Abstract
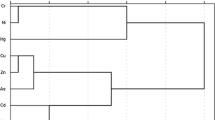
Heavy metal contamination in soils/sediments and its impact on human health and ecological environment have aroused wide concerns. Our study investigated 30 samples of soils and sediments around Dongting Lake to analyze the concentration of As, Cd, Cr, Cu, Fe, Mn, Ni, Pb, and Zn in the samples and to distinguish the natural and anthropogenic sources. Also, the relationship between heavy metals and the physicochemical properties of samples was studied by multivariate statistical analysis. Concentration of Cd at most sampling sites were more than five times that of national environmental quality standard for soil in China (GB 15618-1995), and Pb and Zn levels exceeded one to two times. Moreover, Cr in the soil was higher than the national environmental quality standards for one to two times while in sediment was lower than the national standard. The investigation revealed that the accumulations of As, Cd, Mn, and Pb in the soils, and sediments were affected apparently by anthropogenic activities; however, Cr, Fe, and Ni levels were impacted by parent materials. Human activities around Dongting Lake mainly consisted of industrial activities, mining and smelting, sewage discharges, fossil fuel combustion, and agricultural chemicals. The spatial distribution of heavy metal in soil followed the rule of geographical gradient, whereas in sediments, it was significantly affected by the river basins and human activities. The result of principal component analysis (PCA) demonstrated that heavy metals in soils were associated with pH and total phosphorus (TP), while in sediments, As, Cr, Fe, and Ni were closely associated with cation exchange capacity (CEC) and pH, where Pb, Zn, and Cd were associated with total nitrogen (TN), TP, total carbon (TC), moisture content (MC), soil organic matter (SOM), and ignition lost (IL). Our research provides comprehensive approaches to better understand the potential sources and the fate of contaminants in lakeshore soils and sediments.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alonso Castillo ML, Sánchez TI, Vereda AE, García dTA, Cano Pavón JM (2013) Bioavailability of heavy metals in water and sediments from a typical Mediterranean Bay (Málaga Bay, region of Andalucía, southern Spain). Mar Pollut Bull 76:427–434
Argyraki A, Kelepertzis E (2014) Urban soil geochemistry in Athens, Greece: the importance of local geology in controlling the distribution of potentially harmful trace elements. Sci Total Environ 482–483:366–377
Bella GD, Turco VL, Potortì AG, Rando R, Licata P, Dugo G (2013) Statistical analysis of heavy metals in Cerastoderma edule glaucum and Venerupis aurea laeta from Ganzirri Lake, Messina (Italy). Environ Monit Assess 185:7517–7525. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-013-3116-4
Bolan NS, Adriano DC, Natesan R, Koo BJ (2003) Effects of organic amendments on the reduction and phytoavailability of chromate in mineral soil. J Environ Qual 32:120–128. https://doi.org/10.2134/jeq2003.1200
Chandrasekaran A, Ravisankar R (2015) Spatial distribution of physico-chemical properties and function of heavy metals in soils of Yelagiri hills, Tamilnadu by energy dispersive X-ray florescence spectroscopy (EDXRF) with statistical approach. Spectrochimica Acta Part A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 150:586–601
Davis HT, Aelion CM, Mcdermott S, Lawson AB (2009) Identifying natural and anthropogenic sources of metals in urban and rural soils using GIS-based data, PCA, and spatial interpolation. Environ Pollut 157:2378–2385
Dou Y, Li J, Zhao J, Hu B, Yang S (2013) Distribution, enrichment and source of heavy metals in surface sediments of the eastern Beibu Bay, South China Sea. Mar Pollut Bull 67:137–145
Gao X, Zhuang W, Chen CT, Zhang Y (2015) Sediment quality of the SW coastal Laizhou Bay, Bohai Sea, China: a comprehensive assessment based on the analysis of heavy metals. PLoS One 10:e0122190. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0122190
García JH et al (2004) Characterization and implication of potential fugitive dust sources in the Paso del Norte region. Sci Total Environ 325:95–112
Guillén MT, Delgado J, Albanese S, Nieto JM, Lima A, Vivo BD (2012) Heavy metals fractionation and multivariate statistical techniques to evaluate the environmental risk in soils of Huelva Township (SW Iberian Peninsula). J Geochem Explor 119–120:32–43
Han YM, Du PX, Cao JJ, Posmentier ES (2006) Multivariate analysis of heavy metal contamination in urban dusts of Xi'an, Central China. Sci Total Environ 355:176–186
Kabatapendias A, Pendias HK (2011) Trace elements in soils and plants. CRC Press,
Kalnejais LH, Martin WR, Bothner MH (2010) The release of dissolved nutrients and metals from coastal sediments due to resuspension. Mar Chem 121:224–235
Li F, Huang J, Zeng G, Yuan X, Li X, Liang J, Wang X, Tang X, Bai B (2013) Spatial risk assessment and sources identification of heavy metals in surface sediments from Dongting Lake, middle China. J Geochem Explor 132:75–83
Li J, Jia C, Lu Y, Tang S, Shim H (2015) Multivariate analysis of heavy metal leaching from urban soils following simulated acid rain. Microchem J 122:89–95
Liao J, Chen J, Ru X, Chen J, Wu H, Wei C (2016) Heavy metals in river surface sediments affected with multiple pollution sources, South China: distribution, enrichment and source apportionment. J Geochem Explor 176:9–19
Lin Y, Han P, Huang Y, Yuan GL, Guo JX, Li J (2017) Source identification of potentially hazardous elements and their relationships with soil properties in agricultural soil of the Pinggu district of Beijing, China: multivariate statistical analysis and redundancy analysis. J Geochem Explor 173:110–118
Looi LJ, Aris AZ, Yusoff FM, Hashim Z (2015) Mercury contamination in the estuaries and coastal sediments of the Strait of Malacca. Environ Monitor Assess 187:1–15
Luo XS, Yu S, Zhu YG, Li XD (2012) Trace metal contamination in urban soils of China. Sci Total Environ 421–422:17–30
Mcgregor LA, Gauchottelindsay C, Daéid NN, Thomas R, Kalin RM (2012) Multivariate statistical methods for the environmental forensic classification of coal tars from former manufactured gas plants. Environ Sci Technol 46:3744–3752. https://doi.org/10.1021/es203708w
Navarrete IA, Asio VB, Jahn R, Tsutsuki K (2007) Characteristics and genesis of two strongly weathered soils in Samar, Philippines. Soil Res 45:153–163
Navarrete IA, Gabiana CC, Dumo JR, Guzman MA, Valera NS, Espiritu EQ (2017) Heavy metal concentrations in soils and vegetation in urban areas of Quezon City, Philippines. Environ Monitor Assess 189(145):145. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-017-5849-y
Nicholson FA, Smith SR, Alloway BJ, Carlton-Smith C, Chambers BJ (2003) An inventory of heavy metal input to agricultural soil in England and Wales. Sci Total Environ 311:205–219
Nobi EP, Dilipan E, Thangaradjou T, Sivakumar K, Kannan L (2010) Geochemical and geo-statistical assessment of heavy metal concentration in the sediments of different coastal ecosystems of Andaman Islands, India. Estuarine Coastal & Shelf Sci 87:253–264
Puschenreiter M, Horak O, Friesl W, Hartl W (2005) Low-cost agricultural measures to reduce heavy metal transfer into the food chain—a review. Plant Soil Environ 51:1–11
Rahmanpour S, Ghorghani NF, Lotfi Ashtiyani SM (2014) Heavy metal in water and aquatic organisms from different intertidal ecosystems, Persian gulf. Environ Monitor Assess 186:5401–5409
Ramos L, Hernandez LM, Gonzalez MJ (1994) Sequential fractionation of copper, lead, cadmium and zinc in soils from or near Doñana National Park. J Environ Qual 23:50–57
Satapathy DR, Panda CR (2015) Spatio-temporal distribution of major and trace metals in estuarine sediments of Dhamra, Bay of Bengal, India—its environmental significance. Environ Monitor Assess 187(4133):4133. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-014-4133-7
Shan W, Xia X, Lin C, Xi C, Zhou C (2010) Levels of arsenic and heavy metals in the rural soils of Beijing and their changes over the last two decades (1985–2008). J Hazard Mater 179:860–868
Shi GL, Tian YZ, Guo CS, Feng YC, Xu J, Zhang Y (2012) Sediment–pore water partition of PAH source contributions to the Yellow River using two receptor models. J Soils & Sediments 12:1154–1163
Susaya JP, Kihyun K, Asio VB, Chen ZS, Navarrete I (2010) Quantifying nickel in soils and plants in an ultramafic area in Philippines. Environ Monitor Assess 167:505–514
Tian K, Hu W, Xing Z, Huang B, Jia M, Wan M (2016) Determination and evaluation of heavy metals in soils under two different greenhouse vegetable production systems in eastern China. Chemosphere 165:555–563
Ungureanu T, Iancu GO, Pintilei M, Chicoș MM (2016) Spatial distribution and geochemistry of heavy metals in soils: a case study from the NE area of Vaslui county, Romania. J Geochem Explor 176:20–32
Xu L, Wang T, Ni K, Liu S, Wang P, Xie S, Meng J, Zheng X, Lu Y (2014) Ecological risk assessment of arsenic and metals in surface sediments from estuarine and coastal areas of the southern Bohai Sea, China. Human Ecol Risk Assess Int J 20:388–401
Xu J, Tian YZ, Zhang Y, Guo CS, Shi GL, Zhang CY, Feng YC (2013) Source apportionment of perfluorinated compounds (PFCs) in sediments: using three multivariate factor analysis receptor models. J Hazard Mater 260:483–488
Yidana SM, Ophori D, Banoeng-Yakubo B (2008) A multivariate statistical analysis of surface water chemistry data—the Ankobra Basin, Ghana. J Environ Manag 86:80–87
Yuan GL, Sun TH, Han P, Li J (2013) Environmental geochemical mapping and multivariate geostatistical analysis of heavy metals in topsoils of a closed steel smelter: Capital Iron & Steel Factory, Beijing, China. J Geochem Explor 130:15–21
Yuan GL, Sun TH, Han P, Li J, Lang XX (2014) Source identification and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in topsoil using environmental geochemical mapping: typical urban renewal area in Beijing, China. J Geochem Explor 136:40–47
Zahra A, Hashmi MZ, Malik RN, Ahmed Z (2014) Enrichment and geo-accumulation of heavy metals and risk assessment of sediments of the Kurang Nallah—feeding tributary of the Rawal Lake reservoir, Pakistan. Sci Total Environ 470-471:925–933
Zhao J, Hu B, Li J, Yang J, Bai F, Dou Y, Yin X (2014) One hundred-year sedimentary record of heavy metal accumulation in the southeastern Liaodong Bay of China. Environ Earth Sci 71:1073–1108
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51509087) and the Provincial Natural Science Foundation of Hunan (No. 2015JJ3047).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Zhihong Xu
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 24 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Y., Tian, Y., Shen, M. et al. Heavy metals in soils and sediments from Dongting Lake in China: occurrence, sources, and spatial distribution by multivariate statistical analysis. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25, 13687–13696 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-1590-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-1590-5