Abstract
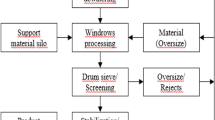
Soil biotechnology (SBT) is a green engineering approach for wastewater treatment and recycling. Five SBT units located in the Mumbai region were under consideration of which holistic assessment of two SBT plants was carried out considering its technical, environmental and economic aspects and was compared with published research of other three. LCA has been done to evaluate the environmental impacts of construction and operation phase of SBT. Chemical oxygen demand (COD) and biochemical oxygen demand (BOD) removal of more than 90% can be achieved using this technology. Also, the nutrient removal proficiency (nitrate, nitrite, ammoniacal nitrogen, TKN, total nitrogen and phosphates) of this technique is good. On the other hand, SBT has low annual operation and maintenance cost, comparable to land-based systems and lower than conventional or advanced technologies. From the life cycle impact assessment, the main contributors for overall impact from the plant were identified as electricity consumption, discharges of COD, P-PO4 3− and N-NH4 + and disposal of sludge. The construction phase was found to have significantly more impact than the operation phase of the plant. This study suggests plant I is not relatively as efficient enough regarding sanitation. SBT provides several benefits over other conventional technologies for wastewater treatment. It is based on a bio-conversion process and is practically maintenance free. It does not produce any odorous bio-sludge and consumes the least energy.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amores MJ, Meneses M, Pasqualino J, Anton A, Castells F (2013) Environmental assessment of urban water cycle on Mediterranean conditions by LCA approach. J Clean Prod 43:84–92
Apha A (2005) WEF, 2005. Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater 21:258–259
Bahgat M, Dewedar A, Zayed A (1999) Sand-filters used for wastewater treatment: buildup and distribution of microorganisms. Water Res 33(8):1949–1955
Benetto E, Nguyen D, Lohmann T, Schmitt B, Schosseler P (2009) Life cycle assessment of ecological sanitation system for small-scale wastewater treatment. Sci Total Environ 407(5):1506–1516
Bester K, Schäfer D (2009) Activated soil filters (bio filters) for the elimination of xenobiotics (micro-pollutants) from storm-and waste waters. Water Res 43(10):2639–2646
Avantika Bhaskar and N. Muthu Karthick (2015) Riparian forests for healthy rivers, Conservation India. Available at: http://www.conservationindia.org/articles/riparian-forests-for-healthy-rivers
Brix H (1999) How “green” are aquaculture, constructed wetlands and conventional wastewater treatment systems? Water Science & Technology 40(3):45–50
Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) (2013) Performance evaluation of sewage treatment plants under NRCD, Ministry of Environment and Forest. Available at: http://cpcb.nic.in/upload/NewItems/NewItem_195_STP_REPORT.pdf
Chen S, Chen B (2013) Net energy production and emissions mitigation of domestic wastewater treatment system: a comparison of different biogas–sludge use alternatives. Bioresour Technol 144:296–303
Coats ER, Watkins DL, Kranenburg D (2011) A comparative environmental life-cycle analysis for removing phosphorus from wastewater: biological versus physical/chemical processes. Water Environ Res 83:750–760
Corcoran, E., C. Nellemann, E. Baker, R. Bos, D. Osborn, H. Savelli (eds) 2010 Sick Water? The central role of wastewater management in sustainable development. A rapid response assessment. United Nations Environment Programme, UN-HABITAT, GRID Arendal. www.grida.no ISBN: 978–82–7701-075-5 Printed by BirkelandTrykkeri AS, Norway
Dixon A, Simon M, Burkitt T (2003) Assessing the environmental impact of two options for small-scale wastewater treatment: comparing a reedbed and an aerated biological filter using a life cycle approach. Ecol Eng 20(4):297–308. doi:10.1016/S0925-8574(03)00007-7
Doka G (2009) Life cycle inventories of waste treatment services. Ecoinvent report No. 13: Swiss Centre for Life Cycle Inventories, Dubendorf, Switzerland
Emmerson RHC, Morse GK, Lester JN, Edge DR (1995) The life-cycle analysis of small-scale sewage-treatment processes. JCIWEM 9:317–325
Foley J, De Haas D, Hartley K, Lant P (2010) Comprehensive life cycle inventories of alternative wastewater treatment systems. Water Res 44(5):1654–1666. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2009.11.031
Gallego A, Hospido A, Moreira MT, Feijoo G (2008) Environmental performance of wastewater treatment plants for small populations. Resour Conserv Recycl 52(6):931–940. doi:10.1016/j.resconrec.2008.02.001
Hao R, Li S, Li J, Meng C (2013) Denitrification of simulated municipal wastewater treatment plant effluent using a three-dimensional biofilm-electrode reactor: operating performance and bacterial community. Bioresour Technol 143:178–186
Heistad A, Paruch AM, Vråle L, Adam K, Jenssen PD (2006) A high–performance compact filter system treating domestic wastewater. Ecol Eng 28(4):374–379
Hench KR, Bissonnette GK, Sexstone AJ, Coleman JG, Garbutt K, Skousen JG (2003) Fate of physical, chemical, and microbial contaminants in domestic wastewater following treatment by small constructed wetlands. Water Res 37(4):921–927
Hospido A, Moreira MT, Fernández-Couto M, Feijoo G (2004) Environmental performance of a municipal wastewater treatment plant. Int J LCA 9(4):261–271
Hospido A, Moreira MT, Feijoo G (2008) A comparison of municipal wastewater treatment plants for big centres of population in Galicia (Spain). Int J Life Cycle Assess 13:57–64
Hospido A, Sanchez I, Rodriguez-Garcia G, Iglesias A, Buntner D, Reif R, Moreira MT et al (2012) Are all membrane reactors equal from an environmental point of view? Desalination 285:263–270. doi:10.1016/j.desal.2011.10.011
International Organization for Standardization (ISO) (2006a) Environmental management. Life cycle assessment. Principle and framework. ISO14040:2006. International Organization for Standardisation, Geneva, CH
International Organization for Standardization (ISO) (2006b) Environmental management. Life cycle assessment. Requirements and guidelines. ISO 14044:2006. International organization for standardisation (ISO), Geneva, CH
Jenssen PD, Krogstad T, Paruch AM, Mæhlum T, Adam K, Arias CA, Yli-Halla M (2010) Filter bed systems treating domestic wastewater in the Nordic countries—performance and reuse of filter media. Ecol Eng 36(12):1651–1659
Kadam AM, Oza GH, Nemade PD, Shankar HS (2008a) Pathogen removal from municipal wastewater in constructed soil filter. Ecol Eng 33(1):37–44
Kadam A, Oza G, Nemade P, Dutta S, Shankar H (2008b) Municipal wastewater treatment using novel constructed soil filter system. Chemosphere 71(5):975–981
Kadam AM, Nemade PD, Oza GH, Shankar HS (2009) Treatment of municipal wastewater using laterite-based constructed soil filter. Ecol Eng 35(7):1051–1061
Kalbar, P. P., Karmakar, S., &Asolekar, S. R. (2012). Assessment of wastewater treatment technologies: life cycle approach. Water and Environment Journal, (3), n/a–n/a. doi:10.1111/wej.12006
Kalbar PP, Karmakar S, Asolekar SR (2013) Assessment of wastewater treatment technologies: life cycle approach. Water and Environment Journal 27(2):261–268
Kalbar PP, Karmakar S, Asolekar SR (2014) Life cycle-based environmental assessment of municipal wastewater treatment plant in India. Int J Environ Waste Manag 14(1):84–98
Khalil, N., Sinha, R., Raghav, A. K., & Mittal, A. K. (2008, March). UASB technology for sewage treatment in India: experience, economic evaluation and its potential in other developing countries. In Twelfth International Water Technology Conference (pp. 1411–1427)
Koottatep T, Surinkul N, Polprasert C, Kamal ASM, Koné D, Montangero A et al (2005) Treatment of septage in constructed wetlands in tropical climate: lessons learnt from seven years of operation. Water Sci Technol 51(9):119–126
Kumar C.P. 2003 Fresh water resources: a perspective, International Year of Fresh Water – 2003. Available at: http://www.angelfire.com/bc/nihhrrc/documents/fresh.html
Leverenz HL, Tchobanoglous G, Darby JL (2009) Clogging in intermittently dosed sand filters used for wastewater treatment. Water Res 43(3):695–705
Li Y, Luo X, Huang X, Wang D, Zhang W (2013) Life cycle assessment of a municipal wastewater treatment plant: a case study in Suzhou, China. J Clean Prod 57:221–227
Llorens M, Pérez-Marin AB, Aguilar MI, Sáez J, Ortuño JF, Meseguer VF (2011) Nitrogen transformation in two subsurface infiltration systems at pilot scale.Ecological. Engineering 37(5):736–743
Lopsik K (2013) Life cycle assessment of small-scale constructed wetland and extended aeration activated sludge wastewater treatment system. Int J Environ Sci Technol 10(6):1295–1308
Luanmanee S, Attanandana T, Masunaga T, Wakatsuki T (2001) The efficiency of a multi-soil-layering system on domestic wastewater treatment during the ninth and tenth years of operation. Ecol Eng 18(2):185–199
Luo W, Yang C, He H, Zeng G, Yan S, Cheng Y (2014) Novel two-stage vertical flow biofilter system for efficient treatment of decentralized domestic wastewater. Ecol Eng 64:415–423
Machado AP, Urbano L, Brito AG, Janknecht P, Salas JJ, Nogueira R (2007) Life cycle assessment of wastewater treatment options for small and decentralized communities. Water Science & Technology 56(3):15. doi:10.2166/wst.2007.497
McDonald RI, Weber K, Padowski J, Flörke M, Schneider C, Green PA, Gleeson T, Eckman S, Lehner B, Balk D, Boucher T, Grill G, Montgomery M (2014) Water on an urban planet: urbanization and the reach of urban water infrastructure. Glob Environ Chang 27:96–105. doi:10.1016/j.gloenvcha.2014.04.022
Mehta P (2012) Impending water crisis in India and comparing clean water standards among developing and developed nations. Archives of Applied Science Research 4(1):497–507 ISSN 0975-508XAvailable at: http://environmentportal.in/files/file/Impending%20water%20crisis%20in%20India.pdf
Memon FA, Zheng Z, Butler D, Shirley-Smith C, Lui S, Makropoulos C, Avery L (2007) Life cycle impact assessment of greywater recycling technologies for new developments. Environ Monit Assess 129(1–3):27–35
Mulkerrins D, Dobson ADW, Colleran E (2004) Parameters affecting biological phosphate removal from wastewaters. Environ Int 30:249–259
Munoz I, Rodriguez A, Rosal R, Fernandez-Alba AR (2009) Life cycle assessment of urban wastewater reuse with ozonation as tertiary treatment: a focus on toxicity-related impacts. Sci Total Environ 407(4):1245–1256
Nemade PD, Kadam AM, Shankar HS (2009a) Wastewater renovation using constructed soil filter (CSF): a novel approach. J Hazard Mater 170(2):657–665
Nemade PD, Kadam AM, Shankar HS (2009b) Removal of iron, arsenic and coliform bacteria from water by novel constructed soil filter system. Ecol Eng 35(8):1152–1157
Niero M, Pizzol M, Bruun HG, Thomsen M (2014) Comparative life cycle assessment of wastewater treatment in Denmark including sensitivity and uncertainty analysis. J Clean Prod 68(1):25–35
Njau KN, Minja RJ, Katima JH (2003) Pumice soil: a potential wetland substrate for treatment of domestic wastewater. Water Sci Technol 48:85–92
Nogueira R, Brito AG, Machado AP, Janknecht P, Salas JJ, Vera L, Martel G (2009) Economic and environmental assessment of small and decentralized wastewater treatment systems. Desalin Water Treat 4(1–3):16–21. doi:10.5004/dwt.2009.349
Pan T, Zhu XD, Ye YP (2011) Estimate of life-cycle greenhouse gas emissions from a vertical subsurface flow constructed wetland and conventional wastewater treatment plants: a case study in China. Ecol Eng 37(2):248–254
Park WH (2009) Integrated constructed wetland systems employing alum sludge and oyster shells as filter media for P removal. Ecol Eng 35(8):1275–1282
Pasqualino JC, Meneses M, Abella M, Castells F (2009) LCA as a decision support tool for the environmental improvement of the operation of a municipal wastewater treatment plant. Environmental science & technology 43(9):3300–3307
Pasqualino JC, Meneses M, Castells F (2011) Life cycle assessment of urban wastewater reclamation and reuse alternatives. J Ind Ecol 15(1):49–63. doi:10.1111/j.1530-9290.2010.00293.x
Rodriguez-Garcia G, Molinos-Senante M, Hospido A, Hernández-Sancho F, Moreira MT, Feijoo G (2011) Environmental and economic profile of six typologies of wastewater treatment plants. Water Res 45(18):5997–6010. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2011.08.053
Rodriguez-Garcia G, Frison N, Vázquez-Padín JR, Hospido A, Garrido JM, Fatone F et al (2014) Life cycle assessment of nutrient removal technologies for the treatment of anaerobic digestion supernatant and its integration in a wastewater treatment plant. Sci Total Environ 490:871–879
Roeleveld PJ, Klapwijk A, Eggels PG, Rulkens WH, Van Starkenburg W (1997) Sustainability of municipal wastewater treatment. Water Science & Technology 35(10):221–228
Roushdi M, El-Hawary A, Mahgoub M (2012) Environmental improvement of Alexandria’s wastewater treatment plants using life cycle assessment approach. GLOBAL NEST JOURNAL 14(4):450–459
Roux P, Boutin C, Risch E, Heduit A (2010) Life cycle environmental assessment (LCA) of sanitation systems including sewerage: case of vertical flow constructed wetlands versus activated sludge. In: 12th IWA International Conference on Wetland Systems for Water Pollution Control, vol. 2
Sato N, Okubo T, Onodera T, Agrawal LK, Ohashi A, Harada H (2007) Economic evaluation of sewage treatment processes in India. J Environ Manag 84(4):447–460
Sato K, Iwashima N, Wakatsuki T, Masunaga T (2011) Quantitative evaluation of treatment processes and mechanisms of organic matter, phosphorus, and nitrogen removal in a multi-soil-layering system. Soil Science and Plant Nutrition 57(3):475–486
Tangsubkul N, Beavis P, Moore SJ, Lundie S, Waite TD (2005) Life cycle assessment of water recycling technology. Water Resour Manag 19(5):521–537
Tietz A, Langergraber G, Watzinger A, Haberl R, Kirschner AK (2008) Bacterial carbon utilization in vertical subsurface flow constructed wetlands. Water Res 42(6):1622–1634
Torrens A, Molle P, Boutin C, Salgot M (2009) Impact of design and operation variables on the performance of vertical-flow constructed wetlands and intermittent sand filters treating pond effluent. Water Res 43(7):1851–1858
Wakatsuki T, Esumi H, Omura S (1993) High performance and N & P-removable on-site domestic waste water treatment system by multi-soil-layering method. Water Sci Technol 27(1):31–40
Wang YY, Peng YZ, Stephenson T (2009) Effect of influent nutrient ratios and hydraulic retention time (HRT) on simultaneous phosphorus and nitrogen removal in a two-sludge sequencing batch reactor process. Bioresour Technol 100(14):3506–3512
Wang DB, Zhang ZY, Li XM, Zheng W, Yang Q, Ding Y, Zeng GM (2010) A full-scale treatment of freeway toll-gate domestic sewage using ecology filter integrated constructed rapid infiltration. Ecol Eng 36(6):827–831
Wang L, Zheng Z, Luo X, Zhang J (2011) Performance and mechanisms of a microbial-earthworm ecofilter for removing organic matter and nitrogen from synthetic domestic wastewater. J Hazard Mater 195:245–253
WHO/FAO (2006)
Yıldırım M, Topkaya B (2012) Assessing environmental impacts of wastewater treatment alternatives for small-scale communities. CLEAN - Soil, Air, Water 40(2):171–178. doi:10.1002/clen.201000423
Yuan H, Nie J, Zhu N, Miao C, Lu N (2013) Effect of temperature on the wastewater treatment of a novel anti-clogging soil infiltration system. Ecol Eng 57:375–379
Zhang J, Huang X, Shao CF, Liu CX, Shi HC, Hu HY, Liu ZQ (2004) Influence of packing media on nitrogen removal in a subsurface infiltration system. J Environ Sci China 16:153–156
Zhang Y, Geißen SU, Gal C (2008) Carbamazepine and diclofenac: removal in wastewater treatment plants and occurrence in water bodies. Chemosphere 73(8):1151–1161
Zhang QH, Wang XC, Xiong JQ, Chen R, Cao B (2010) Application of life cycle assessment for an evaluation of wastewater treatment and reuse project—case study of Xi’an, China. Bioresour Technol 101(5):1421–1425
Zhang Y, Cheng Y, Yang C, Luo W, Zeng G, Lu L (2015) Performance of system consisting of vertical flow trickling filter and horizontal flow multi-soil-layering reactor for treatment of rural wastewater. Bioresour Technol 193:424–432
Zhao, C., Zhang, Y., Liang, K., & Li, J. (2015) Environmental impact analysis of wastewater treatment process based on life cycle assessment
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kamble, S.J., Chakravarthy, Y., Singh, A. et al. A soil biotechnology system for wastewater treatment: technical, hygiene, environmental LCA and economic aspects. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24, 13315–13334 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-8819-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-8819-6