Abstract
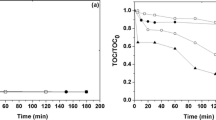
Ethylenethiourea (ETU) is a toxic degradation product of one class of fungicide which is largely employed in the world, the ethylenebisdithiocarbamates. In this study, ETU was degraded by ozonation enhanced by UV-C light irradiation (O3/UV-C) in aqueous medium. Degradation experiments were conducted at natural pH (6.8) and neutral pH (7.0, buffered). ETU was promptly eliminated from the reactive medium during ozonation in the presence and absence of light. Within the first few minutes of reaction conducted in natural pH, the pH decreased quickly from 6.8 to 3.0. Results show that ETU mineralization occurs only in the reaction conducted in neutral pH and that it takes place in a higher rate when enhanced by UV-C irradiation. Main intermediates formed during the O3/UV-C experiments in different conditions tested were also investigated and three different degradation mechanisms were proposed considering the occurrence of direct and indirect ozone reactions. At pH 7, ethylene urea (EU) was quickly generated and degraded. Meanwhile, at natural pH, besides EU, other compounds originated from the electrophilic attack of ozone to the sulfur atom present in the contaminant molecule were also identified during reaction and EU was detected within 60 min of reaction. Results showed that ozonation enhanced by UV-C promotes a faster reaction than the same system in the absence of light, and investigation of the toxicity is recommended.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amir Tahmasseb L, Nélieu S, Kerhoas L, Einhorn J (2002) Ozonation of chlorophenylurea pesticides in water: reaction monitoring and degradation pathways. Sci Total Environ 291:33–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0048-9697(01)01090-7
Amorim CC, Bottrel SEC, Costa EP, Teixeira APC, Leão MMD (2013) Removal of ethylenthiourea and 1,2,4-triazole pesticide metabolites from water by adsorption in commercial activated carbons. J Environ Sci Health B 48:183–190. https://doi.org/10.1080/03601234.2013.730287
Ballesteros Martín M, Sánchez Pérez J, Casas López J, Oller I, Malato Rodríguez S (2009) Degradation of a four-pesticide mixture by combined photo-Fenton and biological oxidation. Water Res 43:653–660
Beltrán FJ, García-Araya JF, Acedo B (1994) Advanced oxidation of atrazine in water—II. Ozonation combined with ultraviolet radiation. Water Res 28:2165–2174. https://doi.org/10.1016/0043-1354(94)90028-0
Bottrel SE, Amorim CC, Leao MM, Costa EP, Lacerda IA (2014) Degradation of ethylenethiourea pesticide metabolite from water by photocatalytic processes. J Environ Sci Health B 49:263–270. https://doi.org/10.1080/03601234.2014.868280
Bottrel S, Amorim C, Ramos V, Romão G, Leao M (2015) Ozonation and peroxone oxidation of ethylenethiourea in water: operational parameter optimization and by-product identification. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:903–908. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-3616-y
Chen WR, Wu C, Elovitz MS, Linden KG, Suffet IH (2008) Reactions of thiocarbamate, triazine and urea herbicides, RDX and benzenes on EPA contaminant candidate list with ozone and with hydroxyl radicals. Water Res 42:137–144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2007.07.037
Colosio C, Fustinoni S, Birindelli S, Bonomi I, de Paschale G, Mammone T, Tiramani M, Vercelli F, Visentin S, Maroni M (2002) Ethylenethiourea in urine as an indicator of exposure to mancozeb in vineyard workers. Toxicol Lett 134:133–140. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-4274(02)00182-0
Colosio C, Visentin S, Birindelli S, Campo L, Fustinoni S, Mariani F, Tiramani M, Tommasini M, Brambilla G, Maroni M (2006) Reference values for ethylenethiourea in urine in northern Italy: results of a pilot study. Toxicol Lett 162:153–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxlet.2005.09.031
David Yao CC, Haag WR (1991) Rate constants for direct reactions of ozone with several drinking water contaminants. Water Res 25:761–773. https://doi.org/10.1016/0043-1354(91)90155-J
De Witte B, Dewulf J, Demeestere K, Van Langenhove H (2009) Ozonation and advanced oxidation by the peroxone process of ciprofloxacin in water. J Hazard Mater 161:701–708. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.04.021
DIRECTIVE (2001) 2455/2001/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 20 November 2001 establishing the list of priority substances in the field of water policy and amending Directive 2000/60/EC vol 15
Dong X, Meng J, Yang B, Zhang Y, Gan J, Shu X, Shu J (2011) Experimental studies on ozonation of ethylenethiourea. J Environ Sci 23:65–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1001-0742(10)60374-9
Fustinoni S, Campo L, Colosio C, Birindelli S, Foà V (2005) Application of gas chromatography-mass spectrometry for the determination of urinary ethylenethiourea in humans. J Chromatogr B 814:251–258. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchromb.2004.10.042
Gago-Ferrero P, Demeestere K, Silvia Díaz-Cruz M, Barceló D (2013) Ozonation and peroxone oxidation of benzophenone-3 in water: effect of operational parameters and identification of intermediate products. Sci Total Environ 443:209–217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2012.10.006
Geissen V, Ramos FQ, de J. Bastidas-Bastidas P, Díaz-González G, Bello-Mendoza R, Huerta-Lwanga E, Ruiz-Suárez LE (2010) Soil and water pollution in a banana production region in tropical Mexico. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 85:407–413. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-010-0077-y
Gottschalk C, Libra JA, Saupe A (2009) Ozonation of water and waste water: a practical guide to understanding ozone and its applications. Wiley
Hoigné J, Bader H (1983a) Rate constants of reactions of ozone with organic and inorganic compounds in water—I: non-dissociating organic compounds. Water Res 17:173–183. https://doi.org/10.1016/0043-1354(83)90098-2
Hoigné J, Bader H (1983b) Rate constants of reactions of ozone with organic and inorganic compounds in water—II: dissociating organic compounds. Water Res 17:185–194. https://doi.org/10.1016/0043-1354(83)90099-4
Hoigné J, Bader H, Haag WR, Staehelin J (1985) Rate constants of reactions of ozone with organic and inorganic compounds in water—III. Inorganic compounds and radicals. Water Res 19:993–1004. https://doi.org/10.1016/0043-1354(85)90368-9
Hwang E-S, Cash JN, Zabik MJ (2001) Ozone and hydrogen peroxyacetic acid treatment to reduce or remove EBDCs and ETU residues in a solution. J Agric Food Chem 49:5689–5694
Hwang E-S, Cash JN, Zabik MJ (2003) Determination of degradation products and pathways of mancozeb and ethylenethiourea (ETU) in solutions due to ozone and chlorine dioxide treatments. J Agric Food Chem 51:1341–1346
Ikeura H, Hamasaki S, Tamaki M (2013) Effects of ozone microbubble treatment on removal of residual pesticides and quality of persimmon leaves. Food Chem 138:366–371. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2012.09.139
James JP, Quistad GB, Casida JE (1995) Ethylenethiourea S-oxidation products: preparation, degradation, and reaction with proteins. J Agric Food Chem 43:2530–2535
Javier Benitez F, Acero JL, Real FJ (2002) Degradation of carbofuran by using ozone, UV radiation and advanced oxidation processes. J Hazard Mater 89:51–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-3894(01)00300-4
Lemes VRR, Martins-Júnior HA, de Souza SVC, Colacioppo S (2014) Ethylenethiourea in fruits: optimization and in-house validation of a method by liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry, occurrence and dietary exposure assessment. Food Control 42:321–328. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2014.01.015
Magnusson B (2014) The fitness for purpose of analytical methods: a laboratory guide to method validation and related topics (2nd ed. 2014). Eurachem Guide. Eurachem
Malato S, Blanco J, Richter C, Maldonado MI (2000) Optimization of pre-industrial solar photocatalytic mineralization of commercial pesticides: application to pesticide container recycling. Appl Catal B Environ 25:31–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0926-3373(99)00114-9
Maranghi F, de Angelis S, Tassinari R, Chiarotti F, Lorenzetti S, Moracci G, Marcoccia D, Gilardi E, di Virgilio A, Eusepi A, Mantovani A, Olivieri A (2013) Reproductive toxicity and thyroid effects in Sprague Dawley rats exposed to low doses of ethylenethiourea. Food Chem Toxicol 59:261–271. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2013.05.048
Marshall WD (1979) Oxidative degradation of ethylenethiourea (ETU) and ETU progenitors by hydrogen peroxide and hypochlorite. J Agric Food Chem 27:295–299
Marshall WD, Singh J (1977) Oxidative inactivation of ethylenethiourea by hypochlorite in alkaline medium. J Agric Food Chem 25:1316–1320
Melgar C, Geissen V, Cram S, Sokolov M, Bastidas P, Ruiz Suárez LE, Javier Que Ramos F, Jarquín Sanchez A (2008) Pollutants in drainage channels following long-term application of mancozeb to banana plantations in southeastern Mexico. J Plant Nutr Soil Sci 171:597–604. https://doi.org/10.1002/jpln.200700171
Murov SL, Carmichael I, Hug GL (1993) Handbook of photochemistry. CRC Press
Poole AJ, Cord-Ruwisch R (2004) Treatment of strongflow wool scouring effluent by biological emulsion destabilisation. Water Res 38:1419–1426. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2003.11.034
Saltmiras DA, Lemley AT (2000) Degradation of ethylene thiourea (ETU) with three Fenton treatment processes. J Agric Food Chem 48:6149–6157
Saraiva Soares AF, Leão MMD, Vianna Neto MR, da Costa EP, de Oliveira MC, Amaral NB (2013) Efficiency of conventional drinking water treatment process in the removal of endosulfan, ethylenethiourea, and 1,2,4-triazole. J Water Supply Res Technol AQUA 62:367
Šojić D, Despotović V, Orčić D, Szabó E, Arany E, Armaković S, Illés E, Gajda-Schrantz K, Dombi A, Alapi T, Sajben-Nagy E, Palágyi A, Vágvölgyi C, Manczinger L, Bjelica L, Abramović B (2012) Degradation of thiamethoxam and metoprolol by UV, O3 and UV/O3 hybrid processes: kinetics, degradation intermediates and toxicity. J Hydrol 472–473:314–327. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2012.09.038
USEPA (2005) Mancozeb facts. Washington, DC
Vilar VJP, Moreira FC, Ferreira ACC, Sousa MA, Gonçalves C, Alpendurada MF, Boaventura RAR (2012) Biodegradability enhancement of a pesticide-containing bio-treated wastewater using a solar photo-Fenton treatment step followed by a biological oxidation process. Water Res 46:4599–4613. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2012.06.038
von Gunten U (2003) Ozonation of drinking water: part I. Oxidation kinetics and product formation. Water Res 37:1443–1467. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1354(02)00457-8
Zapata A, Oller I, Bizani E, Sánchez-Pérez JA, Maldonado MI, Malato S (2009) Evaluation of operational parameters involved in solar photo-Fenton degradation of a commercial pesticide mixture. Catal Today 144:94–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cattod.2008.12.030
López-Fernández O, Yáñez R, Rial-Otero R, Simal-Gándara J (2016) Kinetic modelling of mancozeb hydrolysis and photolysis to ethylenethiourea and other by-products in water. Water Res 102:561–571. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2016.07.006
López-Fernández O, Pose-Juan E, Rial-Otero R, Simal-Gándara J (2017) Effects of hydrochemistry variables on the half-life of mancozeb and on the hazard index associated to the sum of mancozeb and ethylenethiourea. Environ Res 154:253–260. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2017.01.016
Van Leeuwen CJ, Espeldoorn A, Mol F (1986) Aquatic toxicological aspects of dithiocarbamates and related compounds. III. Embryolarval studies with rainbow trout (Salmo gairdneri). Aquat Toxicol 9(2–3):129–145. https://doi.org/10.1016/0166-445X(86)90019-6
Funding
The authors thank Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES), Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa de Minas Gerais (FAPEMIG) and Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPQ) for the financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Vítor Pais Vilar
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 50 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bottrel, S.E.C., Pereira, P.C., de Oliveira Pereira, R. et al. Oxidation of ethylenethiourea in water via ozone enhanced by UV-C: identification of transformation products. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26, 4498–4509 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-2560-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-2560-7