Abstract
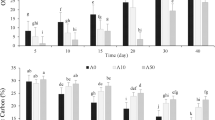
Monensin is a common antiparasitic drug given to poultry that contaminates poultry manure and bedding material (broiler litter). As broiler litter is commonly applied to agricultural fields as fertilizer, monensin could be released beyond the farm if it is not retained or degraded in the soil. This study aimed to assess the impact of long-term surface application of broiler litter (i.e., 17 years) on the capacity of pasture soil to sorb monensin. The soils were exposed to a range of monensin concentrations (0.18 to 1.81 μmol L−1), solution pH (pH 4–9), and temperatures (15, 25, and 35 °C) and monensin was measured as loss from solution (i.e., sorption). Soils receiving long-term litter applications were hypothesized to retain more monensin than unamended soils because they have higher organic matter concentrations. However, soils from broiler litter-amended fields sorbed 46% less monensin than soils from unamended fields, likely because broiler litter also increased soil pH. The sorption of monensin to soil was strongly influenced by pH, with an order of magnitude greater sorption at pH 4 than at pH 9. Both soils had similar capacity to sorb monensin under similar solution pH, despite differences in organic carbon content (with the broiler litter-amended having 25% greater relative to the unamended soil). Temperature did not significantly impact monensin sorption for either soil. Our findings suggest increasing soil pH, for instance through liming, could enhance mobility of monensin.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
American Public Health Association (1992) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 18th edn. APHA-AWWA-WEF, Washington, DC
Biswas S, Mcgrath JM, Sapkota A (2012) Quantification of ionophores in aged poultry litter using liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. J Environ Sci Health B 47(10):959–966. doi:10.1080/03601234.2012.706564
Bhattacharyya R, Prakash V, Kundu S, Srivastva AK, Gupta HS, Mitra S (2010) Long term effects of fertilization on carbon and nitrogen sequestration and aggregate associated carbon and nitrogen in the Indian sub-Himalayas. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 86:1–16. doi:10.1007/s10705-009-9270-y
Bhogal A, Nicholson FA, Chambers BJ (2009) Organic carbon additions: effects on soil-biophysical and physico-chemical properties. Eur J Soil Sci 60:276–286. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2389.2008.01105.x
Boxall ABA, Kolpin DW, Halling-Sørensen B, Tolls J (2003) Are veterinary medicines causing environmental risks? Environ Sci Technol 37(15):286A–294A. doi:10.1021/es032519b
Buettner SW, Kramer MG, Chadwick OA, Thompson A (2014) Mobilization of colloidal carbon during iron reduction in basaltic soils. Geoderma 221:139–145. doi:10.1016/j.geoderma.2014.01.012
Cha JM, Yang S, Carlson KH (2005) Rapid analysis of trace levels of antibiotic polyether ionophores in surface water by solid-phase extraction and liquid chromatography with ion trap tandem mass spectrometric detection. J Chromatogr A 1065:187–198. doi:10.1016/j.chroma.2004.12.091
Chorover J, Amistadi MK, Chadwick OA (2004) Surface charge evolution of mineral-organic complexes during pedogenesis in Hawaiian basalt. Geochim Cosmochim Ac 68(23):4859–4876. doi:10.1016/j.gca.2004.06.005
Doydora SA, Sun P, Cabrera M, Thompson A, Love-Myers K, Rema J, Calvert V II, Pavlostathis SG, Huang CH (2015a) Stacking time and aluminum sulfate effects on polyether ionophores in broiler litter. J Environ Qual 44:1923–1929. doi:10.2134/jeq2015.03.0156
Doydora SA, Franklin D, Sun P, Cabrera M, Thompson A, Love-Myers K, Rema J, Calvert V III, Pavlostathis SG, Huang CH (2015b) Alum and rainfall effects on ionophores in runoff from surface-applied broiler litter. J Environ Qual 44:1657–1666. doi:10.2134/jeq2015.02.0099
Edmeades DC (2003) The long-term effects of manures and fertilisers on soil productivity and quality: a review. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 66:165–180. doi:10.1023/A:1023999816690
European Food Safety Authority (2004) Opinion of the scientific panel on additives and products or substances used in animal feed on a request from the commission on the safety and the efficacy of product “Bio-Cox 120G” as feed additive in accordance with council directive 70/524/eec. EFSA J 75:1–51. doi:10.2903/j.efsa.2004.75
European Food Safety Authority (2005) Opinion of the scientific panel on additives and products or substances used in animal feed on a request from the European Commission on the evaluation of the coccidiostat Coxidin® (monensin sodium). EFSA J 75:1–51. doi:10.2903/j.efsa.2005.283
Franco A, Fu W, Trapp S (2009) Influence of soil pH on the sorption of ionizable chemicals: modeling advances. Environ Toxicol Chem 28(3):458–464
Furtula V, Huang L, Chambers PA (2009) Determination of veterinary pharmaceuticals in poultry litter and soil by methanol extraction and liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J Environ Sci Health B 44:717–723. doi:10.1080/03601230903163863
Gaskin J, Harris G, Franzluebbers A, Andrae J (2013) Poultry litter application on pastures and hayfields. University of Georgia Cooperative Extension Bulletin 1330. http://extension.uga.edu/publications/files/pdf/B%201330_3.PDF. Accessed 6 Apr. 2015
Gee GW, Bauder JW (1986) Particle-size analysis. In: Klute A (ed) Methods of soil analysis. Part 1., 2nd edn. Agron. Monogr. 9. ASA and SSSA, Madison, Wisconsin, pp 383–411
Hansen M, Björklund E, Krogh KA, Halling-Sørensen B (2009a) Analytical strategies for assessing ionophores in the environment. Trends Anal Chem 28(5):521–533. doi:10.1016/j.trac.2009.01.008
Hansen M, Krogh KA, Björklund E, Brandt A, Halling-Sørensen B (2009b) Environmental risk assessment of ionophores. Trends Anal Chem 28(5):534–542. doi:10.1016/j.trac.2009.02.015
Hansen M, Krogh KA, Brandt A, Christensen JH, Halling-Sørensen B (2009c) Fate and antibacterial potency of anticoccidial drugs and their main abiotic degradation products. Environ Pollut 157:474–480. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2008.09.022
Hussain SA, Prasher SO (2011) Understanding the sorption of ionophoric pharmaceuticals in a treatment wetland. Wetlands 31:563–571. doi:10.1007/s13157-011-0171-x
Ilhan ZE, Ong SK, Moorman TB (2012) Herbicide and antibiotic removal by woodchip denitrification filters: sorption processes. Water Air Soil Pollut 223:2651–2662. doi:10.1007/s11270-011-1057-5
Kaiser K, Kaupenjohann M, Zech W (2001) Sorption of dissolved organic carbon in soils: effects of soil sample storage, soil-to-solution ratio, and temperature. Geoderma 99:317–328. doi:10.1016/S0016-7061(00)00077-X
Kim SC, Carlson K (2006) Occurrence of ionophore antibiotics in water and sediments of a mixed-landscape watershed. Water Res 40:2549–2560. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2006.04.036
Kim SC, Carlson K (2007) Quantification of human and veterinary antibiotics in water and sediment using SPE/LC/MS/MS. Anal Bioanal Chem 387:1301–1315. doi:10.1007/s00216-006-0613-0
Kleber M, Eusterhues K, Keiluweit M, Mikutta C, Mikutta R, Nico P (2015) Mineral-organic associations: formation, properties, and relevance in soil environments. Adv Agron 130:1–140
Liu E, Yan C, Mei X, He W, Bing SH, Ding L, Liu Q, Liu S, Fan T (2010) Long-term effect of chemical fertilizer, straw, and manure on soil chemical and biological properties in northwest China. Geoderma 158:173–180. doi:10.1016/j.geoderma.2010.04.029
Maillard É, Angers DA (2014) Animal manure application and soil organic carbon stocks: a meta-analysis. Glob Chang Biol 20:666–679. doi:10.1111/gcb.12438
Miao X-S, March RE, Metcalfe CD (2003) Fragmentation study of salinomycin and monensin A antibiotics using electrospray quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun Mass Sp 17:149–154
Moore PA Jr (2011) Improving the sustainability of animal agriculture by treating manure with alum. In: He Z (ed) Environmental chemistry of animal manure. Nova Science Publishers, Hauppauge, NewYork, pp 349–381
Moore PA Jr, Edwards DR (2005) Long-term effects of poultry litter, alum-treated litter, and ammonium nitrate on aluminum availability in soils. J Environ Qual 34:2104–2111. doi:10.2134/jeq2004.0472
OECD (2000) OECD guidelines for the testing of chemicals. Test no. 106: adsorption–desorption using a batch equilibrium method. http://www.oecd-ilibrary.org/docserver/download/9710601e.pdf?expires=1477577838&id=id&accname=guest&checksum=F4C306E19AD3F7524EE8A1366CBDD2E6 Accessed 27 Oct. 2016
Pan B, Ghosh S, Xing B (2008) Dissolved organic matter conformation and its interaction with pyrene as affected by water chemistry and concentration. Environ Sci Technol 42(5):1594–1599. doi:10.1021/es702431m
Poerschmann J, Kopinke FD (2001) Sorption of very hydrophobic organic compounds (VHOCs) on dissolved humic organic matter (DOM). 2. Measurement of sorption and application of a Flory-Huggins concept to interpret the data. Environ Sci Technol 35(6):1142–1148. doi:10.1021/es0017615
Pressman BC (1976) Biological applications of ionophores. Annu Rev Biochem 45:501–530
Ripszam M, Paczkowska J, Figueira J, Veenaas C, Haglund P (2015) Dissolved organic carbon quality and sorption of organic pollutants in the Baltic Sea in light of future climate change. Environ Sci Technol 49:1445–1452. doi:10.1021/es504437s
Sassman SA, Lee LS (2007) Sorption and degradation in soils of veterinary ionophore antibiotics: monensin and lasalocid. Environ Toxicol Chem 26(8):1614–1621. doi:10.1897/07-073R.1
Site AD (2001) Factors affecting sorption of organic compounds in natural sorbent/water systems and sorption coefficients for selected pollutants. A Review J Phys Chem Ref Data 30:187–439
Sparks DL (2003) Environmental soil chemistry, 2nd edn. Academic Press, London
Sposito G (2008) The chemistry of soils, 2nd edn. Oxford University Press, New York
Sun P (2014) Transformation of veterinary ionophore antibiotics under conditions related to water-soil-litter systems. Dissertation, Georgia Institute of Technology
Sun P, Barmaz D, Cabrera ML, Pavlostathis SG, Huang CH (2013a) Detection and quantification of ionophore antibiotics in runoff, soil and poultry litter. J Chromatogr A 1312:10–17. doi:10.1016/j.chroma.2013.08.044
ten Hulscher TEM, Cornelissen G (1996) Effect of temperature on sorption equilibrium and sorption kinetics of organic micropollutants—a review. Chemosphere 32(4):609–626. doi:10.1016/0045-6535(95)00345-2
Thompson A, Amistadi MK, Chadwick OA, Chorover J (2013) Fractionation of yttrium and holmium during basaltic soil weathering. Geochim Cosmochim Ac 119:18–30. doi:10.1016/j.gca.2013.06.003
Watanabe N, Harter TH, Bergamaschi BA (2008) Environmental occurrence and shallow ground water detection of the antibiotic monensin from dairy farms. J Environ Qual 37:S-78–S-85. doi:10.2134/jeq2007.0371
West LT, Abreu MA, Bishop JP (2008) Saturated hydraulic conductivity of soils in the southern Piedmont of Georgia, USA: field evaluation and relation to horizon and landscape properties. Catena 73:174–179. doi:10.1016/j.catena.2007.07.011
Acknowledgements
This research was funded, in part, by USDA-CSREES-AFRI (2009-65102-05843).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Zhihong Xu
Electronic supplementary material
ESM. 1
(PDF 666 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Doydora, S.A., Sun, P., Cabrera, M. et al. Long-term broiler litter amendments can alter the soil’s capacity to sorb monensin. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24, 13466–13473 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-8727-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-8727-9