Abstract
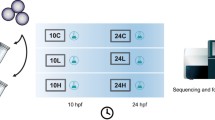
In ecotoxicology, transcriptomics is an effective way to detect gene expression changes in response to environmental pollutants. Such changes can be used to identify contaminants or contaminant classes and can be applied as early warning signals for pollution. To do so, it is important to distinguish contaminant-specific transcriptomic changes from genetic alterations due to general stress. Here we present a first step in the identification of contaminant class-specific transcriptome signatures. Embryos of zebrafish (Danio rerio) were exposed to three substances (methylmercury, chlorpyrifos and Aroclor 1254, each from 24 to 48 hpf exposed) representing sediment typical contaminant classes. We analyzed the altered transcriptome to detect discriminative genes significantly regulated in reaction to the three applied contaminants. By comparison of the results of the three contaminants, we identified transcriptome signatures and biologically important pathways (using Cytoscape/ClueGO software) that react significantly to the contaminant classes. This approach increases the chance of finding genes that play an important role in contaminant class-specific pathways rather than more general processes.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aluru N, Jenny MJ, Hahn ME (2014) Knockdown of a zebrafish aryl hydrocarbon receptor repressor (AHRRa) affects expression of genes related to photoreceptor development and hematopoiesis. Toxicol Sci 139:381–395. doi:10.1093/toxsci/kfu052
Aly HAA, Domènech Ò (2009) Aroclor 1254 induced cytotoxicity and mitochondrial dysfunction in isolated rat hepatocytes. Toxicology 262:175–183. doi:10.1016/j.tox.2009.05.018
Aly HAA, Domènech Ò, Abdel-Naim AB (2009) Aroclor 1254 impairs spermatogenesis and induces oxidative stress in rat testicular mitochondria. Food Chem Toxicol 47:1733–1738. doi:10.1016/j.fct.2009.03.019
Bai S, Thummel R, Godwin AR et al (2005) Matrix metalloproteinase expression and function during fin regeneration in zebrafish: analysis of MT1-MMP, MMP2 and TIMP2. Matrix Biol 24:247–260. doi:10.1016/j.matbio.2005.03.007
Bartosiewicz M, Penn S, Buckpitt A (2001) Applications of gene arrays in environmental toxicology: fingerprints of gene regulation associated with cadmium chloride, benzo(a)pyrene, and trichloroethylene. Environ Health Perspect 109:71–74. doi:10.1289/ehp.0110971
Behra M, Cousin X, Bertrand C et al (2002) Acetylcholinesterase is required for neuronal and muscular development in the zebrafish embryo. Nat Neurosci 5:111–118. doi:10.1038/nn788
Bindea G, Mlecnik B, Hackl H et al (2009) ClueGO: a cytoscape plug-in to decipher functionally grouped gene ontology and pathway annotation networks. Bioinformatics (Oxford, England) 25:1091–1093. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btp101
Borlak J, Jenke HS (2008) Cross-talk between aryl hydrocarbon receptor and mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway in liver cancer through c-raf transcriptional regulation. Molecular cancer research : MCR 6:1326–1336. doi:10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-08-0042
Bradham CA, Qian T, Streetz K et al (1998) The mitochondrial permeability transition is required for tumor necrosis factor alpha-mediated apoptosis and cytochrome c release. Mol Cell Biol 18:6353–6364. doi:10.1128/MCB.18.11.6353
Braunbeck T, Kais B, Lammer E et al (2015) The fish embryo test (FET): origin, applications, and future. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 22:16247–16261. doi:10.1007/s11356-014-3814-7
Cambier S, Gonzalez P, Nathalie MD et al (2012) Effects of dietary methylmercury on the zebrafish brain: histological, mitochondrial, and gene transcription analyses. Biometals 25:165–180. doi:10.1007/s10534-011-9494-6
Carney SA, Chen J, Burns CG et al (2006) Aryl hydrocarbon receptor activation produces heart-specific transcriptional and toxic responses in developing zebrafish. Mol Pharmacol 70:549–561. doi:10.1124/mol.106.025304
Chaty S, Rodius F, Vasseur P (2004) A comparative study of the expression of CYP1A and CYP4 genes in aquatic invertebrate (freshwater mussel, Unio tumidus) and vertebrate (rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss). Aquat Toxicol 69:81–94. doi:10.1016/j.aquatox.2004.04.011
Churchill GA (2004) Using ANOVA to analyze microarray data. BioTechniques 37(173–5):177
Clarkson TW, Magos L (2006) The toxicology of mercury and its chemical compounds. Crit Rev Toxicol 36:609–662. doi:10.1080/10408440600845619
Dalman MR, Deeter A, Nimishakavi G, Duan Z-H (2012) Fold change and p-value cutoffs significantly alter microarray interpretations. BMC bioinformatics 13:S11. doi:10.1186/1471-2105-13-S2-S11
Demir F, Uzun FG, Durak D, Kalender Y (2011) Subacute chlorpyrifos-induced oxidative stress in rat erythrocytes and the protective effects of catechin and quercetin. Pestic Biochem Physiol 99:77–81. doi:10.1016/j.pestbp.2010.11.002
Eisen MB, Spellman PT, Brown PO, Botstein D (1998) Cluster analysis and display of genome-wide expression patterns. Proc Natl Acad Sci 95:14863–14868. doi:10.1073/pnas.95.25.14863
Fedorenkova A, Vonk J (2010) Ecotoxicogenomics: bridging the gap between genes and populations. Environmental science & technology 44:4328–4333
Feiler U, Höss S, Ahlf W et al (2013) Sediment contact tests as a tool for the assessment of sediment quality in German waters. Environ Toxicol Chem 32:144–155. doi:10.1002/etc.2024
Freyhult E, Landfors M, Önskog J et al (2010) Challenges in microarray class discovery: a comprehensive examination of normalization, gene selection and clustering. BMC Bioinformatics 11:1–14. doi:10.1186/1471-2105-11-503
Fujita H, Okimura Y, Utsumi T et al (2006) 4-Hydroxy-3,5,3′,4′-tetrachlorobiphenyl induced membrane permeability transition in isolated rat liver mitochondria. J Clin Biochem Nutr 38:167–175. doi:10.3164/jcbn.38.167
Garcia-Käufer M, Gartiser S, Hafner C et al (2015) Genotoxic and teratogenic effect of freshwater sediment samples from the Rhine and Elbe River (Germany) in zebrafish embryo using a multi-endpoint testing strategy. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 22:16341–16357. doi:10.1007/s11356-014-3894-4
Giancarlo R, Lo Bosco G, Pinello L (2010) Distance functions, clustering algorithms and microarray data analysis. Lecture notes in computer science. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg, pp 125–138
Hahn ME (2001) Dioxin toxicology and the aryl hydrocarbon receptor: insights from fish and other non-traditional models. Marine biotechnology (New York, NY) 3:S224–S238. doi:10.1007/s10126-001-0045-y
Handley-Goldstone HM, Grow MW, Stegeman JJ (2005) Cardiovascular gene expression profiles of dioxin exposure in zebrafish embryos. Toxicol Sci 85:683–693. doi:10.1093/toxsci/kfi116
Hassan SA, Moussa EA, Abbott LC (2012) The effect of methylmercury exposure on early central nervous system development in the zebrafish (Danio rerio) embryo. J Appl Toxicol 32:707–713. doi:10.1002/jat.1675
Henry T, Spitsbergen J, Hornung MW et al (1997) Early life stage toxicity of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 141:56–68
Ho NY, Yang L, Legradi J et al (2013) Gene responses in the central nervous system of zebrafish embryos exposed to the neurotoxicant methyl mercury. Environmental Science & Technology 47:3316–3325. doi:10.1021/es3050967
Hollert H, Keiter S, König N et al (2003) A new sediment contact assay to assess particle-bound pollutants using zebrafish (Danio rerio) embryos. J Soils Sediments 3:197–207. doi:10.1065/jss2003.09.085
Höss S, Ahlf W, Fahnenstich C et al (2010) Variability of sediment-contact tests in freshwater sediments with low-level anthropogenic contamination-determination of toxicity thresholds. Environ Pollut 158:2999–3010. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2010.05.013
Howe K, Clark MD, Torroja CF et al (2013) The zebrafish reference genome sequence and its relationship to the human genome. Nature 496:498–503. doi:10.1038/nature12111
Ishida T, Nakajima T, Kudo A, Kawakami A (2010) Phosphorylation of Junb family proteins by the Jun N-terminal kinase supports tissue regeneration in zebrafish. Dev Biol 340:468–479. doi:10.1016/j.ydbio.2010.01.036
Jönsson ME, Jenny MJ, Woodin BR et al (2007) Role of AHR2 in the expression of novel cytochrome P450 1 family genes, cell cycle genes, and morphological defects in developing zebra fish exposed to 3,3′,4,4′,5-pentachlorobiphenyl or 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin. Toxicol Sci 100:180–193. doi:10.1093/toxsci/kfm207
Jönsson ME, Kubota A, Timme-Laragy AR et al (2012) Ahr2-dependence of PCB126 effects on the swim bladder in relation to expression of CYP1 and cox-2 genes in developing zebrafish. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 265:166–174. doi:10.1016/j.taap.2012.09.023
Keiter S, Peddinghaus S, Feiler U et al (2010) DanTox-a novel joint research project using zebrafish (Danio rerio) to identify specific toxicity and molecular modes of action of sediment-bound pollutants. J Soils Sediments 10:714–717. doi:10.1007/s11368-010-0221-7
Keiter SH, Braunbeck T, Feiler U, et al. (2013) DanTox—Entwicklung und Anwendung eines Verfahrens zur Ermittlung spezifischer Toxizität und molekularer Wirkungsmechanismen sedimentgebundener Umweltschadstoffe mit dem Zebrabärbling (Danio rerio) : Schlussbericht.
Kosmehl T, Otte JC, Yang L et al (2012) A combined DNA-microarray and mechanism-specific toxicity approach with zebrafish embryos to investigate the pollution of river sediments. Reproductive toxicology (Elmsford, NY) 33:245–253. doi:10.1016/j.reprotox.2012.01.005
Kwong TC (2002) Organophosphate pesticides: biochemistry and clinical toxicology. Ther Drug Monit 24:144–149. doi:10.1097/00007691-200202000-00022
Legradi J (2011) Microarray based transcriptomics and the search for biomarker genes in zebrafish. Ruprecht-Karls Universität, Heidelberg
Lettieri T (2006) Recent applications of DNA microarray technology to toxicology and ecotoxicology. Environ Health Perspect 114:4–9. doi:10.1289/ehp.8194
Lewis RS, Noor SM, Fraser FW et al (2014) Regulation of embryonic hematopoiesis by a cytokine-inducible SH2 domain homolog in zebrafish. Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md : 1950) 192:5739–5748. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1301376
Li W (2012) Volcano plots in analyzing differential expressions with mRNA microarrays. J Bioinforma Comput Biol 10:1231003. doi:10.1142/S0219720012310038
Liu H, Nie F-H, Lin H-Y et al (2014) Developmental toxicity, oxidative stress, and related gene expression induced by dioxin-like PCB 126 in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Environmental toxicology n/a-n/a. doi:10.1002/tox.22044
Liu L, Xu Y, Xu L et al (2015) Analysis of differentially expressed proteins in zebrafish (Danio rerio) embryos exposed to chlorpyrifos. Comparative biochemistry and physiology Toxicology & pharmacology : CBP 167:183–189. doi:10.1016/j.cbpc.2014.10.006
McCarthy DJ, Smyth GK (2009) Testing significance relative to a fold-change threshold is a TREAT. Bioinformatics (Oxford, England) 25:765–771. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btp053
Murtagh F, Legendre P (2014) Ward’s hierarchical agglomerative clustering method: which algorithms implement Ward’s criterion? J Classif 31:274–295. doi:10.1007/s00357-014-9161-z
Nishihara Y (1985) Comparative study of the effects of biphenyl and Kanechlor-400 on the respiratory and energy linked activities of rat liver mitochondria. Occup Environ Med 42:128–132. doi:10.1136/oem.42.2.128
Nishihara Y, Utsumi K (1987) 4-Chloro-4′-biphenylol as an uncoupler and an inhibitor of mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation. Biochem Pharmacol 36:3453–3457
Nishihara Y, Robertson LW, Oesch F, Utsumi K (1986) The effects of tetrachlorobiphenyls on the electron transfer reaction of isolated rat liver mitochondria. Life Sci 38:627–635. doi:10.1016/0024-3205(86)90056-1
Pavlidis P (2003) Using ANOVA for gene selection from microarray studies of the nervous system. Methods 31:282–289. doi:10.1016/S1046-2023(03)00157-9
Prochazkova J, Kabatkova M, Bryja V et al (2011) The interplay of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor and beta-catenin alters both AhR-dependent transcription and Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in liver progenitors. Toxicol Sci 122:349–360. doi:10.1093/toxsci/kfr129
Richter CA, Garcia-Reyero N, Martyniuk C et al (2011) Gene expression changes in female zebrafish (Danio rerio) brain in response to acute exposure to methylmercury. Environmental toxicology and chemistry / SETAC 30:301–308. doi:10.1002/etc.409
Salvi M, Toninello A (2001) Aroclor 1254 inhibits the mitochondrial permeability transition and release of cytochrome c: a possible mechanism for its in vivo toxicity. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 176:92–100. doi:10.1006/taap.2001.9271
Samson JC, Shenker J (2000) The teratogenic effects of methylmercury on early development of the zebrafish, Danio rerio. Aquat Toxicol 48:343–354. doi:10.1016/S0166-445X(99)00044-2
Schiwy S, Bräunig J, Alert H et al (2014) A novel contact assay for testing aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR)-mediated toxicity of chemicals and whole sediments in zebrafish (Danio rerio) embryos. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. doi:10.1007/s11356-014-3185-0
Schlezinger JJ, Struntz WDJ, Goldstone JV, Stegeman JJ (2006) Uncoupling of cytochrome P450 1A and stimulation of reactive oxygen species production by co-planar polychlorinated biphenyl congeners. Aquatic toxicology (Amsterdam, Netherlands) 77:422–432. doi:10.1016/j.aquatox.2006.01.012
Shelton DW, Goeger DE, Hendricks JD, Bailey GS (1986) Mechanisms of anti-carcinogenesis: the distribution and metabolism of aflatoxin B1 in rainbow trout fed aroclor 1254. Carcinogenesis 7:1065–1071. doi:10.1093/carcin/7.7.1065
Silkworth JB, Koganti A, Illouz K et al (2005) Comparison of TCDD and PCB CYP1A induction sensitivities in fresh hepatocytes from human donors, Sprague-Dawley rats, and rhesus monkeys and HepG2 cells. Toxicol Sci 87:508–519. doi:10.1093/toxsci/kfi261
Smyth GK (2004) Linear models and empirical Bayes methods for assessing differential expression in microarray experiments. Stat Appl Genet Mol Biol 3:1–26. doi:10.2202/1544-6115.1027
Snape JR, Maund SJ, Pickford DB, Hutchinson TH (2004) Ecotoxicogenomics: the challenge of integrating genomics into aquatic and terrestrial ecotoxicology. Aquatic toxicology (Amsterdam, Netherlands) 67:143–154. doi:10.1016/j.aquatox.2003.11.011
Snell TW, Brogdon SE, Morgan MB (2003) Gene expression profiling in ecotoxicology. Ecotoxicology (London, England) 12:475–483
Straus DL, Chambers JE (1995) Inhibition of acetylcholinesterase and aliesterases of fingerling channel catfish by chlorpyrifos, parathion, and S,S,S-tributyl phosphorotrithioate (DEF). Aquat Toxicol 33:311–324. doi:10.1016/0166-445X(95)00024-X
Uzun FG, Kalender Y (2013) Chlorpyrifos induced hepatotoxic and hematologic changes in rats: the role of quercetin and catechin. Food Chem Toxicol 55:549–556. doi:10.1016/j.fct.2013.01.056
Van Aggelen G, Ankley GT, Baldwin WS et al (2010) Integrating omic technologies into aquatic ecological risk assessment and environmental monitoring: hurdles, achievements, and future outlook. Environ Health Perspect 118:1–5. doi:10.1289/ehp.0900985
Villeneuve D, Volz DC, Embry MR et al (2014a) Investigating alternatives to the fish early-life stage test: a strategy for discovering and annotating adverse outcome pathways for early fish development. Environmental toxicology and chemistry / SETAC 33:158–169. doi:10.1002/etc.2403
Villeneuve DL, Crump D, Garcia-Reyero N et al (2014b) Adverse outcome pathway (AOP) development I: strategies and principles. Toxicol Sci 142:312–320. doi:10.1093/toxsci/kfu199
Whitney K, Seidler F, Slotkin T (1995) Developmental neurotoxicity of chlorpyrifos: cellular mechanisms. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 134:53–62
Xiao Y, Hsiao T-H, Suresh U et al (2014) A novel significance score for gene selection and ranking. Bioinformatics (Oxford, England) 30:801–807. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btr671
Yang L, Kemadjou JR, Zinsmeister C et al (2007) Transcriptional profiling reveals barcode-like toxicogenomic responses in the zebrafish embryo. Genome Biol 8:R227. doi:10.1186/gb-2007-8-10-r227
Yang L, Ho NY, Müller F, Strähle U (2010) Methyl mercury suppresses the formation of the tail primordium in developing zebrafish embryos. Toxicol Sci 115:379–390. doi:10.1093/toxsci/kfq053
Yang D, Lauridsen H, Buels K et al (2011) Chlorpyrifos-oxon disrupts zebrafish axonal growth and motor behavior. Toxicol Sci 121:146–159. doi:10.1093/toxsci/kfr028
Yen J, Donerly S, Levin ED, Linney EA (2011) Differential acetylcholinesterase inhibition of chlorpyrifos, diazinon and parathion in larval zebrafish. Neurotoxicol Teratol 33:735–741. doi:10.1016/j.ntt.2011.10.004
Acknowledgements
The present study was part of the research funding project DanTox (DanTox—a novel joint research project using zebrafish (Danio rerio) to identify specific toxicity and molecular modes of action of sediment-bound pollutants). The authors acknowledge financial support by the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF grant 02WU1053) and data provision from the GENDarT2 project (BMBF grant AZ:0315190 B). The authors thank Thomas-Benjamin Seiler for improving the language. The authors thank Leonie Nüßer and Daniel Koske for their help with the interpretation of the microarrays.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
List of all GO-groups and contained functional terms. A table of all significantly enriched GO-terms as well as their respective GO-groups for all three treatments. Table includes p-values and Benjamini-Hochberg corrected p-values of each term. (CSV 9 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hausen, J., Otte, J.C., Legradi, J. et al. Fishing for contaminants: identification of three mechanism specific transcriptome signatures using Danio rerio embryos. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25, 4023–4036 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-8977-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-8977-6