Abstract
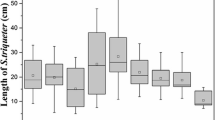
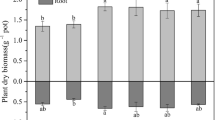
To understand the accumulation and uptake of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) and heavy metals by plants is an important part of the assessment of phytoremediation for PAHs and heavy metals co-contaminated soil. This study was an investigation of the accumulation and uptake of pyrene and lead (Pb) by Scirpus triqueter under the condition of alkyl polyglucoside (APG) and nitrilotriacetic acid (NTA) combined application. The results indicated that the accumulation of Pb by S. triqueter was significantly improved by NTA and APG addition into the soil. The pyrene accumulation in plant was also increased after application of APG when compared to the control treatment. However, the pyrene accumulation was decreased when APG was applied together with NTA. SEM and TEM images of root surface suggested that more Pb in the soil transferred to the plant by combined application of APG and NTA. More importantly, TEM images of xylem cells of S.triqueter root showed that permeability of cell membrane was improved by application of APG.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Almeida CMR, Dias AC, Mucha AP, Bordalo AA, Vasconcelos MTSD (2009) Influence of surfactants on the Cu phytoremediation potential of a salt marsh plant. Chemosphere 75:135–140
Bacosa HP, Inoue C (2015) Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) biodegradation potential and diversity of microbial consortia enriched from tsunami sediments in Miyagi, Japan. J Hazard Mater 283:689–697
Bacosa HP, Suto K, Inoue C (2013) Degradation potential and microbial community structure of heavy oil-enriched microbial consortia from mangrove sediments in Okinawa, Japan. J Environ Sci Health A Tox Hazard Subst Environ Eng 48:835–846
Cachada A, Pato P, Rocha-Santos T, da Silva EF, Duarte AC (2012) Levels, sources and potential human health risks of organic pollutants in urban soils. Sci Total Environ 430:184–192
Cao M, Hu Y, Sun Q, Wang L, Chen J, Lu X (2013) Enhanced desorption of PCB and trace metal elements (Pb and Cu) from contaminated soils by saponin and EDDS mixed solution. Environ Pollut 174:93–99
Chen T, Liu X, Zhang X, Chen X, Tao K, Hu X (2016a) Effect of alkyl polyglucoside and nitrilotriacetic acid combined application on lead/pyrene bioavailability and dehydrogenase activity in co-contaminated soils. Chemosphere 154:515–520
Chen T, Liu X, Zhang X, Hou Y, Chen X, Tao K (2016b) Enhanced Scirpus triqueter phytoremediation of pyrene and lead co-contaminated soil with alkyl polyglucoside and nitrilotriacetic acid combined application. J Soils Sediments 16:2090–2096
Cheng KY, Wong JWC (2006) Effect of synthetic surfactants on the solubilization and distribution of PAHs in water/soil-water systems. Environ Technol 27:835–844
Di Gregorio S, Barbafieri M, Lampis S, Sanangelantoni AM, Tassi E, Vallini G (2006) Combined application of Triton X-100 and Sinorhizobium sp. Pb002 inoculum for the improvement of lead phytoextraction by Brassica juncea in EDTA amended soil. Chemosphere 63:293–299
Fismes J, Perrin-Ganier C, Empereur-Bissonnet P, Morel JL (2002) Soil-to-root transfer and translocation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by vegetables grown on industrial contaminated soils. J Environ Qual 31:1649–1656
Gao Y, Shen Q, Ling W, Ren L (2008) Uptake of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by Trifolium pretense L. from water in the presence of a nonionic surfactant. Chemosphere 72:636–643
Garbisu C, Alkorta I (2001) Phytoextraction: a cost-effective plant-based technology for the removal of metals from the environment. Bioresour Technol 77:229–236
Huang HG, Yu N, Wang LJ, Gupta DK, He ZL, Wang K, Zhu ZQ, Yan XC, Li TQ, Yang XE (2011) The phytoremediation potential of bioenergy crop Ricinus communis for DDTs and cadmium co-contaminated soil. Bioresour Technol 102:11034–11038
Jin ZF, Zhang ZJ, Zhang H, Liu CQ, Li FL (2015) Assessment of lead bioaccessibility in soils around lead battery plants in East China. Chemosphere 119:1247–1254
Kader M, Lamb DT, Mahbub KR, Megharaj M, Naidu R (2016) Predicting plant uptake and toxicity of lead (Pb) in long-term contaminated soils from derived transfer functions. Environ Sci Pollut R 23:15460–15470
Leštan D, Luo C-l, X-d L (2008) The use of chelating agents in the remediation of metal-contaminated soils: a review. Environ Pollut 153:3–13
Li NY, Fu QL, Zhuang P, Guo B, Zou B, Li ZA (2011) Effect of fertilizers on cd uptake of Amaranthus hypochondriacus, a high biomass, fast growing and easily cultivated potential Cd hyperaccumulator. International Journal of Phytoremediation 14:162–173
Liu F, Wang C, Liu X, Liang X, Wang Q (2013a) Effects of alkyl polyglucoside (APG) on phytoremediation of PAH-contaminated soil by an aquatic plant in the Yangtze Estuarine wetland. Water Air Soil Pollut 224:1633:1–10
Liu F, Zhang X, Liu X, Chen X, Liang X, He C, Wei J, Xu G (2013b) Alkyl polyglucoside (APG) amendment for improving the phytoremediation of Pb-PAH contaminated soil by the aquatic plant Scirpus triqueter. Soil & Sediment Contamination 22:1013–1027
Liu HY, Guo SS, Jiao K, Hou JJ, Xie H, Xu H (2015) Bioremediation of soils co-contaminated with heavy metals and 2,4,5-trichlorophenol by fruiting body of Clitocybe maxima. J Hazard Mater 294:121–127
Nowack B, Schulin R, Robinson BH (2006) Critical assessment of chelant-enhanced metal phytoextraction. Environ Sci Technol 40:5225–5232
Qi FF, Zha ZY, Du L, Feng XJ, Wang DG, Zhang D, Fang ZD, Ma LJ, Jin YD, Xia CQ (2014) Impact of mixed low-molecular-weight organic acids on uraniumaccumulation and distribution in a variant of mustard (Brassicajuncea var. tumida). J Radioanal Nucl Chem 302:149–159
Quartacci MF, Irtelli B, Baker AJM, Navari-Izzo F (2007) The use of NTA and EDDS for enhanced phytoextraction of metals from a multiply contaminated soil by Brassica carinata. Chemosphere 68:1920–1928
Roy S, Labelle S, Mehta P, Mihoc A, Fortin N, Masson C, Leblanc R, Châteauneuf G, Sura C, Gallipeau C, Olsen C, Delisle S, Labrecque M, Greer C (2005) Phytoremediation of heavy metal and PAH-contaminated brownfield sites. Plant Soil 272:277–290
Somtrakoon K, Chouychai W, Lee H (2015) Removal of anthracene and fluoranthene by waxy corn, long bean and okra in lead-contaminated soil. B Environ Contam Tox 95:407–413
Sun L, Liao X, Yan X, Zhu G, Ma D (2014) Evaluation of heavy metal and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons accumulation in plants from typical industrial sites: potential candidate in phytoremediation for co-contamination. Environ Sci Pollut R 21:12494–12504
Tandy S, Schulin R, Nowack B (2006) The influence of EDDS on the uptake of heavy metals in hydroponically grown sunflowers. Chemosphere 62:1454–1463
Vargas C, Perez-Esteban J, Escolastico C, Masaguer A, Moliner A (2016) Phytoremediation of Cu and Zn by vetiver grass in mine soils amended with humic acids. Environ Sci Pollut R 23:13521–13530
Wang Z-z, X-y L, X-y Z, Wang J, Z-n C, C-l Z, P-c S (2010) Wetland bacteria isolated from Huangpu River-Yangtze River estuary and its degradation on diesel. Journal of Shanghai University (English Edition) 14:292–296
Zaier H, Ghnaya T, Ghabriche R, Chmingui W, Lakhdar A, Lutts S, Abdelly C (2014) EDTA-enhanced phytoremediation of lead-contaminated soil by the halophyte Sesuvium portulacastrum. Environ Sci Pollut R 21:7607–7615
Zhang X, Liu X, Liu S, Liu F, Chen L, Xu G, Zhong C, Su P, Cao Z (2011) Responses of Scirpus triqueter, soil enzymes and microbial community during phytoremediation of pyrene contaminated soil in simulated wetland. J Hazard Mater 193:45–51
Zhang X, Chen L, Liu X, Wang C, Chen X, Xu G, Deng K (2014) Synergic degradation of diesel by Scirpus triqueter and its endophytic bacteria. Environ Sci Pollut R 21:8198–8205
Zhou LY, Zhao Y, Wang SF, Han SS, Liu J (2015) Lead in the soil-mulberry (Morus alba L.)-silkworm (Bombyx mori) food chain: translocation and detoxification. Chemosphere 128:171–177
Zhu LZ, Zhang M (2008) Effect of rhamnolipids on the uptake of PAHs by ryegrass. Environ Pollut 156:46–52
Acknowledgements
This work was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 21677093 and 41373097) and the Key Laboratory of Water Environment and Marine Biological Resources Protection of Zhejiang Province (No. KF201503).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Xiaoyan Liu and Xinying Zhang are equal contributors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, T., Liu, X., Zhang, X. et al. Assessment of Pb and pyrene accumulation in Scirpus triqueter assisted by combined alkyl polyglucoside and nitrilotriacetic acid application. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24, 19194–19200 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-9579-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-9579-z