Abstract
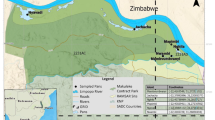
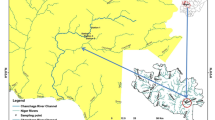
Exploring how water quality and land use shape the benthic macroinvertebrate community composition is of widespread interest in biodiversity conservation and environmental management. In this study, we investigated the structures of benthic macroinvertebrate assemblages and their environmental controls in terms of water quality and riparian land use in the Jinshui River, China. We carried out three campaigns including wet season (August 2009), dry season (November 2009), and normal season (April 2010) based on the hydrological regime in Jinshui basin. The result showed that macroinvertebrate assemblage variations were better explained by water quality factors than land use based on variance partitioning procedure. The land use of 2 km upstream from the sampling sites had explained more variation than that of the whole riparian zone in upstream catchment on macroinvertebrate community, and land use of 2 km upstream also had more interactions with water quality. Canonical correspondence analysis (CCA) indicated that the elements or nutrient of magnesium (Mn), selenium (Se), strontium (Sr), silicon (Si), dissolved inorganic nitrogen (DN), sulfur (S), total organic carbon (TOC), and total nitrogen (TN) in water exhibited a strong relationship with macroinvertebrate assemblages. However, the variance in water quality explained by land use was lower than that explained by water quality in rivers using redundancy analysis. Our study suggested that proximate factors (i.e., water quality) were more important to interpret the macroinvertebrate community compared to ultimate factors (i.e., land use) for macroinvertebrate assemblages in river system.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bere T, Dalu T, Mwedzi T (2016) Detecting the impact of heavy metal contaminated sediment on benthic macroinvertebrate communities in tropical streams. Sci Total Environ 572:147–156
Bizzi S, Surridge BWJ, Lerner DN (2012) Structural equation modelling: a novel statistical framework for exploring the spatial distribution of benthic macroinvertebrates in riverine ecosystems. River Res Appl 29:743–759
Bricker OP, Jones BF (1995) Main factors affecting the composition of natural waters. In: Salbu B, Steinners E (eds) Trace elements in natural waters. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 1–5
Collier KJ (2008) Temporal patterns in the stability, persistence and condition of stream macroinvertebrate communities: relationships with catchment land-use and regional climate. Freshw Biol 53:603–616
Epler JH (2001) Identification manual for the larval chironomidae (Diptera) of North and South Carolina, St. Johns River Water Management District.
Giling DP, Nally RM, Thompson RM (2015) How sensitive are invertebrates to riparian-zone replanting in stream ecosystems? Mar Freshw Res 67:1500–1511
Hale AN, Noble G, Piper K, Garmire K, Tonsor SJ (2015) Controlling for hydrologic connectivity to assess the importance of catchment- and reach-scale factors on macroinvertebrate community structure. Hydrobiologia 763:285–299
Hansen BD, Reich P, Cavagnaro TR, Lake PS (2015) Challenges in applying scientific evidence to width recommendations for riparian management in agricultural Australia. Ecol Manage Restor 16:50–57
Heino J, Muotka T, Mykrä H, Paavola R, Hämäläinen H, Koskenniemi E (2003) Defining macroinvertebrate assemblage type of headwater streams: implications for bioassessment and conservation. Ecol Appl 13:842–852
Kail J, Hering D (2009) The influence of adjacent stream reaches on the local ecological status of central European mountain streams. River Res Appl 25:537–550
Legendre P, Legendre L (1998) Numerical ecology. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Leland HV, Porter SD (2000) Distribution of benthic algae in the upper Illinois River basin in relation to geology and land use. Freshw Biol 44:279–301
Leps J, Smilauer P (2003) Multivariate analysis of ecological data using CANOCO. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Li S, Zhang Q (2010) Spatial characterization of dissolved trace elements and heavy metal in the upper Han River (China) using multivariate statistical techniques. J Hazard Mater 176:579–588
Li S, Gu S, Liu W, Han H, Zhang Q (2008) Water quality in relation to land use and land cover in the upper Han River Basin, China. Catena 75:216–222
Li S, Liu W, Gu S, Cheng X, Xu Z, Zhang Q (2009) Spatio-temporal dynamics of nutrients in the upper Han River basin, China. J Hazard Mater 162:1340–1348
Lorenz AW, Feld CK (2013) Upstream river morphology and riparian land use overrule local restoration effects on ecological status assessment. Hydrobiologia 704:489–501
Malaj E, Gorte M, Schäfer RB, Brack W, Carsten von der Ohe P (2012) Physiological sensitivity of freshwater macroinvertebrates to heavy metals. Environ Toxicol Chem 31:1754–1764
Mantyka-Pringle C, Martin TG, Moffatt DB, Linke S, Rhodes JR (2014) Understanding and predicting the combined effects of climate change and land-use change on freshwater macroinvertebrates and fish. J Appl Ecol 51:572–581
Merritt RW, Cummins KW, Berg MB (2008) An introduction the aquatic insects of North America, 4rd edn. Kendal/Hunt publishing Company, Dubuque
Michailova P, Warchalowska-Śliwa E, Szarek-Gwiazda E, Kownacki A (2012) Does biodiversity of macroinvertebrates and genome response of Chironomidae larvae (Diptera) reflect heavy metal pollution in a small pond? Environ Monit Assess 184:1–14
Morase AB, Wilhelm AE, Boelter T, Stenert C, Schulz UH, Maltchik L (2014) Reduced riparian zone width compromise aquatic macroinvertebrate communities in stream of southern Brazil. Environ Monit Assess 186:7063–7074
Morse JC, Yang L, Tian L (1994) Aquatic insect of China useful for monitoring water quantity. Hehai University Press, Nanjing
Mwedzi T, Bere T, Mangadze T (2016) Macroinvertebrate assemblages in agricultural, mining, and urban tropical streams: implications for conservation and management. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:11181–11192
Mykrä H, Heino J, Muotka T (2007) Scale-related pattern in the spatial and environmental components of stream macroinvertebrate assemblage variation. Glob Ecol Biogeogr 16:149–159
Parreira de Castro DM, Reis de Carvalho D, Pompeu PMZ, Moreira MZ, Nardoto GB, Callisto M (2016) Land use influences niche size and the assimilation of resources by benthic macroinvertebrates in tropical headwater streams. PLoS One 11(3):e0150527. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0150527
Rico A, Van den Brink PJ, Leitner P, Graf W, Focks A (2016) Relative influence of chemical and non-chemical stressors on invertebrate communities: a case study in the Danube River. Sci Total Environ 571:1370–1382
Sandin L (2003) Benthic macroinvertebrates in Swedish streams: community structure, taxon richness, and environmental relations. Ecography 26:269–282
Shen Z, Zhang Q, Yue C, Zhao J, Hu Z, Lv N, Tang Y (2006) The spatial pattern of land use/land cover in the water supplying area of the middle route of the South to North Water Diversion Project. Acta Geograph Sin 61:633–644
Soldner M, Stephen I, Ramos L, Angus R, Wells NC, Grosso A, Crane M (2004) Relationship between macroinvertebrate fauna and environmental variables in small streams of the Dominican Republic. Water Res 38:863–874
Southwood TRE (1977) Habitat, the templet for ecological strategies? J Anim Ecol 46:337–365
Southwood TRE (1988) Tactics, strategies and templates. Oikos 52:3–18
Stoll S, Breyer P, Tonkin JD, Früh D, Haase P (2016) Scale-dependent effects of river habitat quality on benthic invertebrate communities—implications for stream restoration practice. Sci Total Environ 553:495–503
Strayer DL, Beighley RE, Thompson LC, Brooks S, Nilsson C, Pinay G, Naiman RJ (2003) Effects of land cover on stream ecosystems: roles of empirical models and scaling issues. Ecosystems 6:407–423
Tan X, Ma P, Xia X, Zhang Q (2013) Spatial pattern of benthic diatoms and water quality assessment using diatom indices in a subtropical river, China. Clean-Soil Air Water 42:20–28
Tan X, Xia X, Zhao Q, Zhang Q (2014) Temporal variations of benthic diatom community and its main influencing factors in a subtropical river, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21:434–444
Theodoropoulos C, Aspridis D, Iliopoulou-Georgudaki J (2015) The influence of land use on freshwater macroinvertebrates in a regulated and temporary Mediterranean river network. Hydrobiologia 751:201–213
Vörösmarty CJ, McIntyre PB, Gessner MO, Dudgeon D, Prusevich A, Green P, Glidden S, Bunn SE, Sullivan CA, Liermann CR, Davies PM (2010) Global threats to human water security and river biodiversity. Nature 467:555–561
Wang X, Cai Q, Tang T, Yang S, Li F (2012a) Spatial distribution of benthic macroinvertebrates in the Erhai basin of southwestern China. J Freshw Ecol 27:89–96
Wang X, Cai Q, Ye L, Qu X (2012b) Evaluation of spatial and temporal variation in stream water quality by multivariate statistical techniques: a case study of the Xiangxi River basin, China. Quatern Int 282:137–144
White E, Hurlbert A (2010) The combined influence of the local environment and regional enrichment on bird species richness. Am Nat 175:E35–E43
Wu J, Li H (2006) Concepts of scale and scaling. In: Wu J, Jones KB, Li H, Loucks OL (eds) Scaling and uncertainty analysis in ecology: methods and applications. Springer, Netherlands, pp 3–15
Xu M, Wang Z, Duan X, Pan B (2014) Effects of pollution on macroinvertebrates and water quality bio-assessment. Hydrobiologia 729:247–259
Ye L, Cai Q, Liu R, Cao M (2009) The influence of topography and land use on water quality of Xiangxi River in Three Gorged Reservoir region. Environ Geol 58:937–942
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge Ms. Xiaoling Xia for her assistance with the field sampling. We thank Dr. Yulong Zhang in University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill and Mr. Sheng Gu in Jiangxi Provincial Bureau of Environmental Supervision in China for their help with land use analysis. We also thank Qingna Shen for her help with English. This work was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (no. 3130010).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Thomas Hein
Electronic supplementary material
Appendix 1
(DOC 32 kb).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, X., Tan, X. Macroinvertebrate community in relation to water quality and riparian land use in a substropical mountain stream, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24, 14682–14689 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-9042-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-9042-1