Abstract
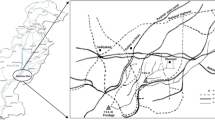
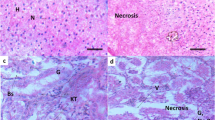
Heavy metals are the most dangerous hazards affecting aquatic biota in Egypt specially the Nile Tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus, which is an important species in commercial fisheries. Some areas were not fully studied to screen the hazards that may affect this economic fish. Therefore, the present study aimed to evaluate the potential hazards of heavy metals on O. niloticus in Al-Gharbiya Governorate in the Middle delta of Egypt. Water and fish samples were collected from Al-Qased canal, Kafr El-Zayaat Nile, El-Maash canal in Al-Gharbiya Governorate plus a reference site which is a fish farm at the Faculty of Agriculture, Damietta University, Damitta Governorate, Egypt. The results showed a significant increase (p < 0.05) in the lead, zinc, magnesium, manganese, and copper levels while showed a significant decrease (p < 0.05) in the iron level in the water from all the investigated areas. Cadmium level was significantly high (p < 0.05) in Kafr El-Zayaat Nile and EL-Maash canal only. These metals were also accumulated in the fish livers and gills. Consequently, ALT and AST activities and creatinine level were significantly (p < 0.05) high in all the investigated areas. Histopathological examination revealed cytoplasmic and nuclear degeneration in the hepatocytes in all the investigated areas. Renal glomeruli and Bowman’s capsule were not completely intact in Al-Qased and El-Maash canals while conspicuous shrinkage of the glomeruli was determined in Kafr El-Zayaat Nile. Furthermore, slight damage in the secondary lamellae was detected in the gill from Al-Qased canal while in the other areas appeared vacuolated or destructed. Finally, spleen sections of fish from different sites showed the absence of melanin pigments and some vacuoles. In conclusion, the Nile Tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus, is affected by the toxic effects of the heavy metals in Al-Gharbiya Governorate in Egypt and this gives an alarm and should be taken into consideration.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdel-Mohsien HS, Mahmoud MA (2015) Accumulation of some heavy metals in Oreochromis niloticus from the Nile in Egypt: potential hazards to fish and consumers. J Environ Prot 6:1003–1013
Abdel-Satar AM, Goher ME (2015) Heavy metals fractionation and risk assessment in surface sediments of Qarun and Wadi El-Rayan Lakes, Egypt. Environ Monit Assess 187(6):346–352
Abdel-tawwab M, Wafeek M (2010) Response of Nile Tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus to enviromental cadmium toxicity during organic selenium supplementation. J World Aquacult Soc 41:106–114
Ajeniyi SA, Solomon RJ (2014) Urea and creatinine of Clarias Gariepinus in three different commercial ponds. Nat Sci 12:124–138
Al-Asgah NA, Abdel-Warith AA, Younis EM, Allam HY (2015) Haematological and biochemical parameters and tissue accumulations of cadmium in Oreochromisniloticus exposed to various concentrations of cadmium chloride. Saudi J Biol Sci 22:543–550
APHA American Public Health Association (APHA) (2005) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 21th edn. APHA, Washington, DC
Attia OE, Ghrefat H (2013) Assessing heavy metal pollution in the recent bottom sediments of Mabahiss Bay, North Hurghada, Red Sea, Egypt. Environ Monit Assess 12:9925–9934
Barak NAE, Mason CF (1990) Mercury, cadmium and lead concentrations in five species of freshwater fish from Eastern England. Sci Total Environ 92:257–263
Benli AC, Köksal G, Ozkul A (2008) Sublethal ammonia exposure of Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Effects on gill, liver and kidney histology. Chemosphere 72(9):1355–1358
Bernet D, Schmidt H, Meier W, Brkhardt-Holm P, Wahli T (1999) Histopathology in fish: proposal for a protocol to assess aquatic pollution. J Fish Dis 22:25–34
Camargo MM, Martinez CB (2007) Histopathology of gills, kidney and liver of neotropical fish caged in an urban stream. Neotropical Ichthyol 5:327–336
Carvalho Cdos S, Bernusso VA, de Araújo HS, Espíndola EL, Fernandes MN (2012) Biomarker responses as indication of contaminant effects in Oreochromisniloticus. Chemosphere 89(1):60–69
Castiglione S, Todeschini V, Franchin C, Torrigiani P, Gastaldi D, Cicatelli A, Rinaudo C, Berta G, Biondi S, Lingua G (2009) Clonal differences in survival capacity, copper and zinc accumulation, and correlation with leaf polyamine levels in poplar: a large-scale field trial on heavily polluted soil. Environ Pollut 157:2108–2117
Cerqueira CCC, Fernandes MN (2002) Gill tissue recovery after cooper exposure and blood parameter responses in the tropical fish Prochilodus scrofa. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 52:83–91
Chen C, Wooster GA, Bowser PR (2004) Comparative blood chemistry and histopathology of tilapia infected with Vibrio vulnificus or Streptococcus iniae or exposed to carbon tetrachloride, gentamicin or copper sulfate. Aquaculture 239:421–443
Dahshan H, Abd-ElallA M, Megahed AM (2013) Trace metal levels in water, fish, and sediment from River Nile, Egypt: potential health risks assessment. J Toxicol Environ Health 21:1183–1187
Dhaneesh KV, Gopi M, Ganeshamurthy R, Kumar TTA, Balasubramanian T (2012) Bio-accumulation of metals on reef associated organisms of Lakshadweep Archipelago. Food Chem 131:985–991
Drishya MK, Kumari S, Kumar M, Ambikadevi AP, Aswin B (2016) Histopathological changes in the gills of fresh water fish, Catla catla exposed to electroplating effluent. Int J Fish Aquat Stud 5:13–16
Elnimr T (2011) Evaluation of some heavy metals in Pangasius hypothalamus and Tilapia nilotica and the role of acetic acid in lowering their levels. Int J Fish Aquacult 3:151–157
FAO/SIDA (1983) Manual of methods in aqautic environment research [Part 9 Analyses of metals and organochorines in fish]. FAO Fish Tech Pap 212:33
Fawcett JK, Scott JE (1960) A rapid and precise method for the determination of urea. J Clin Pathol 13:156–159
Gernhofer M, Pawet M, Schramm M, Müller E, Triebskorn R (2001) Ultrastructural biomarkers as tools to characterize the health status of fish in contaminated streams. J Aquat Ecosyst Stress Recover 8:241–260
Giari L, Manera LM, Simoni E, Dezfuli BS (2007) Cellular alterations in different organs of European sea bass Dicentrarchus labrax (L.) exposed to cadmium. Chemosphere 67:1171–1181
Gupta P, Srivastava N (2006) Effects of sublethal concentrations of zinc on histological changes and bioaccumulation of zinc by kidney of fish Channa punctatus (Bloch). J Environ Biol 27:211–215
Iqbal F, Qureshi IZ, Ali M (2004) Histopathological changes in the kidney of common carp, Cyprinus carpio following nitrate exposure. J Res Sci 15:411–418
Ismail HT, Mahboub HH (2016) Effect of acute exposure to nonylphenol on biochemical, hormonal, and hematological parameters and muscle tissues residues of Nile tilapia; Oreochromis niloticus. Vet World 9:2231–0916
Jalaludeen MD, Arunachalam M, Raja M, Nandagopal S, Sundar S, Palanimuthu D (2012) Histology of the gill, liver and kidney tissues of the fresh water fish Tilapia Mossambica exposed to cadmium sulphate. IJABR 2:572–578
Jasima M, Sofian-Azirun M, Yusoff I, Rahman MM (2016) Bioaccumulation and histopathological changes induced by toxicity of mercury (HgCl2) to tilapia fish Oreochromis niloticus. Sains Malays 45:119–127
Kiran BR, Shashi Shekhar TR, Puttaiah ET, Shivaraj Y (2006) Trace metal levels in the organs of fin fish Oreochromis mossambicus (peter) and relevant water of Jannapura lake, India. J Environ Sci Eng 1:15–20
Larsen K (1972) Creatinine assay by areaction—kinetic principle. Clin Chim Acta 41:209–217
Lukin A, Sharova J, Belicheva L, Camus L (2011) Assessment of fish health status in the Pechora River: effects of contamination. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 74(3):355–365
Martinez CBR, Nagae MY, Zaia CTV, Zaia DAM (2004) Acute morphological and physiological effects of lead in the neotropical fish Prochilodus lineatus. Braz J Biol 64:797–807
Mekkawy AA, Mahmoud UM, Wassif ET, Naguib M (2011) Effects of cadmium on some haematological and biochemical characteristics of Oreochromis niloticus (Linnaeus, 1758) dietary supplemented with tomato paste and vitamin E. Fish Physiol Biochem 37:71–84
Mohamed FAS (2009) Histopathological studies on Tilapia zillii and Solea vulgaris from Lake Qarun, Egypt. World J Fish Mar Sci 1:29–39
Moore JW, Ramamoorthy S (1984) Heavy metals in natural waters: applied monitoring and impact assessment. Springer-Verlag, New York
Murray R (1984) Alanine aminotransferase. Kapln A et al. Clin Chem The C.V. Mosby Co. St Louis, Tronto, Princeton, pp 1088–1090
Naigaga I (2003) Bioaccumulation and histopathology of copper in Oreochromis mossambicus. Ichthyology. Fish Sci 31:119–124
National Kidney Foundation (2002) K/DOQI clinical practice guidelines for chronic kidney disease: evaluation, classification and stratification. Am J Kidney Dis 39:1–266
Oliveira Ribeiro CA, Vollaire Y, Sanchez-Chez A, Roche H (2005) Bioaccumulation and the effects of organochlorine pesticides, PAH and heavy metals in the eel (Anguilla anguilla) at the Camargue Nature Reserve, France. Aquat Toxicol 74(1):53–69
Omar WA, Zaghloul KH, Abdel-Khalek AA, Abo Hegab S (2013) Risk assessment and toxic effects of metal pollution in two cultured and wild fish species from highly degraded aquatic habitats. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 65:753–764
Omar WA, Mikhail WZ, Abdo HM, Abou El Defan TA, Poraas MM (2015) Ecological risk assessment of metal pollution along greater Cairo sector of the River Nile, Egypt, using Nile Tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus, as bioindicator. J Toxicol 3:1–11
Paulo DV, Fontes FM, Flores-Lopes F (2012) Histopathological alterations observed in the liver of Poecilia vivipara (Cyprinodontiformes: Poeciliidae) as a tool for the environmental quality assessment of the Cachoeira River, BA. Braz J Biol 72(1):131–140
Qadir A, Malik RN (2011) Heavy metals in eight edible fish species from two polluted tributaries (Aik and Palkhu) of the river Chenab, Pakistan. Biol Trace Elem Res 143:1524–1540
Ramachandiran K, Prakash Sahaya Leon J, Mariappan M, Manivelu D (2017) Biochemical changes induced by heavy metal copper on gill and liver of fresh water fish, Oreochromis mossambicus (Tilapia). Int J Modn Res Revs 5:1457–1459
Rashed MN (2001) Cadmium and lead levels in fish (Tilapia nilotica) tissues as biological indicator for Lake water pollution. Environ Monit Assess 68:75–89
Rodrigues EL, Fanta E (1998) Liver histopathology of the fish Brachydanio rerio after acute exposure to sublethal levels of the organophosphate Dimetoato 500. Rev Bras Zool 15:441–450
Saad SM, El-Deeb AE, Tayel SI, Ahmed NAM (2011) Haematological and histopathological studies on Clarias gariepinus in relation to water quality along Rosetta branch, River Nile, Egypt. J Exp Biol (Zool) 7:223–233
Samanta P, Mukherjee AK, Pal S, Kole D, Ghosh AR (2016) Toxic effects of glyphosate-based herbicide, Excel Mera 71 on gill, liver, and kidney of Heteropneustes fossilis under laboratory and field conditions. J Microsc Ultrastruct 4:147–155
Shalaby AME (2007) Effect of EDTA on toxicity reduction of cadmium in relation to growth, some haematological and biochemicalprofiles of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). J Fish Aquat Sci 2:100–109
Thophon S, Kruatrachue M, Upathan ES, Pokethitiyook P, Sahaphong S, Jarikhuan S (2003) Histopathological alterations of white seabass, Latescalcarifer in acute and subchronic cadmium exposure. Environ Pollut 21:307–320
Triebskorn R, Telcean H, Casper A, Sandu C, Stan G, Colarescu O, Dori T, Köhler H (2008) Monitoring pollution in River Mures, Romania, part II: metal accumulation and histopathology in fish. Environ Monit Assess 141:177–188
van Dyk JC, Pieterse GM, van Vuren JHJ (2007) Histological changes in the liver of Oreochromis mossambicus (Cichlidae) after exposure to cadmium and zinc. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 66:432–440
Waseem A, Arshad J, Iqbal F, Sajjad A, Mehmood Z, Murtaza G (2014) Pollution status of Pakistan: a retrospective review on heavy metal contamination of water, soil, and vegetables. Biomed Res Int 32:1–29
Young DS (1995) Effects of Drugs on Clinical Laboratory Tests, 4th ed. AACC Press, Washington, DC
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The experimental research on fish was ethically approved by Animal Ethics Committee of Faculty of Science, Tanta University, Egypt.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alm-Eldeen, A.A., Donia, T. & Alzahaby, S. Comparative study on the toxic effects of some heavy metals on the Nile Tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus, in the Middle Delta, Egypt. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25, 14636–14646 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-1677-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-1677-z