Abstract
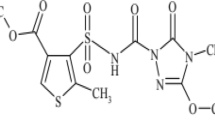
The physicochemical properties of soil are fundamental to quantification of the fate of herbicides. Thus, the aim of this research was to evaluate the fate of diuron, hexazinone, and metribuzin in five soils (Clay-1, Clay-2, Loam-1, Loam-2, and Sand), presenting variation in clay content, cation exchange capacity (CEC), pH, and organic carbon (OC). Herbicides radiolabeled with 14C were applied, and the 14C–CO2 released from mineralization was trapped in 0.2 mol L−1 sodium hydroxide solution. The degradation ratio, as well as herbicide-bound residues (non-extractable), transformation products, and residues extractable from soil, was also evaluated. Average 14C–CO2 evolution accumulated for diuron mineralization was higher (22.24%) than hexazinone (7.73%) and metribuzin (3.20%). The degradation time half-life (DT50) values for hexazinone correlated with soil OC content. Although no correlation between soil properties and DT50 values was found for metribuzin, the degradation rate and total degree of mineralization were low in sand soil for metribuzin. Regarding diuron, OC content and CEC value appear to be related to mineralization and degradation rate, respectively. Differences in soil properties can influence the persistence and fate of herbicides, affecting their impact on the environment, weed control, and possible effects on subsequent crops.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Antonious GF, Turley ET, Hill RR (2014) Impact of soil amendments on metribuzin and DCPA half-lives and mobility into agricultural runoff water. J Environ Sci Health B 49(5):313–323. https://doi.org/10.1080/03601234.2014.882158
Cabrera A, Cox L, Velarde P, Koskinen WC, Cornejo J (2007) Fate of diuron and terbuthylazine in soils amended with two-phase olive oil mill waste. J Agric Food Chem 55(12):4828–4834. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf070525b
Cerejeira M, Viana P, Batista S et al (2003) Pesticides in Portuguese surface and ground waters. Water Res 37(5):1055–1063. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1354(01)00462-6
Clay SA, Koskinen WC (1999) Characterization of alachlor and atrazine desorption from soils. Weed Sci 38:74–80. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0043174500056149
Cox L, Celis R, Hermosin MC, Becker A, Cornejo J (1997) Porosity and herbicide leaching in soils amended with olive-mill wastewater. Agric Ecosyst Environ 65(2):151–161. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0167-8809(97)00063-7
Dalton RL, Evans AW, Rhodes RC (1966) Disappearance of diuron from cotton field soils. Weeds 14(1):31–33
Dores EFGC, Spadotto CA, Weber OLS, Carbo L, Vecchiato AB, Pinto AA (2009) Environmental behaviour of metolachlor and diuron in a tropical soil in the central region of Brazil. Water Air Soil Pollut 197(1-4):175–183. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-008-9801-1
El Sebaï T, Devers-Lamrani M, Lagacherie B et al (2010) Isoproturon mineralization in an agricultural soil. Biol Fertil Soils 47(4):427–435. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-011-0549-1
Ellegaard-Jensen L, Knudsen BE, Johansen A, Albers CN, Aamand J, Rosendahl S (2014) Fungal–bacterial consortia increase diuron degradation in water-unsaturated systems. Sci Total Environ 466–467:699–705. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.07.095
EMBRAPA EB de PA (2013) Sistema Brasileiro de Classificação de Solos, 3rd edn. Embrapa Solos, Brasília
Environmental Protection Agency - Epa (1998) Soil thin layer chromatography. (EPA – Fate. transport and transformation test guidelines – OPPTS 835.1210). EPA, Washington D.C, p 6
Essandoh M, Wolgemuth D, Pittman CU, Mohan D, Mlsna T (2017) Adsorption of metribuzin from aqueous solution using magnetic and nonmagnetic sustainable low-cost biochar adsorbents. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24(5):4577–4590. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-8188-6
Fried B, Sharma J (1999) Thin-layer chromatography. Marcel Dekker Inc., Basel, New York
Garrett LG, Watt MS, Rolando CA, Pearce SH (2015) Environmental fate of terbuthylazine and hexazinone in a New Zealand planted forest pumice soil. For Ecol Manag 337:67–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foreco.2014.10.028
Giacomazzi S, Cochet N (2004) Environmental impact of diuron transformation: a review. Chemosphere 56(11):1021–1032. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2004.04.061
Giori FG, Tornisielo VL, Cerri CEP, Regitano JB (2014) Sugarcane straw management and soil attributes on alachlor and diuron sorption in highly weathered tropical soils. J Environ Sci Health Part B-Pestic Food Contam Agric Wastes 49(5):352–360. https://doi.org/10.1080/03601234.2014.882172
Gustafson DI (1989) Groundwater ubiquity score: a simple method for assessing pesticide leachability. Environ Toxicol Chem 8(4):339–357. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.5620080411
Kasozi GN, Nkedi-Kizza P, Agyin-Birikorang S, Zimmerman AR (2010) Characterization of adsorption and degradation of diuron in carbonatic and noncarbonatic soils. J Agric Food Chem 58(2):1055–1061. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf902792p
Khan SU (1982) Bound pesticide residues in soil and plants. Residue Rev 84:1–25
Khoury R, Geahchan A, Coste CM, Cooper JF, Bobe A (2003) Retention and degradation of metribuzin in sandy loam and clay soils of Lebanon. Weed Res 43(4):252–259. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-3180.2003.00341.x
Lalah JO, Muendo BM, Getenga ZM (2009) The dissipation of hexazinone in tropical soils under semi-controlled field conditions in Kenya. J Environ Sci Health B 44(7):690–696. https://doi.org/10.1080/03601230903163772
Lawrence JR, Eldan M, Sonzogni WC (1993) Metribuzin and metabolites in Wisconsin (U.S.A.) well water. Water Res 27(8):1263–1268. https://doi.org/10.1016/0043-1354(93)90212-Z
Locke MA, Harper SS (1991) Metribuzin degradation in soil: II-effects of tillage. Pestic Sci 31(2):239–247. https://doi.org/10.1002/ps.2780310211
Marinho DA, Bicalho ST, Ferreira EM (2012) Distribution and mineralization of 14C-hexazinone in soil-plant microcosm with the riparian forest specie Cecropia hololeuca. J Bioremediation Biodegrad 1:10–15. https://doi.org/10.4172/2155-6199.S1-002
Navarro S, Vela N, Navarro G (2007) Review. An overview on the environmental behaviour of pesticide residues in soils. Spanish J Agric Res 5:357–375
Ngigi A, Getenga Z, Boga H, Ndalut P (2014) Isolation and identification of hexazinone-degrading bacterium from sugarcane-cultivated soil in Kenya. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 92(3):364–368. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-014-1207-8
OECD (2002) Test no. 307: aerobic and anaerobic transformation in soil. http://www.oecd-ilibrary.org/environment/test-no-307-aerobic-and-anaerobic-transformation-in-soil_9789264070509-en. Accessed 23 Feb 2017
Oliveira Jr RS, Koskinen WC, Ferreira FA (2001) Sorption and leaching potential of herbicides on Brazilian soils. Weed Res 41(2):97–110. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-3180.2001.00219.x
Oukali-Haouchine O, Barriuso E, Mayata Y, Moussaoui KM (2013) Factors affecting metribuzin retention in Algerian soils and assessment of the risks of contamination. Environ Monit Assess 185(5):4107–4115. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-012-2853-0
Regitano JB, Koskinen WC, Sadowsky MJ (2006) Influence of soil aging on sorption and bioavailability of simazine. J Agric Food Chem 54(4):1373–1379. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf052343s
Reiser RW, Belasco IJ, Rhodes RC (1983) Identification of metabolites of hexazinone by mass spectrometry. Biomed Mass Spectometry 10(11):581–585. https://doi.org/10.1002/bms.1200101102
Rhodes RC (1980) Soil studies with 14C-labeled hexazinone. J Agric Food Chem 28(2):311–315. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf60228a012
Saison C, Louchart X, Schiavon M, Voltz M (2010) Evidence of the role of climate control and reversible aging processes in the fate of diuron in a Mediterranean topsoil. Eur J Soil Sci 61:576–587. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2389.2010.01262.x
Salvestrini S (2013) Diuron herbicide degradation catalyzed by low molecular weight humic acid-like compounds. Environ Chem Lett 11(4):359–363. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-013-0415-5
Shaner DL (2014) Herbicide Handbook. Weed Science Society of America, Champaign
Shareef A, Page D, Vanderzalm J, Williams M, Gupta VVSR, Dillon P, Kookana R (2014) Biodegradation of simazine and diuron herbicides under aerobic and anoxic conditions relevant to managed aquifer recharge of storm water. CLEAN - Soil, Air, Water 42(6):745–752. https://doi.org/10.1002/clen.201300092
Singh N, Raunaq, Singh SB (2012) Effect of fly ash on sorption behavior of metribuzin in agricultural soils. J Environ Sci Health B 47(2):89–98. https://doi.org/10.1080/03601234.2012.616767
University of Hertfordshire (2017) Pesticide properties database. http://sitem.herts.ac.uk/aeru/footprint/index2.htm. Accessed 4 Feb 2017
Vienneau DM, Sullivan CA, House SK, Stratton GW (2004) Effects of the herbicide hexazinone on nutrient cycling in a low-pH blueberry soil. Environ Toxicol 19(2):115–122. https://doi.org/10.1002/tox.20003
Vinther FP, Brinch UC, Elsgaard L, Fredslund L, Iversen BV, Torp S, Jacobsen CS (2008) Field-scale variation in microbial activity and soil properties in relation to mineralization and sorption of pesticides in a sandy soil. J Environ Qual 37(5):1710. https://doi.org/10.2134/jeq2006.0201
Volova T, Zhila N, Kiselev E, Prudnikova S, Vinogradova O, Nikolaeva E, Shumilova A, Shershneva A, Shishatskaya E (2016) Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate)/metribuzin formulations: characterization, controlled release properties, herbicidal activity, and effect on soil microorganisms. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23(23):23936–23950. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7636-7
Wang H, Li Y, Lu Y, Huang C, Zhang M, Wang X (2009) Influence of bovine manure on dissipation of hexazinone in soil. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 72(1):93–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2008.01.026
Wang H, Wang C, Chen F, Ma M, Lin Z, Wang W, Xu Z, Wang X (2012) Modification to degradation of hexazinone in forest soils amended with sewage sludge. J Hazard Mater 199–200:96–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.10.073
Zeng T, Arnold WA (2013) Pesticide photolysis in prairie potholes: probing photosensitized processes. Environ Sci Technol 47(13):6735–6745. https://doi.org/10.1021/es3030808
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by FAPESP—São Paulo State Research Foundation and CNPq—National Council for Scientific and Technological Development.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Zhihong Xu
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guimarães, A.C.D., Mendes, K.F., dos Reis, F.C. et al. Role of soil physicochemical properties in quantifying the fate of diuron, hexazinone, and metribuzin. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25, 12419–12433 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-1469-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-1469-5