KK (1999) A study of chemical structure of soft and hardwood and wood polymers by FTIR spectroscopy. J Appl Polym Sci 71:1969–1975. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1097-4628(19990321)71:12<1969::AID-APP6>3.0.CO;2-D
Payne CM, Knott BC, Mayes HB, Hansson H, Himmel ME, Sandgren M, Sta J, Beckham GT (2015) Fungal Cellulases. Chem Rev 115:1308–1448. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr500351c
Raffa KF (2007) Composition of the bacterial community in the gut of the pine engraver, Ips pini ( Say ) ( Coleoptera ) colonizing red pine. Symbiosis 43:97–104
Saha BC, Qureshi N, Kennedy GJ, Cotta MA (2016) Biological pretreatment of corn stover with white-rot fungus for improved enzymatic hydrolysis. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 109:29–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2015.12.020
Scherrer P (1918) Estimation of the size and internal structure of colloidal particles by means of röntgen. Nachr Ges Wiss Göttingen 2:98–100
Segal L, Creely JJ, Martin AE, Conrad CM (1959) Empirical method for estimating the degree of crystallinity of native cellulose using the X-ray diffractometer. Tex Res J 29:786–794
Sluiter A, Hames B, Ruiz R, Scarlata C, Sluiter J, Templeton D, Nrel DC (2008) Determination of structural carbohydrates and lignin in biomass determination of structural carbohydrates and lignin in biomass. Lab Anal Proceed 1617:1–16
Smuga-kogut M, Zgórska K, Kogut T, Kukiełka K, Wojdalski J, Kupczyk A, Dró B (2017) The use of ionic liquid pretreatment of rye straw for bioethanol production. Fuel 191:266–274. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2016.11.066
Tarayre C, Brognaux A, Bauwens J, Brasseur C, Mattéotti C, Millet C, Destain J, Vandenbol M, Portetelle D, De Pauw E, Eric H, Francis F, Thonart P (2014) Isolation of amylolytic, xylanolytic, and cellulolytic microorganisms extracted from the gut of the termite Reticulitermes santonensis by means of a micro-aerobic atmosphere. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 30:1655–1660. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-013-1585-9
Tomás-pejó E, Fermoso J, Herrador E, Hernando H, Jiménez-sánchez S, Ballesteros M (2017) Valorization of steam-exploded wheat straw through a biorefinery approach : bioethanol and bio-oil co-production. Fuel 199:403–412. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2017.03.006
Tsegaye B, Balomajumder C, Roy P (2017) Alkali pretreatment of wheat straw followed by microbial hydrolysis for bioethanol production. Environ Technol:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2017.1418911
Tsegaye B, Balomajumder C, Roy P (2018) Isolation and characterization of novel lignolytic, cellulolytic, and hemicellulolytic Bacteria from wood-feeding termite Cryptotermes brevis. Int Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10123-018-0024-z
Varma VS, Ramu K, Kalamdhad AS (2015) Carbon decomposition by inoculating Phanerochaete chrysosporium during drum composting of agricultural waste. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:7851–7858. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-3989-y
Wang M, Zhou D, Wang Y, Wei S, Yang W, Kuang M, Ma L, Fang D, Xu S, Du S (2016) Bioethanol production from cotton stalk : a comparative study of various pretreatments. Fuel 184:527–532. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2016.07.061
Xu F, Zhou Q, Sun J, Liu C, Ren J, Sun R, Curling S, Fowler P, Baird MS (2007) Fractionation and characterization of chlorophyll and lignin from de-juiced Italian ryegrass ( Lolium multifolrum ) and timothy grass ( Phleum pratense ). Process Biochem 42:913–918. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2007.02.001
Xu F, Sun J, Konda NM, Shi J, Dutta T, Scown CD, Simmons A, Singh S (2016) Environmental science liquids : process intensification and the for the production of cellulosic ethanol. Energy Environ Sci 9:1042–1049. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5EE02940F
Xu Z, Qin L, Cai M, Hua W, Jin M (2018) Biodegradation of kraft lignin by newly isolated Klebsiella pneumoniae, Pseudomonas putida, and Ochrobactrum tritici strains. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-1633-y
Yang C, Wang T, Gao LN, Yin HJ, Lu X (2017) Isolation, identification and characterization of lignin-degrading bacteria from Qinling, China. J Appl Microbiol 123:1447–1460. https://doi.org/10.1111/jam.13562
Yao Y, David A, Davaritouchaee M (2018) Methane recovery from anaerobic digestion of urea-pretreated wheat straw. Renew Energy 115:139–148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2017.08.038
Yu M, Li J, Chang S, Zhang L, Mao Y, Cui T, Yan Z, Luo C, Li S (2016) Bioethanol production using the sodium hydroxide pretreated sweet sorghum bagasse without washing. Fuel 175:20–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2016.02.012
Zhang YP, Lynd LR (2004) Toward an aggregated understanding of enzymatic hydrolysis of cellulose : noncomplexed cellulase systems. Wiley Intersci 88:797–824. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.20282
Zhang K, Johnson L, Prasad PV, Pei Z, Wang D (2015) Big bluestem as a bioenergy crop : a review. Renew Sust Energ Rev 52:740–756. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2015.07.144
Zhang Q, Huang H, Han H, Qiu Z, Achal V (2017) Stimulatory effect of in-situ detoxification on bioethanol production by rice straw. Energy 135:32–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2017.06.099
Acknowledgments
The authors are thankful to the Indian Institute of Technology, Roorkee, India, for providing necessary facilities and technical support. Our gratitude is extended to the National Center for Microbial Resources, Pune, India, for performing 16S rRNA sequencing. One of the authors, Bahiru Tsegaye, would like to thank the Ministry of Education of Ethiopia for providing him fellowship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tsegaye, B., Balomajumder, C. & Roy, P. Biodegradation of wheat straw by Ochrobactrum oryzae BMP03 and Bacillus sp. BMP01 bacteria to enhance biofuel production by increasing total reducing sugars yield. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25, 30585–30596 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-3056-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-3056-1