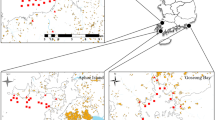
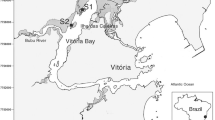
Abstract
A number of severe norovirus outbreaks due to the consumption of contaminated shellfish have been reported recently. In this study, we evaluated the distribution of coliphage densities to determine their efficacy as fecal indicators of enteric viruses, including noroviruses, in water samples collected from a shellfish growing area in Republic of Korea over a period of approximately 1 year. Male-specific and somatic coliphages in water samples were analyzed using the single agar layer method, and norovirus genogroups I and II, which infect mainly humans, were analyzed using duplex reverse transcription quantitative PCR. Male-specific and somatic coliphages were detected widely throughout the study area. Several environmental parameters, including salinity, precipitation, temperature, and wind speed were significantly correlated with coliphage concentrations (P < 0.05). Moreover, the concentrations of male-specific coliphages were positively correlated with the presence of human noroviruses (r = 0.443; P < 0.01). The geospatial analysis with coliphage concentrations using a geographic information system revealed that densely populated residential areas were the major source of fecal contamination. Our results indicate that coliphage monitoring in water could be a useful approach to prevent norovirus contamination in shellfish.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allwood PB, Malik YS, Hedberg CW, Goyal SM (2003) Survival of F-specific RNA coliphage, feline calicivirus, and Escherichia coli in water: a comparative study. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:5707–5710. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.69.9.5707-5710.2003
Alm EW, Burke J, Spain A (2003) Fecal indicator bacteria are abundant in wet sand at freshwater beaches. Water Res 37:3978–3982. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1354(03)00301-4
American Public Health Association (1970) Recommended procedures for the examination of sea water and shellfish. American Public Health Association, Washington, DC
Bertrand I, Schijven JF, Sánchez G, Wyn-Jones P, Ottoson J, Morin T, Muscillo M, Verani M, Nasser A, de Roda Husman AM, Myrmel M, Sellwood J, Cook N, Gantzer C (2012) The impact of temperature on the inactivation of enteric viruses in food and water: a review. J Appl Microbiol 112:1059–1074. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2672.2012.05267.x
Bower PA, Scopel CO, Jensen ET, Depas MM, McLellan SL (2005) Detection of genetic markers of fecal indicator bacteria in Lake Michigan and determination of their relationship to Escherichia coli densities using standard microbiological methods. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:8305–8313. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.71.12.8305-8313.2005
Campos CJ, Avant J, Gustar N, Lowther J, Powell A, Stockley L, Lees DN (2015) Fate of human noroviruses in shellfish and water impacted by frequent sewage pollution events. Environ Sci Technol 49:8377–8385. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.5b01268
Casanovas-Massana A, Gómez-Doñate M, Sánchez D, Belanche-Muñoz LA, Muniesa M, Blanch AR (2015) Predicting fecal sources in waters with diverse pollution loads using general and molecular host-specific indicators and applying machine learning methods. J Environ Manag 151:317–325. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2015.01.002
Chung H, Jaykus LA, Lovelace G, Sobsey MD (1998) Bacteriophages and bacteria as indicators of enteric viruses in oysters and their harvest waters. Water Sci Technol 38:37–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0273-1223(98)00797-5
Cole D, Long SC, Sobsey MD (2003) Evaluation of F+ RNA and DNA coliphages as source-specific indicators of fecal contamination in surface waters. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:6507–6514. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.69.11.6507-6514.2003
Contreras-Coll N, Lucena F, Mooijman K, Havelaar A, Pierzo V, Boque M, Gawler A, Höller C, Lambiri M, Mirolo G (2002) Occurrence and levels of indicator bacteriophages in bathing waters throughout Europe. Water Res 36:4963–4974. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1354(02)00229-4
Cornax R, Moriñigo MA, Balebona MC, Castro D, Borrego JJ (1991) Significance of several bacteriophage groups as indicators of sewage pollution in marine waters. Water Res 25:673–678. https://doi.org/10.1016/0043-1354(91)90042-O
Eftim SE, Hong T, Soller J, Boehm A, Warren I, Ichida A, Nappier SP (2017) Occurrence of norovirus in raw sewage—a systematic literature review and meta-analysis. Water Res 111:366–374 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2017.01.017
Flannery J, Rajko-Nenow P, Keaveney S, O'Flaherty V, Doré W (2013) Simulated sunlight inactivation of norovirus and FRNA bacteriophage in seawater. J Appl Microbiol 115:915–922. https://doi.org/10.1111/jam.12279
Fout G, Brinkman N, Cashdollar J, Griffin S, McMinn B, Rhodes E, Varughese E, Karim M, Grimm A, Spencer S (2010) Method 1615: measurement of enterovirus and norovirus occurrence in water by culture and RT-qPCR. National Exposure Research Laboratory,Office of Research and Development, US Environmental Protection Agency, Cincinnati
Gantzer C, Gillerman L, Kuznetsov M, Oron G (2001) Adsorption and survival of faecal coliforms, somatic coliphages and F-specific RNA phages in soil irrigated with wastewater. Water Sci Technol 43:117–124
Gibbons CD, Rodríguez RA, Tallon L, Sobsey MD (2010) Evaluation of positively charged alumina nanofibre cartridge filters for the primary concentration of noroviruses, adenoviruses and male-specific coliphages from seawater. J Appl Microbiol 109:635–641. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2672.2010.04691.x
Goblick GN, Anbarchian JM, Woods J, Burkhardt WIII, Calci K (2011) Evaluating the dilution of wastewater treatment plant effluent and viral impacts on shellfish growing areas in Mobile Bay, Alabama. J Shellfish Res 30:979–987. https://doi.org/10.2983/035.030.0341
Gourmelon M, Caprais M-P, Le Mennec C, Mieszkin S, Ponthoreau C, Gendronneau M (2010) Application of library-independent microbial source tracking methods for identifying the sources of faecal contamination in coastal areas. Water Sci Technol 61:1401–1409. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2010.033
Grabow WOK, Holtzhausen CS, De Villiers JC (1993) Research on bacteriophages as indicators of water quality: 1 January 1990 to 31 December 1992: final report (WRC report). Water Research Commission, Pretoria
Hall AJ, Eisenbart VG, Etingue AL, Gould LH, Lopman BA, Parashar UD (2012) Epidemiology of foodborne norovirus outbreaks, United States, 2001–2008. Emerg Infect Dis 18:1566–1573. https://doi.org/10.3201/eid1810.120833
Haramoto E, Fujino S, Otagiri M (2015) Distinct behaviors of infectious F-specific RNA coliphage genogroups at a wastewater treatment plant. Sci Total Environ 520:32–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.03.034
Jofre J (2007) Indicators of waterborne enteric viruses. Perspect Med Virol 17:227–249. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0168-7069(07)17011-7
Jończyk E, Kłak M, Międzybrodzki R, Górski A (2011) The influence of external factors on bacteriophages—review. Folia Microbiol 56:191–200. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12223-011-0039-8
Ko HY, Cho K, Park S, Kim JH, Kang J-H, Jeong YS, Choi JD, Sin Y, Lee C, Ko G (2018) Host-specific Bacteroides markers-based microbial source tracking in aquaculture areas. Microbes Environ 33:151-161. https://doi.org/10.1264/jsme2.ME17166
Korea Meteorological Administration (2016) Korea Meteorological Administration observation source. Korea Meteorological Administration, Seoul. http://www.kma.go.kr. Accessed 18 Feb 2018
Le Guyader FS, Atmar RL, Le Pendu J (2012) Transmission of viruses through shellfish : when specific ligands come into play. Curr Opin Virol 2:103–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coviro.2011.10.029
Lee JE, Lim MY, Kim SY, Lee S, Lee H, Oh HM, Hur HG, Ko G (2009) Molecular characterization of bacteriophages for microbial source tracking in Korea. Appl Environ Microbiol 75:7107–7114. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.00464-09
Lee DY, Weir SC, Lee H, Trevors JT (2010) Quantitative identification of fecal water pollution sources by TaqMan real-time PCR assays using Bacteroidales 16S rRNA genetic markers. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 88:1373–1383. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-010-2880-0
Lee H, Kim M, Lee JE, Lim M, Kim M, Kim J-M, Jheong WH, Kim J, Ko G (2011) Investigation of norovirus occurrence in groundwater in metropolitan Seoul, Korea. Sci Total Environ 409:2078–2084. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2011.01.059
Leight A, Hood R, Wood R, Brohawn K (2016) Climate relationships to fecal bacterial densities in Maryland shellfish harvest waters. Water Res 89:270–281. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres
Liang Z, He Z, Zhou X, Powell CA, Yang Y, He LM, Stoffella PJ (2013) Impact of mixed land-use practices on the microbial water quality in a subtropical coastal watershed. Sci Total Environ 449:426–433. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.01.087
Love DC, Lovelace GL, Money ES, Sobsey MD (2010a) Microbial fecal indicator concentrations in water and their correlation to environmental parameters in nine geographically diverse estuaries. Water Qual Expo Health 2:85–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.01.087
Love DC, Silverman A, Nelson KL (2010b) Human virus and bacteriophage inactivation in clear water by simulated sunlight compared to bacteriophage inactivation at a southern California beach. Environ Sci Technol 44:6965–6970. https://doi.org/10.1021/es1001924
McMinn BR, Ashbolt NJ, Korajkic A (2017) Bacteriophages as indicators of faecal pollution and enteric virus removal. Lett Appl Microbiol 65:11–26. https://doi.org/10.1111/lam.12736
Mehaffey MH, Nash MS, Wade TG, Ebert DW, Jones KB, Rager A (2005) Linking land cover and water quality in New York City’s water supply watersheds. Environ Monit Assess 107:29–44. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-005-2018-5
Mieszkin S, Caprais MP, Le Mennec C, Le Goff M, Edge TA, Gourmelon M (2013) Identification of the origin of faecal contamination in estuarine oysters using Bacteroidales and F-specific RNA bacteriophage markers. J Appl Microbiol 115:897–907. https://doi.org/10.1111/jam.12260
Ministry of Food and Drug Safety (2013) Guideline for investigation on the cause of food poisoning. Chapter 5. Ministry of Food and Drug Safety, Chungcheonbuk-do, Korean
Mok JS, Lee KJ, Kim PH, Lee TS, Lee HJ, Jung YJ, Kim JH (2016) Bacteriological quality evaluation of seawater and oysters from the Jaranman-Saryangdo area, a designated shellfish growing area in Korea: impact of inland pollution sources. Mar Pollut Bull 108:147–154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2016.04.036
Montazeri N, Maite M, Liu D, Cormier J, Landry M, Shackleford J, Lampila LE, Achberger EC, Janes ME (2015) Surveillance of enteric viruses and microbial indicators in the eastern oysters (Crassostrea virginica) and harvest waters along Louisiana Gulf Coast. J Food Sci 80:M1075–M1082. https://doi.org/10.1111/1750-3841.12871
Moriñigo MA, Wheeler D, Berry C, Jones C, Muñoz MA, Cornax R, Borrego JJ (1992) Evaluation of different bacteriophage groups as faecal indicators in contaminated natural waters in southern England. Water Res 26:267–271. https://doi.org/10.1016/0043-1354(92)90022-V
Noble RT, Griffith JF, Blackwood AD, Fuhrman JA, Gregory JB, Hernandez X, Liang X, Bera AA, Schiff K (2006) Multitiered approach using quantitative PCR to track sources of fecal pollution affecting Santa Monica Bay, California. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:1604–1612. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.72.2.1604-1612.2006
Ohad S, Vaizel-Ohayon D, Rom M, Guttman J, Berger D, Kravitz V, Pilo S, Huberman Z, Kashi Y, Rorman E (2015) Microbial source tracking in adjacent Karst Springs. Appl Environ Microbiol 81:5037–5047. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.00855-15
Polo D, Álvarez C, Díez J, Darriba S, Longa Á, Romalde JL (2014) Viral elimination during commercial depuration of shellfish. Food Control 43:206–212. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2014.03.022
Pouillot R, Van Doren JM, Woods J, Plante D, Smith M, Goblick G, Roberts C, Locas A, Hajen W, Stobo J, White J, Holtzman J, Buenaventura E, Burkhardt W 3rd, Catford A, Edwards R, DePaola A, Calci KR (2015) Meta-analysis of the reduction of norovirus and male-specific coliphage concentrations in wastewater treatment plants. Appl Environ Microbiol 81:4669–4681. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.00509-15
Pratt B, Chang H (2012) Effects of land cover, topography, and built structure on seasonal water quality at multiple spatial scales. J Hazard Mater 209-210:48–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.12.068
R Core Team (2016) Pheatmap package. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna
Rezaeinejad S, Vergara GG, Woo CH, Lim TT, Sobsey MD, Gin KY (2014) Surveillance of enteric viruses and coliphages in a tropical urban catchment. Water Res 58:122–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2014.03.051
Shibata T, Solo-Gabriele HM, Fleming LE, Elmir S (2004) Monitoring marine recreational water quality using multiple microbial indicators in an urban tropical environment. Water Res 38:3119–3131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2004.04.044
Sinton LW, Finlay RK, Lynch PA (1999) Sunlight inactivation of fecal bacteriophages and bacteria in sewage-polluted seawater. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:3605–3613
Sinton LW, Hall CH, Lynch PA, Davies-Colley RJ (2002) Sunlight inactivation of fecal indicator bacteria and bacteriophages from waste stabilization pond effluent in fresh and saline waters. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:1122–1131. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.68.3.1122-1131.2002
Tong ST, Chen W (2002) Modeling the relationship between land use and surface water quality. J Environ Manag 66:377–393. https://doi.org/10.1006/jema.2002.0593
Ueki Y, Shoji M, Suto A, Tanabe T, Okimura Y, Kikuchi Y, Saito N, Sano D, Omura T (2007) Persistence of caliciviruses in artificially contaminated oysters during depuration. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:5698–5701. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.00290-07
US Environmental Protection Agency (2001) Method 1602: male specific (F+) and somatic coliphage in water by single agar layer (SAL) procedure. Office of Water,US Environmental Protection Agency, Washington, DC
US Environmental Protection Agency (2015) Review of coliphages as possible indicators of fecal contamination for ambient water quality. 820-R-15-098, Office of Water, US Environmental Protection Agency, Washington, DC
Vieira CB, de Abreu CA, de Jesus MS, Luz SLB, Wyn-Jones P, Kay D, Vargha M, Miagostovich MP (2016) Viruses surveillance under different season scenarios of the Negro River Basin, Amazonia, Brazil. Food Environ Virol 8:57–69. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12560-016-9226-8
Vinjé J, Oudejans SJG, Stewart JR, Sobsey MD, Long SC (2004) Molecular detection and genotyping of male-specific coliphages by reverse transcription-PCR and reverse line blot hybridization. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:5996–6004. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.70.10.5996-6004.2004
Wilkes G, Brassard J, Edge TA, Gannon V, Gottschall N, Jokinen CC, Jones TH, Khan IU, Marti R, Sunohara MD, Topp E, Lapen DR (2014) Long-term monitoring of waterborne pathogens and microbial source tracking markers in paired agricultural watersheds under controlled and conventional tile drainage management. Appl Environ Microbiol 80:3708–3720. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.00254-14
Funding
This research was supported by a grant (14162MFDS973) from Ministry of Food and Drug Safety in 2016.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Diane Purchase
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 802 KB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cho, K., Lee, C., Park, S. et al. Use of coliphages to investigate norovirus contamination in a shellfish growing area in Republic of Korea. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25, 30044–30055 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-2857-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-2857-6