Abstract
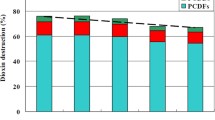
Municipal solid waste incineration (MSWI) fly ash has been classified as hazardous waste and needs treatment in an environmentally safe manner. Mechanochemical (MC) treatment is such a detoxification method, since it destroys dioxins and solidifies heavy metals. Milling, however, also introduces supplemental metals (Fe, Ni, Cr, Mn…), following wear of both steel balls and housing. Milling moreover reduces the particle size of fly ash and disperses catalytic metal, potentially rising the reactivity of fly ash to form and destroy ‘dioxins’, i.e. polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans (PCDD + PCDF or PCDD/F). To test this issue, model fly ash (MFA) samples were composed by mixing of silica, sodium chloride, and activated carbon, and doped with CuCl2. Then, these samples were first finely milled without any additives for 0 h (original sample), 1 h and 8 h, and the effect of milling time (and hence particle size) was investigated on the formation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs), and of polychlorinated phenols (CP), benzenes (CBz), biphenyls (PCB) and dioxins (PCDD + PCDF) during de novo tests at 300 °C for 1 h, thus simulating the conditions prevailing in the post-combustion zone of an incinerator, where dioxins are formed and destroyed. These compounds are all characterized by their rate of generation (ng/g MFA) and their signature, i.e. internal distribution over congeners as a means of gathering mechanistic indications. PAH and CBz total yield did not decrease in MC treated MFA with milling time, while total pentachlorophenol (PeCP), PCB and PCDD/F yield decreased up to 86, 94 and 97%, respectively. International Toxic Equivalents (I-TEQ) concentration decreased more than 90%, while degree of chlorination varied inconsistently for PCB and PCDD/F, and average congener patterns of PCDD/F do not vary considerably with milling time for both gas and solid phase.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Addink R, Olie K (1995) Mechanisms of formation and destruction of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans in heterogeneous systems. Environ Sci Technol 29:1425–1435
Addink R, Cnubben P, Olie K (1995) Formation of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins/dibenzofurans on fly ash from precursors and carbon model compounds. Carbon 33:1463–1471
Addink R, Antonioli M, Olie K, Govers HAJ (1996) Reactions of dibenzofuran and 1,2,3,4,7,8-hexachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin on municipal waste incinerator fly ash. Environ Sci Technol 30:833
Baláž P, Achimovičová M, Baláž M, Billik P et al (2013) Hallmarks of mechanochemistry: from nanoparticles to technology. Chem Soc Rev 42:7571–7637
Birke V, Mattik J, Runne D, Benning H, Zlatovic D (2006) Dechlorination of Recalcitrant Polychlorinated Contaminants Using Ball Milling. NATO Security through Science Series C: Environmental Security. 111–127
Butyagin PY (1994) Problems in mechanochemistry and prospects for its development. Russ Chem Rev 63(12):965–976
Cagnetta G, Hassan MM, Huang J, Yu G, Weber R (2016a) Dioxins reformation and destruction in secondary copper smelting fly ash under ball milling. Sci Rep. doi:10.1038/srep22925
Cagnetta G, Huang J, Wang B, Deng S, Yu G (2016b) A comprehensive kinetic model for mechanochemical destruction of persistent organic pollutants. Chem Eng J 291:30–38
Chen CN, Chen YL, Tseng WJ (2007) Surfactant-assisted de-agglomeration of graphite nanoparticles by wet ball mixing. J Mater Process Technol 190:61–64. doi:10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2007.03.109
Chen Z, Lu S, Mao Q, Buekens A, Chang W, Wang X, Yan J (2016) Suppressing heavy metal leaching through ball milling of fly ash. Energies. doi:10.3390/en9070524
Dickson LC, Lenoir D, Hutzinger O (1989) Surface- catalyzed formation of chlorinated dibenzodioxins and dibenzofurans during incineration. Chemosphere 19:277
Everaert K, Baeyens J (2002) The formation and emission of dioxins in large scale thermal processes. Chemosphere 46:439–448
Ferreira C, Ribeiro A, Ottosen L (2003) Possible applications for municipal solid waste fly ash. J Hazard Mater 96:201–216
Fujimori T, Takaoka M, Takeda N (2009) Influence of Cu, Fe, Pb, and Zn chlorides and oxides on formation of chlorinated aromatic compounds in MSWI fly ash. Environ Sci Technol 43:8053–8059
Fullana A, Nakka H, Sidhu S (2004) PCDF formation from PAH reactions. Organohalogen Cpds 66:1226
Hagenmaier H, Kraft M, Brunner M, Haag R (1987) Catalytic effect of fly ash from waste incinerator facilities on the formation and decomposition of PCDD/Fs. Environ Sci Technol 19:1080–1084
Heinicke G, Hennig HP, Linke E, Steinike U, Thiessen K, Meyer PK (1984) Tribochemistry, Akademie-Verlag Berlin 1984, 495 S., 329 Abb., 106 Tab. Preis: 98, –M, Cryst Res Technol 19:1424
Hell K, Stieglitz L, Dinjus E (2001) Mechanistic aspects of the de-novo synthesis of PCDD/PCDF on model mixtures and MSWI fly ashes using amorphous 12C- and 13C-labeled carbon. Environ Sci Technol 35:3892–3898
Huang H, Buekens A (1995) On the mechanisms of dioxin formation in combustion processes. Chemosphere 31:4099–4117
Huang J-X, Chen J-H, Lu S-Y (2017) Measurement of chlorobenzenes and chlorophenols in fly ashes from MSWI using GC-ECD and LC-MS/MS. Chin J Environ Eng 11(2):1293–1299 (in Chinese)
Hue NT, Thuy NTT, Tung NH (2016) Polychlorobenzenes and polychlorinated biphenyls in ash and soil from several industrial areas in North Vietnam: residue concentrations, profiles and risk assessment. Environ Geochem Health 38:399
Iino F, Imagawa T, Takeuchi M, Sadakata M (1999) De novo synthesis mechanism of polychlorinated dibenzofurans from polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and the characteristic isomers of polychlorinated naphthalenes. Environ Sci Technol 33(7):1038–1043
Iino F, Imagawa T, Gullett B (2000) Dechlorination-controlled polychlorinated dibenzofuran isomer patterns from municipal waste incinerators. Environ Sci Technol 34:3143–3147
Iino F, Tsuchiya K, Imagawa T, Gullett B (2001) An isomer prediction model based on dechlorination kinetics for polychlorinated naphthalenes, polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins, and polychlorinated biphenyls from municipal waste incinerators. Environ Sci Technol 35:3175–3181
Karasek FW, Dickson LC (1987) Model studies of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxin formation during municipal refuse incineration. Science 237(4816):754–756. doi:10.1126/science.3616606
Kim K-S, Hong K-H, Ko Y-H, Kim M-G (2004) Emission characteristics of PCDD/Fs, PCBs, chlorobenzenes, chlorophenols, and PAHs from polyvinylchloride combustion at various temperatures. J Air Waste Manage Assoc 54:555–562
Kuzuhara S, Sato H, Kasai E, Nakamura T (2003) Influence of metallic chlorides on the formation of PCDD/Fs during low-temperature oxidation of carbon. Environ Sci Technol 37:2431–2435
Lemieux PM, Lee CW, Ryan JV, Lutes CC (2001) Bench-scale studies on the simultaneous formation of PCBs and PCDD/Fs from combustion systems. Waste Manag 21:419–425
Loiselle S, Branca M, Mulas G, Cocco G (1997) Selective mechanochemical dehalogenation of chlorobenzenes over calcium hydride. Environ Sci Technol 31(1):261–265
Lu S, Huang J, Peng Z, Li X, Yan J (2012) Ball milling 2,4,6-trichlorophenol with calcium oxide: dechlorination experiment and mechanism considerations. Chem Eng J 195–196:62–68
Luijk R, Dorland C, Smit P, Jansen J, Govers HAJ (1994) The role of bromine in the de novo synthesis in a model fly ash system. Chemosphere 28:1299–1309
Mio H, Saeki S, Kano J, Saito F (2002) Estimation of mechanochemical dechlorination rate of poly vinyl chloride. Environ Sci Technol 36:1344–1348
Nah IW, Hwang KY, Shul YG (2008) Effect of metal and glycol on mechanochemical dechlorination of polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs). Chemosphere 73(1):138–141
Nomura Y, Nakai S, Hosomi M (2005) Elucidation of degradation mechanism of dioxins during mechanochemical treatment. Environ Sci Technol 39:3799–3804
Pandelova M, Lenoir D, Schramm KW (2006) Correlation between PCDD/F, PCB and CBz in coal/waste combustion. Influence of various inhibitors. Chemosphere 62(7:1196–1205
Pandelova M, Stanev I, Henkelmanna B, Lenoira D, Schramm KW (2009) Correlation of PCDD/F and PCB at combustion experiments using wood and hospital waste. Influence of (NH4)2SO4 as additive on PCDD/F and PCB emissions. Chemosphere 75( 5:685–691
Peng Z, Ding Q, Sun Y, Jiang C, Gao X, Yan J (2010) Characterization of mechanochemical treated fly ash from a medical waste incinerator. J Environ Sci 22(10):1643–1648
Peng Y, Chen J, Lu S, Huang J, Zhang M, Buekens A, Li X, Yan J (2016) Chlorophenols in municipal solid waste incineration: a review. Chem Eng J 292:398–414
Ryu J-Y, Mulholland JA, Chu B (2003a) Chlorination of dibenzofuran and dibenzo-p-dioxin vapor by copper(II) chloride. Chemosphere 51:1031–1039
Ryu J-Y, Mulholland JA, Dunn JE (2003b) Polychlorinated dibenzofuran (PCDF) prediction from dibenzofuran chlorination. Organohalogen Compd 63:49–52
Ryu J-Y, Mulholland JA, Dunn JE, Iino F, Gullett BK (2004) Potential role of chlorination pathways in PCDD/F formation in a municipal waste incinerator. Environ Sci Technol 38:5112–5119
Ryu J–Y, Choi K, Mulholland JA (2006) Polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxin (PCDD) and dibenzofurna (PCDF) isomer patterns from municipal waste combustion: formation mechanism fingerprints. Chemosphere 65:1526–1536
Schwarz G, Stieglitz L (1992) Formation of organohalogen compounds in fly ash by metal-catalyzed oxidation of residual carbon. Chemosphere 25:277–282
Shu S, Junya K, Fumio S, Kaoru S, Seiichi M, Tsuyoshi I (2001) Effect of additives on dechlorination of PVC by mechanochemical treatment. J Mater Cycles Waste Manage 3(1):20–23
Stieglitz L (1998) Selected topics on the de novo synthesis of PCDD/PCDF on fly ash. Environ. Eng Sci 15:5–18
Stieglitz L, Bautz H, Roth W, Zwick G (1997) Investigation of precursor reactions in the de-novo-synthesis of PCDD/PCDF on fly ash. Chemosphere 34:1083–1090
Suryanarayana C (1995) Bibliography on mechanical alloying and milling. Cambridge International Science Publishing, Cambridge
Suryanarayana C (2001) Mechanical alloying and milling. Prog Mater Sci 46:1–184
Tuppurainen KA, Ruokojärvi PH, Asikainen AH, Aatamila M, Ruuskanen J (2000) Chlorophenols as precursors of PCDD/Fs in incineration processes: correlations, PLS modeling, and reaction mechanisms. Environ Sci Technol 34:4958–4962
Urakaev FK, Boldyrev VV (2000) Mechanism and kinetics of mechanochemical processes in comminuting devices: 1. Theory. Powder Technol 107:93–107
USEPA (1994) Method 1613: tetra- through octa-chlorinated dioxins and furans by isotope dilution HRGC/HRMS, USEPA. USEPA Press, Washington
USEPA (2008) Method 1668B: chlorinated biphenyl congeners in water, soil, sediment, biosolids, and tissue by HRGC/HRMS, USEPA. USEPA Press, Washington
Vogg H, Stieglitz L (1986) Thermal behavior of PCDD/PCDF in fly ash from municipal incinerator. Chemosphere 15:1373–1378
Weber R, Iino F, Imagawa T, Takeuchi M, Sakurai T, Sadakata M (2001) Formation of PCDF, PCDD, PCB, and PCN in de novo synthesis from PAH: mechanistic aspects and correlation to fluidized bed incinerators. Chemosphere 44:1429–1438
Wei YL, Yan JH, Lu SY, Li XD (2009) Mechanochemical decomposition of pentachlorophenol by ball milling. J Environ Sci-China 21(12):1761–1768
Wiesmuller T (1990) Examinations of the catalytic dechlorination of octachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin and octachlorodibenzofuran and application of the obtained mixtures in toxicological studies. Dissertation, University of Tubingen, Federal Republic of Germany
Wikström E, Marklund S (2000) Secondary formation of chlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins, dibenzofurans, biphenyls, benzenes and phenols during MSW combustion. Environ Sci Technol 34:604–609
Yan JH, Peng Z, Lu SY, Li XD, Ni MJ, Cen KF, Dai HF (2007) Degradation of PCDD/Fs by mechanochemical treatment of fly ash from medical waste incineration. J Hazard Mater 147:652–657
Yang J, Yan M, Li X, Lu S, Chen T, Yan J, Olie K, Buekens A (2015) Formation of dioxins on NiO and NiCl2 at different oxygen concentrations. Chemosphere 133:97–102
Zhang Q, Matsumoto W, Saito HF, Baron M (2002) Debromination of hexabromobenzene by its co-grinding with CaO. Chemosphere 48(7):787–793
Zhang KL, Huang J, Yu G, Zhang QW, Deng SB, Wang B (2013) Destruction of perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS) and perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) by ball milling. Environ Sci Technol 47(12):6471–6477
Zhang W, Wang H, Jun H, Yu M, Wang F, Zhou L (2014) Acceleration and mechanistic studies of the mechanochemical dechlorination of HCB with iron powder and quartz sand. Chem Eng J 239:185–191
Zhang M, Yang J, Buekens A, Olie K, Li X (2016) PCDD/F catalysis by metal chlorides and oxides. Chemosphere 159:536–544
Acknowledgements
This Project was Supported by the General Program of National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51676172), the Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (R14E060001), National Basic Research Program (973 Program) of China (No. 2011CB201500), the Science and Technology Project of Zhejiang Province (No. 2009C13004), and the Program of Introducing Talents of Discipline to University (B08026) and the Zhejiang University’s Pao Yu-Kong International Fund.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Roland Kallenborn
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mubeen, I., Buekens, A., Chen, Z. et al. De novo formation of dioxins from milled model fly ash. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24, 19031–19043 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-9528-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-9528-x