Abstract
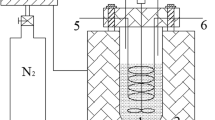
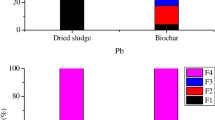
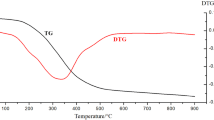
A feasible and efficient type of biological sludge-activated carbon (BSAC) was produced by co-pyrolysis of municipal sewage sludge (MSS) and walnut shell (4:1, w/w) at 500 °C. It was found that BSAC was typical mesoporous material with favorable pore structure and abundant surface functional groups, whose performance was improved compared with conventional sludge-activated carbon (CSAC), combined with walnut shell-activated carbon (WSAC). The migration and transformation behavior of heavy metals (Zn, Cu, Ni, Cd, and Cr) in raw material after co-pyrolysis process were investigated. The results indicated that co-pyrolysis could promote mobile fraction (acid soluble/exchangeable and reducible fractions) of heavy metals to stable fraction (oxidizable and residual fractions). The leaching concentrations Cu, Ni, Cd, Cr, and Zn were lower than restrictive standards in China, and the environmental risk assessment results showed that after co-pyrolysis, the risk levels of Cu, Ni, and Cd were decreased to low risk, especially Cr in product was confirmed to no risk.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agrafioti E, Bouras G, Kalderis D, Diamadopoulos E (2013) Biochar production by sewage sludge pyrolysis. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis 101:72–78
Bondarczuk K, Markowicz A, Piotrowska-Seget Z (2016) The urgent need for risk assessment on the antibiotic resistance spread via sewage sludge land application. Environ Int 87:49–55
Boualema T, Debab A, Martinez de Yuso A, Izquierdo MT (2014) Activated carbons obtained from sewage sludge by chemical activation: gas-phase environmental applications. J Environ Manag 140:145–151
Cao Y, Pawłowski A (2012) Sewage sludge-to-energy approaches based on anaerobic digestion and pyrolysis: brief overview and energy efficiency assessment. Renew Sust Energ Rev 16:1657–1665
Chen H, Yan S-H, Ye Z-L, Meng H-J, Zhu Y-G (2012) Utilization of urban sewage sludge: Chinese perspectives. Environ Sci Pollut Res 19:1454–1463
Chen D, Yin L, Wang H, He P (2014) Pyrolysis technologies for municipal solid waste: a review. Waste Manag 34:2466–2486
Choi SB, Yun Y-S (2006) Biosorption of cadmium by various types of dried sludge: an equilibrium study and investigation of mechanisms. J Hazard Mater 138:378–383
Devi P, Saroha AK (2014) Risk analysis of pyrolyzed biochar made from paper mill effluent treatment plant sludge for bioavailability and eco-toxicity of heavy metals. Bioresour Technol 162:308–315
Fan SS, Tang J, Wang Y, Li H, Zhang H, Tang J, Wang Z, Li XD (2016) Biochar prepared from co-pyrolysis of municipal sewage sludge and tea waste for the adsorption of methylene blue from aqueous solutions: kinetics, isotherm, thermodynamic and mechanism. J Mol Liq 220:432–441
Fang S, Yu Z, Lin Y, Lin Y, Fan Y, Liao Y, Ma X (2017) A study on experimental characteristic of co-pyrolysis of municipal solid waste and paper mill sludge with additives. Appl Therm Eng 111:292–300
Fuentes A, Lloréns M, Sáez J, Isabel Aguilar M, Ortuño JF, Meseguer VF (2008) Comparative study of six different sludges by sequential speciation of heavy metals. Bioresour Technol 99:517–525
Fytili D, Zabaniotou A (2008) Utilization of sewage sludge in EU application of old and new methods—a review. Renew Sust Energ Rev 12:116–140
Gao NB, Quan C, Liu BL, Li ZY, Wu CF, Li AM (2017) Continuous pyrolysis of sewage sludge in a screw-feeding reactor: products characterization and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals. Energy Fuel 31:5063–5072
Gu Z, Wu M, Li K, Ning P (2017) Variation of heavy metal speciation during the pyrolysis of sediment collected from the Dianchi Lake, China. Arab J Chem 10:S2196–S2204
Huang H, Yuan X, Zeng G, Zhu H, Li H, Liu Z, Jiang H, Leng L, Bi W (2011) Quantitative evaluation of heavy metals’ pollution hazards in liquefaction residues of sewage sludge. Bioresour Technol 102:10346–10351
Jin J, Li Y, Zhang J, Wu S, Cao Y, Liang P, Zhang J, Wong MH, Wang M, Shan S, Christie P (2016) Influence of pyrolysis temperature on properties and environmental safety of heavy metals in biochars derived from municipal sewage sludge. J Hazard Mater 320:417–426
Jin J, Wang M, Cao Y, Wu S, Liang P, Li Y, Zhang J, Zhang J, Wong MH, Shan S, Christie P (2017) Cumulative effects of bamboo sawdust addition on pyrolysis of sewage sludge: biochar properties and environmental risk from metals. Bioresour Technol 228:218–226
Jung M-W, Ahn K-H, Lee Y, Kim K-P, Rhee J-S, Tae Park J, Paeng K-J (2001) Adsorption characteristics of phenol and chlorophenols on granular activated carbons (GAC). Microchem J 70:123–131
Leng LJ, Yuan XZ, Huang HJ, Jiang HW, Chen XH, Zeng GM (2014) The migration and transformation behavior of heavy metals during the liquefaction process of sewage sludge. Bioresour Technol 167:144–150
Ministry of Environmental Protection (MEP), P.R. China, Beijing, China (2010) Solid waste-extraction procedure for leaching toxicity—horizontal vibration method (HJ 557-2010)
Ministry of Environmental Protection (MEP), P.R. China, China Environmental Status Bulletin, P.R. China (2006) http://www.zhb.gov.cn/hjzl/zghjzkgb/lnzghjzkgb/201605/P020160526558688821300.pdf. Accessed 22 Jan 2017
Ministry of Environmental Protection (MEP), P.R. China, China Environmental Status Bulletin, P.R. China (2016) http://www.zhb.gov.cn/hjzl/zghjzkgb/lnzghjzkgb/201605/P020160526558688821300.pdf. Accessed 22 Jan 2017
Ministry of Environmental Protection (MEP), P.R. China, General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine, P.R. China, Beijing, China (2003) Discharge standard of pollutants for municipal wastewater treatment plant (GB18918–2002)
Ministry of Environmental Protection (MEP), P.R. China, General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine, P.R. China, Beijing, China (2007) Identification standards for hazardous wastes—identification for extraction toxicity (GB5085.3–2007)
Pan H (2010) Effects of liquefaction time and temperature on heavy metal removal and distribution in liquefied CCA-treated wood sludge. Chemosphere 80:438–444
Ros A, Lillo-Rodenas MA, Canals-Batlle C, Fuente E, Montes-Moran MA, Martin MJ, Linares-Solano A (2007) A new generation of sludge-based adsorbents for H2S abatement at room temperature. Environ Sci Technol 41:4375–4381
Rozada F, Otero M, Moran A, Garcia AI (2005) Activated carbons from sewage sludge and discarded tyres: production and optimization. J Hazard Mater 124:181–191
Shao J, Yuan X, Leng L, Huang H, Jiang L, Wang H, Chen X, Zeng G (2015) The comparison of the migration and transformation behavior of heavy metals during pyrolysis and liquefaction of municipal sewage sludge, paper mill sludge, and slaughterhouse sludge. Bioresour Technol 198:16–22
Shi W, Liu C, Ding D, Lei Z, Yang Y, Feng C, Zhang Z (2013) Immobilization of heavy metals in sewage sludge by using subcritical water technology. Bioresour Technol 137:18–24
Yuan XZ, Huang HJ, Zeng GM, Li H, Wang JY, Zhou CF, Zhu HN, Pei XK, Liu ZF, Liu ZT (2011) Total concentrations and chemical speciation of heavy metals in liquefaction residues of sewage sludge. Bioresour Technol 102:4104–4110
Zhang J, Zheng P (2015) A preliminary investigation of the mechanism of hexavalent chromium removal by corn-bran residue and derived chars. RSC Adv 5:17768–17774
Zhao B, Xu X, Xu S, Chen X, Li H, Zeng F (2017) Surface characteristics and potential ecological risk evaluation of heavy metals in the bio-char produced by co-pyrolysis from municipal sewage sludge and hazelnut shell with zinc chloride. Bioresour Technol 243:375–383
Acknowledgements
This study received financial support from the SWPU Pollution Control of Oil and Gas Fields Science and Technology Innovation Youth Team (No. 2013XJZT003), National Science Foundation of China (41601341), and Sichuan Science and Technology Support Project (2017ZDYF3166).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Bingcai Pan
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Y., Liu, Q., Chen, M. et al. Evaluation of migration of heavy metals and performance of product during co-pyrolysis process of municipal sewage sludge and walnut shell. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24, 22082–22090 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-9858-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-9858-8