Abstract
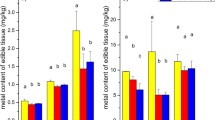
The widespread use of cadmium (Cd)-containing organic fertilizers is a source of heavy metal inputs to agricultural soils in suburban areas. Therefore, the research and development of new materials and technologies for the remediation of Cd-contaminated soil is of great significance and has the potential to guarantee the safety of agricultural products and the protection of human health. We performed pot experiments to determine the potential of combined amendments of illite/smectite (I/S) clay with bone chars for the remediation of Cd-contaminated agricultural soils in a suburban area of Beijing, China. The results showed that both diethylene triamine pentaacetic acid (DTPA)-extractable Cd in soil and the Cd in Brassica chinensis were significantly decreased by the application of 1, 2, or 5% combined amendments with various I/S and bone char (BC) ratios. The higher proportions of BC used in the combined amendments resulted in a better immobilization of soil Cd. The application of the 5% amendment that combined I/S with either pig or cattle BC resulted in the best immobilization. All of the combined amendments, regardless of the composition and ratio of the components, had no negative effects on the growth of B. chinensis. Therefore, it was concluded that combined amendments of I/S and BC have a good potential for remediating Cd-contaminated soils.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aikpokpodion PE, Lajide L, Aiyesanmi AF (2012) In situ remediation activities of rock phosphate in heavy-metal contaminated cocoa plantation soil in Owena, South Western, Nigeria. Glob J Environ Res 6(2):51–57
Alfven T, Jarup L, Elinder CG (2002) Cadmium and lead in blood in relation to low bone mineral density and tubular proteinuria. Eviron Health Persp 110:699–702
Azevedo RA, Gratao PL, Monteiro CC, Carvalho RF (2012) What is new in the research on cadmium-induced stress in plants? Food Energy Secur 1(2):133–140
Bao SD (2000) Soil agro-chemistrical analysis. Beijing. China agriculture press
Bolan N, Kunhikrishnan A, Thangarajan R, Kumpiene J, Park J, Makino T, Kirkham MB, Scheckel K (2014) Remediation of heavy metal(loid)s contaminated soils—to mobilize or to immobilize? J Hazard Mater 266:141–166
Brown S, Chrisitensen B, Lombi E et al (2005) An inter-laboratory study to test the ability of amendments to the availability of Cd, Pb, and Zn in situ. Environ Pollut 138:34–45
Chen SB, Zhu YG, Ma YB, McKay G (2006) Effect of bone char application on Pb bioavailability in a Pb-contaminated soil. Environ Pollut 139:433–439
Chen CX, Lu Y, Yin W et al (2011) Effect of bonemeal and zeolite on bioavailability of lead and cadmium in contaminated soils. Guangdong Agric Sci 38(14):60–62 (in Chinese)
Estêvo VM et al (2012) Sorption of heavy metals in tropical soils 171–214 CRC Press
Fang Y (2011) The effect and evaluation of long-term application of chicken manure on heavy metal accumulation in soil. Guangdong Trace Elem Sci 18:27–31 (in Chinese)
Feng R, Qiu WW, Lian F, Yu Z, Yang YX, Song Z (2013) Field evaluation of in situ remediation of Cd-contaminated soil using four additives, two foliar fertilisers and two varieties of pakchoi. J Environ Manag 124:17–24
Hodson ME, Valsami-Jones E, Cotter-Howells JD (2000) Bonemeal additions as a remediation treatment for metal contaminated soil. Environ Sci Technol 34:3501–3507
Huang YZ, Hao XW (2012) The influence of red mud, bone char and lime on uptake and accumulation of Pb, Zn and As by maize (Zea mays) planted in contaminated soil. Third International Conference on Digital Manufacturing & Automation 922–926
Huang YZ, Hu Y, Liu YX et al (2006) Effects of bone char on uptake and accumulation of heavy metals by three rice genotypes (Oryza sativa L.). J Agro-Environ Sci 25:1481–1148 (in Chinese)
Khorzughy SH, Eslamkish T, Ardejani FD, Heydartaemeh MR (2015) Cadmium removal from aqueous solutions by pumice and nano-pumice. Korean J Chem Eng 32(1):88–96
Kumpiene J, Lagerkvist A, Maurice C (2008) Stabilization of As, Cr, Cu, Pb and Zn in soil using amendments—a review. Waste Manag 28(1):215–225
Liang XF, Xu Y, Xu YM, Wang P, Wang L, Sun Y, Huang Q, Huang R (2016) Two-year stability of immobilization effect of sepiolite on Cd contaminants in paddy soil. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23(13):12922–12931
Luo L, Ma YB, Zhang SZ, Wei D, Zhu YG (2009) An inventory of trace element inputs to agricultural soils in China. J Environ Manag 90:2524–2530
Lv L, Jin MY, Bo W et al (2009) Study on remediation of the soil contaminated with cadmium by applying four minerals. J Agric Univ Hebei 32:1–5 (in Chinese)
Recatalá L, Sánchez J, Arbelo C, Sacristán D (2010) Testing the validity of a Cd soil quality standard in representative Mediterranean agricultural soils under an accumulator crop. Sci Total Environ 409:9–18
Sidik P, Talip D, Dawlet A (2014) Adsorption of Hg (II) from waste water using cow bone charcoal. Arid Environ Monit 28(1):4–13
Sparks DL (2003) Environmental soil chemistry, Second edn. Academic Press, Burlington
Sun YB, Xu YM, Shi X et al (2012) The effects of sepiolite on immobilization remediation of Cd contaminated red soil. Acta Sci Circumst 32(6):1465–1472 (in Chinese)
Sun YB, Wang PC, Xu YM et al (2014) Immobilization remediation of Cd and Pb contaminated soil: remediation potential and soil environmental quality. Environ Sci 35(12):4720–4726
Sun YB, Li Y, Xu YM, Liang X, Wang L (2015) In situ stabilization remediation of cadmium (Cd) and lead (Pb) co-contaminated paddy soil using bentonite. Appl Clay Sci 105-106:200–206
Uddin (2017) A review on the adsorption of heavy metals by clay minerals, with special focus on the past decade. Chem Eng J 308:438–462
Wu HP, Lai C, Zeng GG, Liang J, Chen J, Xu J, Dai J, Li X, Liu J, Chen M, Lu L, Hu L, Wan J (2017) The interactions of composting and biochar and their implications for soil amendment and pollution remediation: a review. Crit Rev Biotechnol 37(6):754–764
Xu Y, Liang XF, Xu YM et al (2017) Remediation of heavy metal-polluted agricultural soils using clay minerals: a review. Pedosphere 27(2):193–204
Yang X, Liu JJ, McGrouther K, Huang H, Lu K, Guo X, He L, Lin X, Che L, Ye Z, Wang H (2016) Effect of biochar on the extractability of heavy metals (Cd, Cu, Pb, and Zn) and enzyme activity in soil. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:974–984
Yao AJ, Wang YN, Ling XD, Chen Z, Tang Y, Qiu H, Ying R, Qiu R (2017) Effects of an iron-silicon material, a synthetic zeolite and an alkaline clay on vegetable uptake of As and Cd from a polluted agricultural soil and proposed remediation mechanisms. Environ Geochem Hlth 39(2):353–367
Yin F, Wang HJ, Li YY et al (2015) Remediation of multiple heavy metal polluted soil using different immobilizing agents. J Agro-Environ Sci 34(03):438–448(in Chinese)
Yuan SS, Li ZY, Wang YM (2016) Removal of copper and cadmium ions in aqueous solution via adsorption by nano-sized illite-smectite clay. J Chin Ceram Soc 01:43–49 (in Chinese)
Zenteno MDC, Freitas RCAD, Fernandes RBA et al (2013) Sorption of cadmium in some soil amendments for in situ recovery of contaminated coils. Water Air Soil Poll 224:1418
Zhang G, Lin Y, Wang M (2011) Remediation of copper polluted red soils with clay materials. J Environ Sci 23:461–467
Zhang LH, Yuan YH, Yan ZG et al (2016) Application of nano illite/smectite clay for adsorptive removal of metals in water. Res Environ Sci 29(1):115–123
Zhao FJ, Ma YB, Zhu YG, Tang Z, McGrath SP (2015) Soil contamination in China: current status and mitigation strategies. Environ Sci Technol 49(2):750–759
Zotiadis V, Argyraki A, Theologou E (2012) Pilot scale application of attapulgitic clay for stabil ization of toxic elements in contaminated soil. J Geotech Geoenviron 138(5):1–5
Funding
This work was financially supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China (project no. 41271492), Beijing Municipal Commission of Education Foundation (project no. KM201610028012), and National Key Technology Research and Development Program of the Ministry of Science and Technology (2014BAD14B02).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Hailong Wang
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, H., Ou, J., Wang, X. et al. Immobilization of soil cadmium using combined amendments of illite/smectite clay with bone chars. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25, 20723–20731 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-2227-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-2227-4