Abstract
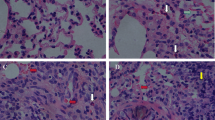
Exposure to fine particulate matter (PM2.5) may increase lung cancer risk, but the underlying mechanisms are poorly understood. This study explored the potential carcinogenicity in rat lung induced by chronic exposure to PM2.5. Adult male rats (200–220 g) were treated with PM2.5 (10 mg/kg body weight) by tracheal perfusion once per week for 1 year; the rats were killed, and expression of tumor markers (carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA), neuron-specific enolase (NSE), squamous cell carcinoma antigen (SCCA)), cancer-related genes, and pathological changes were detected. Chronic treatment with PM2.5 significantly increased SCCA and NSE expression in rat lung tissue and serum. Damaged lung tissue structure was observed by hematoxylin and eosin staining. Although no evidence of tumors was detected, the Wnt/β-catenin signaling, epithelial–mesenchymal transition, vascular endothelial growth factor, and epidermal growth factor receptor pathways were all activated or overexpressed and likely involved in the potential carcinogenicity in the rat model. Additionally, abnormal expression of the proto-oncogenes c-Myc and K-Ras and tumor suppressor p53 can be seen in lung tissue induced by PM2.5 exposure. Chronic exposure to PM2.5 has the potential to be carcinogenic in rat lung.





Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
14 September 2017
An erratum to this article has been published.
References
Atkinson RW, Kang S, Anderson HR, Mills IC, Walton HA (2014) Epidemiological time series studies of PM2.5 and daily mortality and hospital admissions: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Thorax 69:660–665
Bianco R, Melisi D, Ciardiello F, Tortora G (2006) Key cancer cell signal transduction pathways as therapeutic targets. Eur J Cancer 42:290–294
Bierie B, Moses HL (2010) Transforming growth factor beta (TGF-beta) and inflammation in cancer. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 21:49–59
Brook RD, Franklin B, Cascio W, Hong Y, Howard G, Lipsett M, Luepker R, Mittleman M, Samet J, Smith SC Jr et al (2004) Air pollution and cardiovascular disease: a statement for healthcare professionals from the Expert Panel on Population and Prevention Science of the American Heart Association. Circulation 109:2655–2671
Cesaroni G, Badaloni C, Gariazzo C, Stafoggia M, Sozzi R, Davoli M, Forastiere F (2013)Long-term exposure to urban air pollution and mortality in a cohort of more than a million adults in Rome. Environ Health Perspect 121:324–331
Chen RH, Ding WV, Mc Cormick F (2000) Wnt signaling to beta-catenin involves two interactive components. Glycogen synthase kinase-3beta inhibition and activation of protein kinase C. J Biol Chem 275:17894–17899
Creighton CJ, Gibbons DL, Kurie JM (2013) The role of epithelial-mesenchymal transition programming in invasion and metastasis: a clinical perspective. Cancer Manag Res 5:187–195
Deng X, Zhang F, Rui W, Long F, Wang L, Feng Z, Chen D, Ding W (2013) PM2.5-induced oxidative stress triggers autophagy in human lung epithelial A549 cells. Toxicol in Vitro 27:1762–1770
Ellermeier J, Wei J, Duewell P, Hoves S, Stieg MR, Adunka T, Noerenberg D, Anders HJ, Mayr D, Poeck H et al (2013) Therapeutic efficacy of bifunctional siRNA combining TGF-beta1 silencing with RIG-I activation in pancreatic cancer. Cancer Res 73:1709–1720
Fuchs M, Hutzler P, Brunner I, Schlegel J, Mages J, Reuning U, Hapke S, Duyster J, Hirohashi S, Genda T et al (2002) Motility enhancement by tumor-derived mutant E-cadherin is sensitive to treatment with epidermal growth factor receptor and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase inhibitors. Exp Cell Res 276:129–141
Gatcliffe TA, Monk BJ, Planutis K, Holcombe RF (2008) Wnt signaling in ovarian tumorigenesis. Int J Gynecol Cancer 18:954–962
Gavert N, Ben-Ze’ev A (2007)beta-Catenin signaling in biological control and cancer. J Cell Biochem 102:820–828
Govindan R, Weber J (2014) TP53 mutations and lung cancer: not all mutations are created equal. Clin Cancer Res 20:4419–4421
Gregory CA, Gunn WG, Reyes E, Smolarz AJ, Munoz J, Spees JL, Prockop DJ (2005) How Wnt signaling affects bone repair by mesenchymal stem cells from the bone marrow. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1049:97–106
Gualtieri M, Longhin E, Mattioli M, Mantecca P, Tinaglia V, Mangano E, Proverbio MC, Bestetti G, Camatini M, Battaglia C (2012) Gene expression profiling of A549 cells exposed to Milan PM2.5. Toxicol Lett 209:136–145
Hamra GB, Guha N, Cohen A, Laden F, Raaschou-Nielsen O, Samet JM, Vineis P, Forastiere F, Saldiva P, Yorifuji T, Loomis D (2014) Outdoor particulate matter exposure and lung cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Environ Health Perspect 122:906–911
Heldin CH, Landstrom M, Moustakas A (2009) Mechanism of TGF-beta signaling to growth arrest, apoptosis, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Curr Opin Cell Biol 21:166–176
Herbst RS (2004) Review of epidermal growth factor receptor biology. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 59:21–26
Jensen LJ, Kuhn M, Stark M, Chaffron S, Creevey C, Muller J, Doerks T, Julien P, Roth A, Simonovic M et al (2009) STRING 8—a global view on proteins and their functional interactions in 630 organisms. Nucleic Acids Res 37:D412–D416
Jiang C, Zhang S, Liu H, Guan Z, Zeng Q, Zhang C, Lei R, Xia T, Wang Z, Yang L et al (2014) Low glucose utilization and neurodegenerative changes caused by sodium fluoride exposure in rat’s developmental brain. NeuroMolecular Med 16:94–105
Kushner EJ, Bautch VL (2013) Building blood vessels in development and disease. Curr Opin Hematol 20:231–236
Li Q, Liu H, Alattar M, Jiang S, Han J, Ma Y, Jiang C (2015a) The preferential accumulation of heavy metals in different tissues following frequent respiratory exposure to PM2.5 in rats. Sci Rep 5:16936
Li R, Kou X, Xie L, Cheng F, Geng H (2015b) Effects of ambient PM2.5 on pathological injury, inflammation, oxidative stress, metabolic enzyme activity, and expression of c-fos and c-jun in lungs of rats. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 22:20167–20176
Libalova H, Uhlirova K, Klema J, Machala M, Sram RJ, Ciganek M, Topinka J (2012) Global gene expression changes in human embryonic lung fibroblasts induced by organic extracts from respirable air particles. Part Fibre Toxicol 9:1
Lim SS, Vos T, Flaxman AD, Danaei G, Shibuya K, Adair-Rohani H, Amann M, Anderson HR, Andrews KG, Aryee M et al (2012) A comparative risk assessment of burden of disease and injury attributable to 67 risk factors and risk factor clusters in 21 regions, 1990-2010: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet 380:2224–2260
Liu FF, Liu CY, Li XP, Zheng SZ, Li QQ, Liu Q, Song L (2015) Neuroprotective effects of SMADs in a rat model of cerebral ischemia/reperfusion. Neural Regen Res 10:438–444
Logan CY, Nusse R (2004) The Wnt signaling pathway in development and disease. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 20:781–810
Mack M, Yanagita M (2015) Origin of myofibroblasts and cellular events triggering fibrosis. Kidney Int 87:297–307
Molina R, Marrades RM, Auge JM, Escudero JM, Vinolas N, Reguart N, Ramirez J, Filella X, Molins L, Agusti A (2016) Assessment of a combined panel of six serum tumor markers for lung cancer. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 193:427–437
Pope CA 3rd, Burnett RT, Thun MJ, Calle EE, Krewski D, Ito K, Thurston GD (2002) Lung cancer, cardiopulmonary mortality, and long-term exposure to fine particulate air pollution. JAMA 287:1132–1141
Quintans JS, Antoniolli AR, Onofre FM, Onofre AS (2013) Detection of lung cancer using multiple genetic markers—a systematic review. Diagn Cytopathol 41:834–842
Schmalhofer O, Brabletz S, Brabletz T (2009) E-cadherin, beta-catenin, and ZEB1 in malignant progression of cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev 28:151–166
Schneider J (2006) Tumor markers in detection of lung cancer. Adv Clin Chem 42:1–41
Shi L, Zanobetti A, Kloog I, Coull BA, Koutrakis P, Melly SJ, Schwartz JD (2016)Low-concentration PM2.5 and mortality: estimating acute and chronic effects in a population-based study. Environ Health Perspect 124:46–52
Shibuya M (2006) Differential roles of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-1 and receptor-2 in angiogenesis. J Biochem Mol Biol 39:469–478
Shu Y, Zhu L, Yuan F, Kong X, Huang T, Cai YD (2016) Analysis of the relationship between PM2.5 and lung cancer based on protein-protein interactions. Comb Chem High Throughput Screen 19:100–108
Sun M, Song J, Zhou Z, Zhu R, Jin H, Ji Y, Lu Q, Ju H (2016) Comparison of serum microRNA21 and tumor markers in diagnosis of early non-small cell lung cancer. Dis Markers 2016:3823121
Sunaga N, Kaira K, Imai H, Shimizu K, Nakano T, Shames DS, Girard L, Soh J, Sato M, Iwasaki Y et al (2013) Oncogenic KRAS-induced epiregulin overexpression contributes to aggressive phenotype and is a promising therapeutic target in non-small-cell lung cancer. Oncogene 32:4034–4042
Tangudu NK, Verma VK, Clemons TD, Beevi SS, Hay T, Mahidhara G, Raja M, Nair RA, Alexander LE, Patel AB et al (2015) RNA interference using c-Myc-conjugated nanoparticles suppresses breast and colorectal cancer models. Mol Cancer Ther 14:1259–1269
Turner MC, Krewski D, Pope CA 3rd, Chen Y, Gapstur SM, Thun MJ (2011)Long-term ambient fine particulate matter air pollution and lung cancer in a large cohort of never-smokers. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 184:1374–1381
Vizirianakis IS, Chen YQ, Kantak SS, Tsiftsoglou AS, Kramer RH (2002)Dominant-negative E-cadherin alters adhesion and reverses contact inhibition of growth in breast carcinoma cells. Int J Oncol 21:135–144
Vousden KH, Lane DP (2007) p53 in health and disease. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 8:275–283
Vousden KH, Prives C (2009) Blinded by the light: the growing complexity of p53. Cell 137:413–431
Wang X, Xu D, Liao Y, Zhong S, Song H, Sun B, Zhou BP, Deng J, Han B (2015) Epithelial neoplasia coincides with exacerbated injury and fibrotic response in the lungs of Gprc5a-knockout mice following silica exposure. Oncotarget 6:39578–39593
Yorifuji T, Bae S, Kashima S, Tsuda T, Doi H, Honda Y, Kim H, Hong YC (2015) Health impact assessment of PM10 and PM2.5 in 27 southeast and east Asian cities. J Occup Environ Med 57:751–756
Zhang M, Wang A, He W, He P, Xu B, Xia T, Chen X, Yang K (2007) Effects of fluoride on the expression of NCAM, oxidative stress, and apoptosis in primary cultured hippocampal neurons. Toxicology 236:208–216
Zhang S, Jiang C, Liu H, Guan Z, Zeng Q, Zhang C, Lei R, Xia T, Gao H, Yang L et al (2013)Fluoride-elicited developmental testicular toxicity in rats: roles of endoplasmic reticulum stress and inflammatory response. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 271:206–215
Zhou W, Tian D, He J, Wang Y, Zhang L, Cui L, Jia L, Zhang L, Li L, Shu Y et al (2016) Repeated PM2.5 exposure inhibits BEAS-2B cell P53 expression through ROS-Akt-DNMT3Bpathway-mediated promoter hypermethylation. Oncotarget 7:20691–20703
Zou Y, Wang L, Zhao C, Hu Y, Xu S, Ying K, Wang P, Chen X (2013) CEA, SCC and NSE levels in exhaled breath condensate—possible markers for early detection of lung cancer. J Breath Res 7:047101
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
C.Y.J., Q.W., X.L.H., S.F.J., and Q.Z.L. conceived, designed, and carried out the experiments, analyzed the experimental data, and wrote the paper; C.Y.J., Q.W., and Q.Z.L. guided the experiments. S.F.S. and Q.Z. also performed experiments and prepared figures and table; N.Y. and M.M.H. also performed experiments; C.Y.J. and Q.W. supervised and directed the project. All authors discussed the results and commented on the manuscript and reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Funding
This work was supported by grant from the Tianjin Health and Family Planning Commission of Science and Technology Project Foundation (No. 16KG153).
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
An erratum to this article is available at https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0173-1.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, X., Li, Q., Shao, S. et al. Potential lung carcinogenicity induced by chronic exposure to PM2.5 in the rat. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24, 18991–19000 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-9430-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-9430-6