Abstract
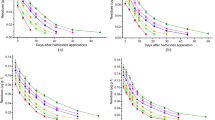
Arsenic (As) removal through microbially driven biovolatilization can be explored as a potential method for As bioremediation. However, its effectiveness needs to be improved. Biostimulation with organic matter amendment and bioaugmentation with the inoculation of genetic engineered bacteria could be potential strategies for As removal and site remediation. Here, the experiments were conducted to evaluate the impacts of rice straw and biochar amendment, inoculation of genetic engineered Pseudomonas putida KT2440 (GE P. putida) with high As volatilization activity, on microbial mediated As volatilization and removal from three different arseniferous soils. In general, the addition of rice straw (5%) significantly enhanced As methylation and volatilization in comparison with corresponding non-amended soils. Biochar amendments and inoculation of the GE P. putida increased As methylation and volatilization, respectively, but less than that of rice straw addition. The effectiveness of As volatilizations are quite different in the various paddy soils. The combined amendments of rice straw and GE P. putida exhibited the highest As removal efficiency (483.2 μg/kg/year) in Dayu soil, with 1.2% volatilization of the total As annually. The highest water-soluble As concentration (0.73 mg/kg) in this soil could be responsible for highest As volatilization besides the rice straw and bacteria in this soil.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akins MB, Lewis RJ (1976) Chemical distribution and gaseous evolution of arsenic-74 added to soils as DSMA-74As. Soil Sci Soc Am J 40:655–658
Akter KF, Owens G, Davey DE, Naidu R (2005) Arsenic speciation and toxicity in biological systems. Rev Environ Contam Toxicol 184:97–149
Beesley L, Moreno-Jimenez E, Gomez-Eyles JL, Harris E, Robinson B, Sizmur T (2011) A review of biochars’ potential role in the remediation, revegetation and restoration of contaminated soils. Environ Pollut 159:3269–3282
Beesley L, Marmiroli M, Pagano L, Pigoni V, Fellet G, Fresno T, Vamerali T, Bandiera M, Marmiroli N (2013) Biochar addition to an arsenic contaminated soil increases arsenic concentrations in the pore water but reduces uptake to tomato plants (Solanum lycopersicum L.) Sci Total Environ 454:598–603
Bentley R, Chasteen TG (2002) Microbial methylation of metalloids: arsenic, antimony, and bismuth. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 66:250–271
Brown S, Chaney RL, Hallfrisch JG, Xue Q (2003) Effect of biosolids processing on lead bioavailability in an urban soil. J Environ Qual 32:100–108
Challenger F (1945) Biological methylation. Chem Rev 36:315–361
Chen J, Qin J, Zhu YG, Lorenzo VD, Rosen BP (2013) Engineering the soil bacterium Pseudomonas putida for arsenic methylation. Appl Environ Microbiol 79:4493–4495
Chen J, Sun GX, Wang XX, Lorenzo VD, Rosen BP, Zhu YG (2014) Volatilization of arsenic from polluted soil by Pseudomonas putida engineered for expression of the arsM arsenic(III) S-adenosine methyltransferase gene. Environ Sci Technol 48:10337–10344
Cheng CN, Focht DD (1979) Production of arsine and methylarsines in soil and in culture. Appl Environ Microbiol 38:494–498
Cheng CH, Lehmann J (2009) Ageing of black carbon along a temperature gradient. Chemosphere 75:1021–1027
Crawford JM, Portmann C, Zhang X, Roeffaers MBJ, Clardy J (2012) Small molecule perimeter defense in entomopathogenic bacteria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109:10821–10826
Cullen WR, Bentley R (2005) The toxicity of trimethylarsine: an urban myth. J Environ Monit 7:11–15
Cullen WR, Reimer KJ (1989) Arsenic speciation in the environment. Chem Rev 89:713–764
Edvantoro BB, Naidu R, Megharaj M, Merrington G, Singleton I (2004) Microbial formation of volatile arsenic in cattle dip site soils contaminated with arsenic and DDT. Appl Soil Ecol 25:207–217
Feldmann J, Devalla S, Raab A, Hansen HR, Hirner AV, Emons H (2004) Analytical strategies for arsenic speciation in environmental and biological samples. In: Hirner AV, Emons H (Eds) Organic metal and metalloid species in the environment: analysis, distribution, processes and toxicological evaluation. Springer, New York, pp 41–70
Fellet G, Marchiol L, Delle Vedove G, Peressotti A (2011) Application of biochar on mine tailings: effects and perspectives for land reclamation. Chemosphere 83:1262–1267
Gao S, Burau RG (1997) Environmental factors affecting rates of arsine evolution from and mineralization of arsenicals in soil. J Environ Qual 26:753–763
Gbaruko BC, Ana G, Nwachukwu JK (2008) Ecotoxicology of arsenic in the hydrosphere: implications for public health. Afr J Biotechnol 7:4737–4742
Glaser B, Lehmann J, Zech W (2002) Ameliorating physical and chemical properties of highly weathered soils in the tropics with charcoal—a review. Biol Fertil Soils 35:219–230
Gong Z, Lu X, Ma M, Watt C, Le XC (2002) Arsenic speciation analysis. Talanta 58:77–96
Groffman PM, Tiedje JM (1991) Relationship between denitrification, CO2 production and air filled porosity in soils of different texture and drainage. Soil Biol Biochem 23:299–302
Hartley W, Dickinson NM, Riby P, Lepp NW (2009) Arsenic mobility in brownfield soils amended with green waste compost or biochar and planted with Miscanthus. Environ Pollut 157:2654–2662
Huang JH, Hu KN, Decker B (2011) Organic arsenic in the soil environment: speciation, occurrence, transformation, and adsorption behavior. Water Air Soil Pollut 219:401–415
Huang H, Zhu YG, Chen Z, Yin XX, Sun GX (2012a) Arsenic mobilization and speciation during iron plaque decomposition in a paddy soil. J Soils Sediments 12:402–410
Huang H, Jia Y, Sun GX, Zhu YG (2012b) Arsenic speciation and volatilization from flooded paddy soils amended with different organic matters. Environ Sci Technol 46:2163–2168
Huang K, Chen C, Zhang J, Tang Z, Shen QR, Rosen BP, Zhao FJ (2016) Efficient arsenic methylation and volatilization mediated by a novel bacterium from an arsenic-contaminated paddy soil. Environ Sci Technol 50:6389–6396
Jenkinson D S. 1981. The fate of plant and animal residues in soil. In: Greenland DS, Hayes MHB (Eds) The Chemistry of Soil Processes. John Wiley, New York, pp. 505–601
Jia Y, Huang H, Zhong M, Wang FH, Zhang LM, Zhu YG (2013a) Microbial arsenic methylation in soil and rice rhizosphere. Environ Sci Technol 47:3141–3148
Jia Y, Sun GX, Huang H, Zhu YG (2013b) Biogas slurry application elevated arsenic accumulation in rice plant through increased arsenic release and methylation in paddy soil. Plant Soil 365:387–396
Lehmann J, Rondon M (2006) Bio-char soil management on highly weathered soils in the humid tropics biological approaches to sustainable soil systems. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 517–530
Lehmann J, Silva JPD, Steiner C, Nehls T, Zech W, Glaser B (2003) Nutrient availability and leaching in an archaeological Anthrosol and a Ferralsol of the central Amazon basin: fertilizer, manure and charcoal amendments. Plant Soil 249:343–357
Liao HC, Chu YJ, Su YC, Hsiao SY, Wei CC, Liu CW, Liao CM, Shen WC, Chang FJ (2011) Arsenite-oxidizing and arsenate-reducing bacteria associated with arsenic-rich groundwater in Taiwan. J Contam Hydrol 123:20–29
Liu WJ, Zhu YG, Hu Y, Williams PN, Gault AG, Meharg AA, Charnock JM, Smith FA (2006) Arsenic sequestration in iron plaque, its accumulation and speciation in mature rice plants (Oryza sativa L). Environ Sci Technol 40:5730–5736
Liu S, Zhang F, Chen J, Sun GX (2011) Arsenic removal from contaminated soil via biovolatilization by genetically engineered bacteria under laboratory conditions. J Environ Sci 23:1544–1550
Lomax C, Liu WJ, Wu L, Xue K, Xiong J, Zhou J, Mcgrath SP, Meharg AA, Miller AJ, Zhao FJ (2012) Methylated arsenic species in plants originate from soil microorganisms. New Phytol 193:665–672
Mestrot A, Uroic MK, Plantevin T, Islam MR, Krupp EM, Feldmann J, Meharg AA (2009) Quantitative and qualitative trapping of arsines deployed to assess loss of volatile arsenic from paddy soil. Environ Sci Technol 43:8270–8275
Mestrot A, Feldmann J, Krupp EM, Hossain MS, Romanross G, Meharg AA (2011a) Field fluxes and speciation of arsines emanating from soils. Environ Sci Technol 45:1798–1804
Mestrot A, Merle JK, Broglia A, Feldmann J, Krupp EM (2011b) Atmospheric stability of arsine and methylarsines. Environ Sci Technol 45:4010–4015
Mestrot A, Planer-Friedrich B, Feldmann J (2013) Biovolatilisation: a poorly studied pathway of the arsenic biogeochemical cycle. Environ Sci Proc Impacts 15(9):1639–1651
Meyer J, Schmidt A, Michalke K, Hensel R (2007) Volatilisation of metals and metalloids by the microbial population of an alluvial soil. Syst Appl Microbiol 30:229–238
Namgay T, Singh B, Singh BP, Krull E, Singh B, Joseph S (2010) Influence of biochar application to soil on the availability of As, Cd, Cu, Pb, and Zn to maize (Zea mays L). Aust J Soil Res 48:638–647
Novak JM, Busscher WJ, Watts DW, Laird DA, Ahmedna MA, Niandou MAS (2010) Short-term CO2 mineralization after additions of biochar and switchgrass to a Typic Kandiudult. Geoderma 154:281–288
Pakulska D, Czerczak S (2006) Hazardous effects of arsine: a short review. Int J Occup Med Environ Health 19:36–44
Petit C, Peterson GW, Mahle J, Bandosz TJ (2010) The effect of oxidation on the surface chemistry of sulfurcontaining carbons and their arsine adsorption capacity. Carbon 48:1779–1787
Qin J, Rosen BP, Zhang Y, Wang GJ, Franke S, Rensing C (2006) Arsenic detoxification and evolution of trimethylarsine gas by a microbial arsenite S-adenosylmethionine methyltransferase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103:2075–2080
Qin J, Lehr CR, Yuan CG, Le XC, McDermott TR, Rosen BP (2009) Biotransformation of arsenic by a Yellowstone thermoacidophilic eukaryotic alga. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106:5213–5217
Quinn R, Dahl TA, Diamond BW, Toseland BA (2006) Removal of arsine from synthesis gas using a copper on carbon adsorbent. Ind Eng Chem Res 45(18):6272–6278
Redman AD, Macalady DL, Ahmann D (2002) Natural organic matter affects arsenic speciation and sorption onto hematite. Environ Sci Technol 36:2889–2896
Rhine ED, Garcia-Dominguez E, Phelps CD, Young LY (2005) Environmental microbes can speciate and cycle arsenic. Environ Sci Technol 39:9569–9573
Sanford RA, Klein DA (1988) Environmental bioremediation for organometallic compounds: microbial growth and arsenic volatillization from soil and retorted shale. Appl Organomet Chem 2:159–169
Shiowatana J, McLaren RG, Chanmekha N, Samphao A (2001) Fractionation of arsenic in soil by a continuous-flow sequential extraction method. J Environ Qual 30(6):1940–1949
Solaiman ARM, Meharg AA, Gault AG, Charnock JM (2009) Arsenic mobilization from iron oxyhydroxides is regulated by organic matter carbon to nitrogen (C:N) ratio. Environ Int 35:480–484
Spokas KA, Koskinen WC, Baker JM, Reicosky DC (2009) Impacts of woodchip biochar additions on greenhouse gas production and sorption/degradation of two herbicides in a Minnesota soil. Chemosphere 77:574–581
Sun GX, Lu XA, Williams PN, Zhu YG (2010) Distribution and translocation of selenium from soil to grain and its speciation in paddy rice (Oryza sativa L). Environ Sci Technol 44:6706–6711
Thomas JE, Rhue RD (1997) Volatilization of arsenic in contaminated cattle dipping vat soil. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 59:882–887
Thomas B, Ruben K, Andreas K, Philippe Van C, Matthew GV, Andreas V, Kate C (2010) Biogeochemical redox processes and their impact on contaminant dynamics. Environ Sci Technol 44:15–23
Turpeinen R, Pantsar M (2002) Role of microbes in controlling the speciation of arsenic and production of arsines in contaminated soils. Sci Total Environ 285:133–145
Wang PP, Sun GX, Jia Y, Meharg AA, Zhu YG (2014a) A review on completing arsenic biogeochemical cycle: microbial volatilization of arsines in environment. J Environ Sci 26:371–381
Wang PP, Sun GX, Zhu YG (2014b) Identification and characterization of arsenite methyltransferase from an archaeon, Methanosarcina acetivorans C2A. Environ Sci Technol 48:12706–12713
Wang PP, Bao P, Sun GX (2015) Identification and catalytic residues of the arsenite methyltransferase from a sulfate-reducing bacterium, Clostridium sp BXM. FEMS Microbiol Lett 362:1–8
Wang HY, Wen SL, Chen P, Zhang L, Cen K, Sun GX (2016) Mitigation of cadmium and arsenic in rice grain by applying different silicon fertilizers in contaminated fields. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:3781–3788
Weng LP, Van Riemsdijk WH, Hiemstra T (2009) Effects of fulvic and humic acids on arsenate adsorption to goethite: experiments and modeling. Environ Sci Technol 43:7198–7204
Woolson EA (1977) Generation of alkylarsines from soil. Weed Sci 25:412–416
Yin XX, Chen J, Qin J, Sun GX, Rosen BP, Zhu YG (2011) Biotransformation and volatilization of arsenic by three photosynthetic cyanobacteria. Plant Physiol 156:1631–1638
Yuan CG, Zhang KG, Wang ZH, Jiang GB (2010) Rapid analysis of volatile arsenic species released from lake sediment by a packed cotton column coupled with atomic fluorescence spectrometry. J Anal At Spectrom 25:1605–1611
Zheng RL, Cai C, Liang JH, Huang Q, Chen Z, Huang YZ, Arp HPH, Sun GX (2012) The effects of biochars from rice residue on the formation of iron plaque and the accumulation of Cd, Zn, Pb, As in rice (Oryza sativa L) seedlings. Chemosphere 89:856–862
Zheng RL, Sun GX, Zhu YG (2013) Effects of microbial processes on the fate of arsenic in paddy soil. Chin Sci Bull 58:186–193
Zheng RL, Chen Z, Cai C, Tie BQ, Liu XL, Reid BJ, Huang Q, Lei M, Sun GX, Baltrėnaitė E (2015) Mitigating heavy metal accumulation into rice (Oryza sativa L) using biochar amendment—a field experiment in Hunan, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:11097–11108
Zhu YG, Sun GX, Lei M, Teng M, Liu YX, Chen NC, Wang LH, Carey AM, Deacon C, Raab A, Meharg AA, Williams PN (2008) High percentage inorganic arsenic content of mining impacted and nonimpacted Chinese rice. Environ Sci Technol 42:5008–5013
Acknowledgements
This project was financially supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 41371459, 41501336, 41501336), the State Key Program of Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 41330853), the National High Technology Research and Development Program of China (863 Program, 2013AA06A209), and Beijing Outstanding Talent Training Project (2015000020060G141).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Elena Maestri
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, P., Li, J., Wang, HY. et al. Evaluation of bioaugmentation and biostimulation on arsenic remediation in soil through biovolatilization. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24, 21739–21749 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-9816-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-9816-5